Table of Contents
Basic EIGRP configuration procedure
There are two basic configuration procedures for EIGRP
Enabling the EIGRP Routing Process
Allowing routers to process EIGRP
Enable EIGRP on interfaces
Enables an interface to send and receive EIGRP packets, and registers the network address of the enabled interface in the topology table as EIGRP route information.
Enabling the EIGRP Routing Process
The first step is to enable the EIGRP routing process so that it can process EIGRP.To enable the EIGRP routing process, enter the following command in global configuration mode.
(config)#router eigrp <AS>
(config-router)#
<AS> : AS number
The AS number is an arbitrary number from 1 to 65535. the EIGRP routing process can also be initiated by a single router. In the case of EIGRP. you must match the AS number with the other routers. Because the AS numbers may match the conditions for establishing a neighbor in EIGRP.
Enable EIGRP on interfaces
EIGRP, like RIP and OSPF, is enabled on a per-interface basis. It’s important to clarify that the routing protocol is enabled on the router’s interface.
To enable EIGRP on an interface, use the network command in EIGRP’s configuration mode.
(config-router)#network <ip-address> [<wildcard>]
<ip-address> : IP address
<wildcardmask> : Wildcard mask
As with the OSPF network command, the wildcard mask allows for flexibility in specifying the IP address bit pattern. If you omit the wildcard mask, it is treated as a natural mask of the class. The interface whose IP address matches the bit pattern of the specified IP address and the wildcard mask is the interface for which EIGRP is enabled.
A simple configuration example
As an example of such a two-step configuration for EIGRP, consider the following simple network diagram.
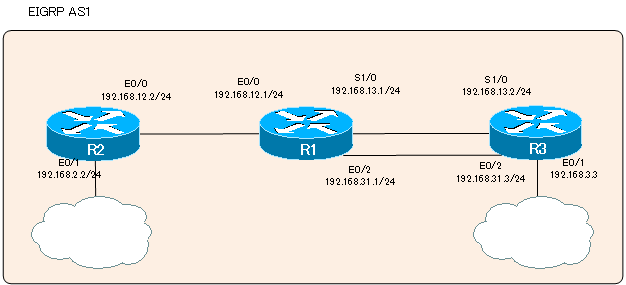
R1
router eigrp 1 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
R1 is a configuration that enables EIGRP on interfaces with IP addresses beginning with “192.168” by checking only the first 16 bits of the wildcard mask. A one-line network command enables EIGRP on three interfaces, E0/0, E0/2, and Se1/0.
R2
router eigrp 1 network 192.168.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.12.2 0.0.0.0
In R2, this is a configuration that specifies an interface with an exact matching IP address with a wildcard mask 32 bits.
R3
router eigrp 1 network 192.168.3.0 network 192.168.13.0 network 192.168.31.0
The R3 configuration is an example of a natural mask of a class when the wildcard mask is omitted.
Other configurations of EIGRP
Router ID
Like OSPF, EIGRP also identifies a router by its router ID. The method for determining the router ID is the same as for OSPF. To configure the router ID manually, use the following command in EIGRP configuration mode.
(config-router)#eigrp router-id <router-id>
<router-id> : Router ID
Disabling Auto Summary
EIGRP, like RIP, auto-summary at class boundaries. However, it is now rarely used for auto-summary. To disable auto-summary, enter the following command in EIGRP configuration mode
(config-router)#no auto-summary
Change the hello interval/hold down timer
The interval between sending Hello packets of EIGRP is the Hello interval. Also, the time at which the neighbor is considered to be down is the hold down timer. To change it, enter the following command in interface configuration mode.
(config-if)#ip hello-interval eigrp <AS> <hello>
(config-if)#ip hold-time eigrp <AS> <hold_time>
<AS> : AS number
<hello> : Hello interval
<hold_time> : Hold down timer
passive-interface
There is no need to send EIGRP packets to an interface to which only PCs, servers, etc. are connected and to which no EIGRP router is connected. Such an interface will stop sending EIGRP packets as a passive-interface.
