Table of Contents
DTP(Dynamic Trunking Protocol)
DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for negotiating with the opposite port to determine whether the port is an access port or a trunk port. In the case of a trunk port, it also negotiates the IEEE802.1Q or Cisco ISL encapsulation protocol.
DTP has the following operating modes.
- Dynamic desirable
- Dynamic auto
- Trunk
- Access
Dynamic desirable
The Dynamic desirable mode of DTP is a mode that actively requests the opposite port to negotiate to become a trunk port. If the opposite port responds to the negotiation request, the port acts as a trunk port. If there is no response, the port acts as an access port. Therefore, when Dynamic desirable ports are connected to each other, they will automatically become trunk ports.
To set the mode to Dynamic desirable, configure the interface configuration mode as follows
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic desirable
Dynamic auto
The Dynamic auto mode of DTP is a mode that acts as a trunk port in response to a request from the opposite port to become a trunk port.If there is no request from the opposite port to become a trunk port, it will act as an access port; there will be no request from the Dynamic auto port to become a trunk port. Even if Dynamic auto ports are connected to each other, they will not become trunk ports.
To set the mode to Dynamic auto, configure the interface configuration mode as follows.
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic auto
Trunk
The Trunk mode of DTP allows a port to act as a trunk port. It also requests the opposite port to become a trunk port. Unlike Dynamic desirable, Trunk mode makes its own port a trunk port, regardless of whether the opposite port becomes a trunk port or an access port.In other words, it can be said to be a static trunk port configuration.
As we summarize later, depending on the configuration of the opposite port, the opposite port may become the access port while your own port is the trunk port, so be careful.
To set the interface to Trunk mode, configure it in interface configuration mode as follows.
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
If your system supports both ISL and 1Q trunk protocols, such as Catalyst 3560/3750, you need to configure the trunk protocol with the switchport trunk encapsulation command first.
Access
The Access mode of DTP allows the port to act as an access port. Make it an access port regardless of whether the opposite port is a trunk port or an access port. This is a static access port configuration. Note that if your own port is set as the access port, but the opposite port is set as the trunk port, communication will not work properly.
To set the interface to Access mode, configure it in interface configuration mode as follows
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
The VLAN assignment, or VLAN membership, is VLAN 1 by default. to change the VLAN membership, use the following command
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan <vlan-number>
Be careful with the default DTP mode.
The default DTP mode varies depending on the Catalyst switch model. The Catalyst 3560/3750, for example, is in Dynamic auto mode by default, while the Catalyst 3550/2950, for example, is in Dynamic desirable mode by default. Therefore, when two Catalyst 3750s are connected, they become access ports; when a Catalyst 3550 is connected to a Catalyst 3750, it becomes a trunk port.
If you are using a Catalyst switch in the default DTP mode and you change the model of the Catalyst switch, you may find that the access port has somehow become the trunk port, or vice versa. So be careful.
Disable DTP
To disable DTP negotiation, enter the following command in interface configuration mode.
Switch(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate
DTP is only used on Catalyst switches, so it is best to disable DTP on the ports where PCs, servers, etc. are connected using the switchport nonegotiate command.
DTP mode combination
The combination of DTP mode configuration and actual switch ports between two Catalyst switches is as follows

|
SW1 |
|
SW2 |
|
| DTP mode | Operating mode | DTP mode | Operating mode |
|
Dynamic desirable |
Trunk |
Dynamic desirable |
Trunk |
|
|
Trunk |
Dynamic auto |
Trunk |
|
|
Trunk |
Trunk |
Trunk |
|
|
Access |
Access |
Access |
|
Dynamic auto |
Trunk |
Dynamic desirable |
Trunk |
|
|
Access |
Dynamic auto |
Access |
|
|
Trunk |
Trunk |
Trunk |
|
|
Access |
Access |
Access |
|
Trunk |
Trunk |
Dynamic desirable |
Trunk |
|
|
Trunk |
Dynamic auto |
Trunk |
|
|
Trunk |
Trunk |
Trunk |
|
| Trunk |
Access | Access |
|
Access |
Access |
Dynamic desirable |
Access |
|
|
Access |
Dynamic auto |
Access |
|
| Access |
Trunk | Trunk |
|
|
Access |
Access |
Access |
If you set the DTP mode to Trunk mode on one port and Access mode on the other, the operation mode (trunk port/access port) between the opposite ports will not match. If the trunk port or access port does not match the opposite port, VLAN frames will not communicate properly, Spanning Tree calculations will not work properly, and other problems will occur. Make sure that the access/trunk matches between the opposite ports.
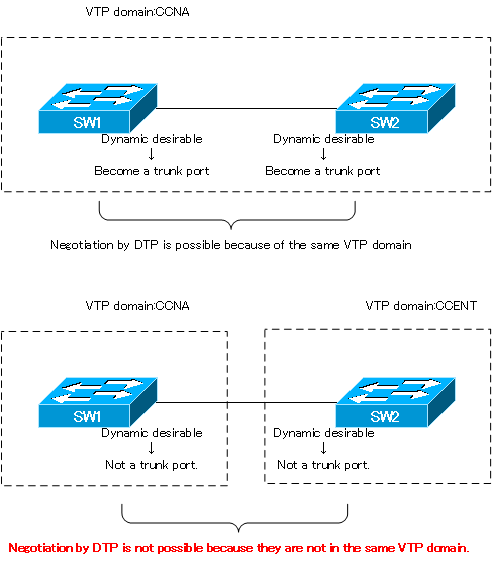
DTP negotiation is not valid for different VTP domains.
Note that DTP negotiation is performed between switches that belong to the same VTP domain, and cannot be performed between switches in different VTP domains. If the VTP domains do not match and DTP negotiation cannot be performed, the following log will be output.
00:12:25: %DTP-5-DOMAINMISMATCH: Unable to perform trunk negotiation on port Fa1/0/21 because of VTP domain mismatch.
VLAN(Virtual LAN)
- The need to divide the network
- Details of dividing the network
- VLAN Overview
- VLAN behavior
- Access port : Port assigned to only one VLAN
- Trunk port : Port assigned to multiple VLANs
- Summary of Trunk Protocols – IEEE802.1Q and ISL
- Native VLAN
- Specific example of native VLAN mismatch
- Cisco DTP
- Cisco Configuring and Verifying VLAN
- Cisco VLAN Detailed Configuration Example
- Notes on deleting VLANs
- Voice VLAN – VLAN for connecting IP phones
- VTP :Synchronize VLAN configuration
- VTP pruning – Stopping unnecessary flooding of trunk links
- Configuring and Verifying Cisco VTP
- Inter VLAN routing overview
- Inter-VLAN routing by router
- Inter-VLAN routing by Layer 3 switch
- Configuring and Verifying Inter-VLAN Routing by Cisco Router
- Cisco Configuring Inter-VLAN routing by Layer3 switch : SVI/routed port
- Cisco Layer3 Switch Basic Configuration Example
- Summary of Layer 3 Switch Port Concepts – Access Port/Trunk Port/SVI/Routed Port
- LAN Design pattern : 2-tier and 3-tier