How the OSPF works
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is the most commonly used routing protocol in enterprise networks. It is important to understand how it works in order to use OSPF effectively. This section explains how the OSPF works.
OSPF Overview

OSPF FeaturesOSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a routing protocol that can be used f...
Read moreOSPF process flow
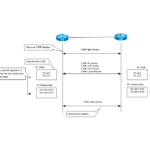
In order to understand how OSPF works, it is first important to have a firm grasp of the overall OSPF process flow
Read moreOSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
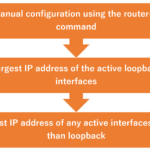
The router ID is a 32-bit number that identifies the OSPF router. Just like IPv4 addresses, it's an 8-bit decimal number separated by ". (dot)" and then write four of them in a row.
Read moreWhat if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?

In OSPF, each router is identified by its router ID. For this reason, router IDs must not be duplicated. In this section, we will explain what happens if a router ID is duplicated.
Read moreOSPF Neighbor and Adjacency

There are two types of relationships between OSPF routers: neighbor and adjacency. This section describes the two relationships between OSPF routers.
Read moreOSPF DR/BDR
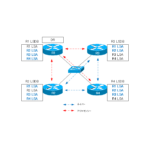
DR (Designed Router)/BDR (Backup Designated Router) is a router that is elected to efficiently synchronize LSDB on a multi-access network such as Ethernet.
Read moreHow show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
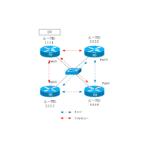
Configure OSPF on the four Cisco routers on the Ethernet and make sure that they are only adjacent with DR.
Read moreOSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces

The OSPF network type is a classification of OSPF enabled interfaces.
This section explains the main network types and what is determined by the network type.
Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
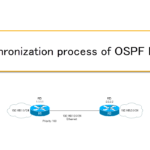
This section describes the LSDB synchronization process between two OSPF routers that are adjacency on Ethernet.
Read moreProblems with large-scale OSPF network
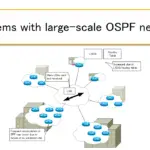
This section describes the issues that arise when OSPF networks become large.
Read moreOSPF Area - Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
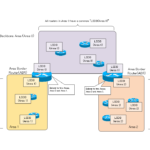
An OSPF area is "a group of OSPF routers with the same LSDB. This section explains the OSPF area in detail.
Read moreOSPF Router Type
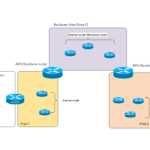
By dividing the OSPF network into areas, there are different types of OSPF routers. This section describes the different types of OSPF routers.
Read moreOSPF LSA Type
There are various types of LSAs that are exchanged between OSPF routers.
This section describes the major types of LSAs.
OSPF Area Type

There are several types of OSPF areas, and this section explains the characteristics of the OSPF area types.
Read moreOSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
There are two basic configuration procedures for OSPF
1. Enable the OSPF routing process.
2. Enable OSPF on the interface
Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
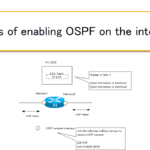
Routing protocols such as OSPF are enabled on the router interface.
This section explains in detail about enabling OSPF on the router interface.
OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface

OSPF advertises the route of a loopback interface as a host route.
This section explains in detail about the advertising of loopback interfaces in OSPF.
Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval

Describes the commands for configuring and verifying the OSPF Hello/Dead interval on Cisco routers.
Read moreOSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
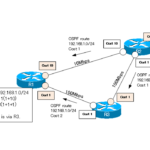
The metric for determining the best route in OSPF is the path cost. It is the cumulative cost of an interface on a route.
This section explains the concept of path cost and how to change and check the cost on a Cisco router.
Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority

This section describes the commands for configuring and verifying the router priority value to determine DR/BDR on Cisco routers.
Read moreConfiguring OSPF Neighbor Authentication

OSPF has an authentication feature for neighbors. The authentication feature prevents a router from becoming a neighbor of an unauthorized router.
Read moreNeighbor Authentication over Virtual-link

This section will specifically explain the precautions for neighbor authentication on virtual-link.
Read moreOSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]

This section describes how to configure and verify stub, totaly stub, NSSA, and totaly NSSA on Cisco routers.
Read moreOSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]

