Table of Contents
How to generate default routes in EIGRP
There are several ways to generate a default route as an EIGRP route and advertise it to other routers, as follows.
- Redistribute the static default route to EIGRP
- Route summarization
- ip default-network command
In the following sections, we will explain the configuration example of redistributing the static default route.
Redistribute the static default route to EIGRP
【Network diagram】
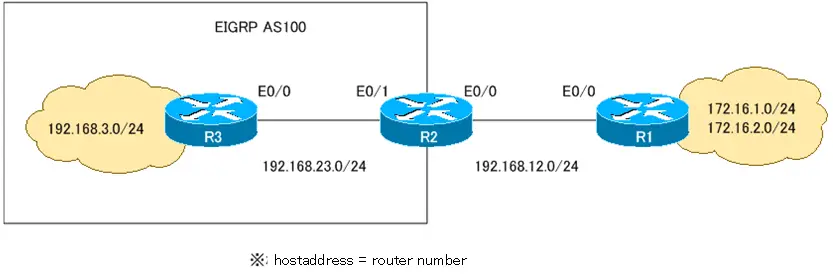
【Condition】
- Allow R2 to advertise the default route to R3 via EIGRP to ensure connectivity for all interfaces.
- The default route generation is done by static route redistribution.
【Initial configuration】
R1 initial configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.12.2
R2 initial configuration
interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.23.0 no auto-summary
R3 initial configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.3.0 network 192.168.23.0 no auto-summary
【Step1:Configure static default route】
Configure the default route as a static route on R2.
R2 Configure static default route
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.12.1
【Step2:Redistribute static routes to EIGRP】
Redistribute the static route to EIGRP on R2 in order to make the default route configured in Step 1 as the EIGRP route.
R2 Redistribute static routes to EIGRP
router eigrp 100 redistribute static
【Step3:Verifying the default route】
Verify that the default route is registered as an EIGRP route in the routing table of R3.
R3
R3#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.23.2 to network 0.0.0.0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/307200] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:03, Ethernet0/0
【Step4:Vefifying communication】
Execute a ping from R3 to R1 to verify that communication is possible.
R3
R3#ping 172.16.1.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/12/20 ms R3#ping 172.16.2.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/10/20 ms