(config-router)#passive-interface <interface-name>
<interface-name> : Interface name for passive-interface
As with OSPF, the passive-interface interface does not establish a neighbor.
unequal cost load balance
To configure unequal cost load balancing, which registers not only the successors but also the feasible successors in the routing table, enter the following command in EIGRP configuration mode.
(config-router)#variance <value>
<value> : coefficient
The default is 1, so it is an equal cost load balance.
Verification of EIGRP
The table below summarizes the main commands used to verify the operation of EIGRP.
| Verification commands | Summary |
| #show ip protocols | Displays general information about the routing protocol. |
| #show ip eigrp interface | Displays information about EIGRP-enabled interfaces. |
| #show ip eigrp neighbor | Display the EIGRP neighbor. |
| #show ip eigrp topology | Displays the EIGRP topology table. |
| #show ip route eigrp | Displays the EIGRP route in the routing table. |
show ip protocols
show ip protocols displays general information about the routing protocol. you can verify the AS number, K-value, variance value, etc. for EIGRP.
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 20
Redistributing: eigrp 1
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Automatic address summarization:
192.168.31.0/24 for Ethernet0/0, Serial1/0
192.168.13.0/24 for Ethernet0/0, Ethernet0/2
192.168.12.0/24 for Ethernet0/2, Serial1/0
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.0.0/16
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.13.3 90 00:00:03
192.168.12.2 90 00:00:03
192.168.31.3 90 00:00:03
Distance: internal 90 external 170
show ip eigrp interface
You can use show ip eigrp interface to check the EIGRP-enabled interfaces.
R1#show ip eigrp interfaces
IP-EIGRP interfaces for process 1
Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Et0/0 1 0/0 32 0/2 144 0
Et0/2 1 0/0 25 0/2 64 0
Se1/0 1 0/0 28 0/15 99 0
show ip eigrp neighbor
Use show ip eigrp neighbor to verify the EIGRP neighbor. as with OSPF. route information is exchanged only after the neighbor is established. it is important to verify EIGRP operation by checking the neighbor using the show ip eigrp neighbor command.
R1#show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
2 192.168.31.3 Et0/2 13 00:27:25 25 200 0 11
1 192.168.13.3 Se1/0 13 00:27:29 28 200 0 9
0 192.168.12.2 Et0/0 13 00:28:10 32 200 0 5
show ip eigrp topology
Use the show ip eigrp topolgy command to display the EIGRP topology table successors and feasible successors.
R1#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(1)/ID(192.168.31.1)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.12.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 281600
via Connected, Ethernet0/0
P 192.168.13.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2169856
via Connected, Serial1/0
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 307200
via 192.168.12.2 (307200/281600), Ethernet0/0
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 307200
via 192.168.31.3 (307200/281600), Ethernet0/2
via 192.168.13.3 (2195456/281600), Serial1/0
P 192.168.31.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 281600
via Connected, Ethernet0/2
‘via Connected’ means that this is the EIGRP route generated by the network command. show ip eigrp topology followed by a specific network address for more detailed information.
R1#show ip eigrp topology 192.168.3.0/24
IP-EIGRP (AS 1): Topology entry for 192.168.3.0/24
State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 307200
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
192.168.31.3 (Ethernet0/2), from 192.168.31.3, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (307200/281600), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 10000 Kbit
Total delay is 2000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 1
192.168.13.3 (Serial1/0), from 192.168.13.3, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (2195456/281600), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 1544 Kbit
Total delay is 21000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 1
show ip route eigrp
The show ip route eigrp command displays only the EIGRP routes in the routing table.
R1#show ip route eigrp
D 192.168.2.0/24 [90/307200] via 192.168.12.2, 00:15:54, Ethernet0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/307200] via 192.168.31.3, 00:15:54, Ethernet0/2
[90/2195456] via 192.168.13.3, 00:15:54, Serial1/0
There are two codes for the EIGRP root, as follows
| Code | Summary |
| D | EIGRP routes |
| D EX | The routes of a non-EIGRP domain |