Stub area configuration can reduce the number of LSAs advertised to small networks; here is a specific example of stub area configuration on a Cisco router.
Read moreOSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
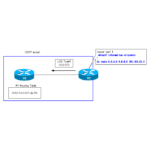
You can generate a default route in OSPF and advertise it to other OSPF routers. on Cisco routers, the default-information originate command is mainly used.
Read moreConfiguration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area

By configuring the OSPF area as a stub area, the ABR will automatically generate a default route (0.0.0.0/0).
This section describes a configuration example of default route generation by stub area.
OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link

OSPF virtual link is a virtual area 0 point-to-point link. Virtual-link is explained in this section.
Read moreConfiguring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]

This section describes the configuration and verification commands for OSPF virtual-link on Cisco routers.
Read moreOSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]

This is an example of configuring OSPF virtual-link on Cisco routers. The virtual-link provides a virtual connection to the backbone area.
Read moreOSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example

A link failure in the backbone area may result in a discontinuous backbone. In such a case, Virtual-link can be used to configure the backbone area to be continuous.
Read moreOSPF Route Summary and Configuration

In OSPF, route summary can be performed with ABR and ASBR.
This section explains the mechanism of route summary with ABR/ASBR in OSPF and the configuration commands on Cisco routers.
Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example

This is an example of configuring OSPF inter-area route summary on a Cisco router. Notice the default cost of the default summary route.
Read moreOSPF Route Type Preference

When the OSPF route type is different, the priority is determined regardless of the path cost.
Read moreWhy the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?

This section details how OSPF neighbors can get stuck in the Exstart state.
Read moreOSPF packet type and header format
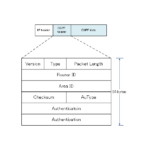
OSPF defines five types of packets to perform various processes; this section describes the types of OSPF packets and the header formats common to OSPF packets.
Read moreOSPF Hello Packet
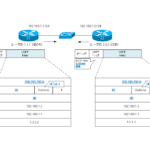
OSPF Hello packets are used to establish OSPF neighbors; this section details the format of OSPF Hello packets and the conditions for establishing a neighbor.
Read moreOSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
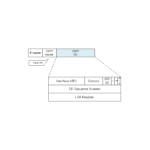
OSPF DD packets are packets that provide an overview of LSDB. the format of DD packets is explained.
Read moreOSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
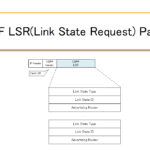
Request the LSA with OSPF LSR Packet. This section describes the format of LSR packet.
Read moreOSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
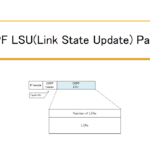
The OSPF LSU packet is used to advertise the LSAs requested in the LSR packet.
Read moreOSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet

OSPF LSAck packet is a packet to confirm the reception of LSAs.
Read moreLimitation of OSPF redistribution routes - redistribute maximum-prefix command

The redistribute maximum-prefix command is used to prevent an unexpectedly large amount of route information from being redistributed to OSPF.
This section describes the redistribute maximum-prefix command.
Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF - Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5

The route filters in OSPF are LSA type 3 and LSA type 5 filters.
This section provides an overview of LSA type 3/LSA type 5 filters.
Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
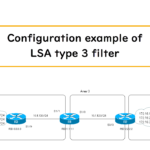
This is a configuration example of an OSPF LSA type 3 filter in a simple network diagram. Make sure you have a good grasp of the in and out directions to which the filter will be applied.
Read moreConfiguration example of LSA type 5 filter
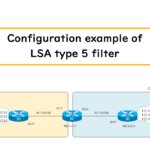
This is a configuration example of filtering LSA type 5 in a simple network diagram. We will configure a filter using distribute-list and route-map.
Read moreOSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
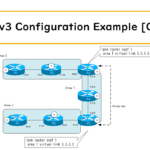
Build an IPv6 routing table by OSPFv3. This is a configuration example for a normal OSPF process that does not support address-family. Also, it takes an area layout that requires virtual links. The basic concept of a virtual link is the same as OSPFv2 for IPv4.
Read moreConfiguration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]
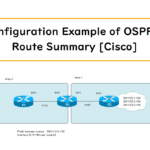
This is a configuration example for summarizing OSPFv3 inter-area routes on Cisco router. The concept of the cost of summarized route is different for OSPFv3 than for OSPFv2 for IPv4.
Read more