Table of Contents
Overview
This is an example of a VRF-aware IPSec VTI configuration that uses FVRF. Please make sure you understand that “IPSec communication is performed in the FVRF (underlay network)” and configure it accordingly.
Related article
The following article explains the concept of configuring IPSec VTI with FVRF.
Network Diagram
Consider the following network diagram. This is same network diagram of “Point-to-Point GRE Tunnel with FVRF (tunnel vrf command)”. The underlay network in this network diagram is not the Internet, but is assumed to be the Internet.
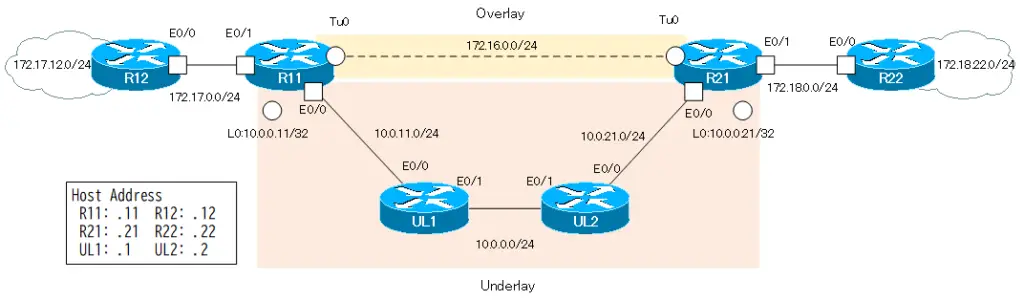
Configuration conditions
Build a point-to-point IPSec VTI overlay network between R11 and R12. Then, separate the overlay network from the underlay network with VRF; as VRF, configure the following
| Router | VRF name | RD | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| R11 | FVRF | 65001:100 | Lo0 Eth0/0 |
| IVRF | 65001:200 | Tunnel0 Eth0/1 | |
| R21 | FVRF | 65001:100 | Lo0 Eth0/0 |
| IVRF | 65001:200 | Tunnel0 Eth0/1 |
In addition, the address ranges of IVRF in the overlay network and FVRF in the underlay network do not overlap. IVRF is addressing with Class B private addresses such as 172.16.x.x and 172.17.x.x and 172.18.x.x. And FVRF is addressing with class A private addresses of 10.x.x.x.
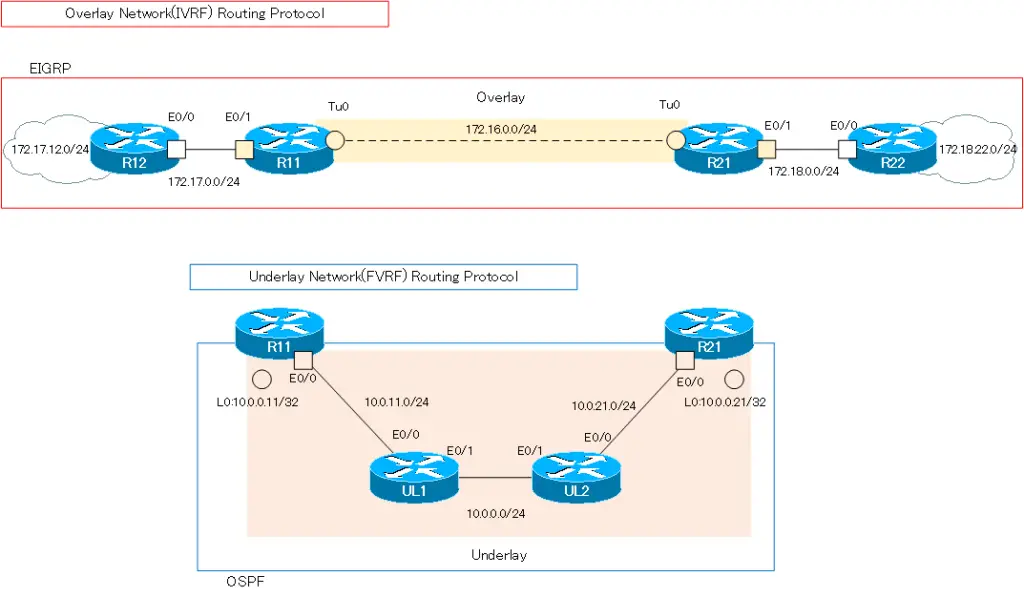
As routing protocols, IVRF uses EIGRP and FVRF uses OSPF.
| Address Range | Routing Protocol | |
|---|---|---|
| Overlay Network(IVRF) | 172.16.0.0/16 172.17.0.0/16 172.18.0.0/16 | EIGRP |
| Underlay Network(FVRF) | 10.0.0.0/8 | OSPF |
Overlay network data is encrypted with IPSec and transferred over the underlay network. The various IPSec parameters are as follows
| Encryption algorithm | 3DES |
| Hash Algorithm | MD5 |
| Peer Authentication | PSK |
| DH group | 2 |
| Security protocol | ESP |
| Encryption algorithm | 3DES |
| Hash Algorithm | MD5 |
Initial Configuration
Start with an overlay network with a point-to-point GRE tunnel between R11 and R21 to separate VRFs. This is the completion phase of “Point-to-Point GRE Tunnel with FVRF (tunnel vrf command)”. Focus on configurations that change from point-to-point GRE tunnels to IPSec VTI.
R11 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname R11 ! ip vrf FVRF rd 65001:100 ! ip vrf IVRF rd 65001:200 ! interface Loopback0 ip vrf forwarding FVRF ip address 10.0.0.11 255.255.255.255 ! interface Tunnel0 ip vrf forwarding IVRF ip address 172.16.0.11 255.255.255.0 tunnel vrf FVRF ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding FVRF ip address 10.0.11.11 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip vrf forwarding IVRF ip address 172.17.0.11 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 ! address-family ipv4 vrf IVRF autonomous-system 1 network 172.16.0.0 network 172.17.0.0 exit-address-family eigrp router-id 11.11.11.11 ! router ospf 1 vrf FVRF router-id 11.11.11.11 network 10.0.0.11 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.0.11.11 0.0.0.0 area 0
R21 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname R21 ! ip vrf FVRF rd 65100:100 ! ip vrf IVRF rd 65100:200 ! interface Loopback0 ip vrf forwarding FVRF ip address 10.0.0.21 255.255.255.255 ! interface Tunnel0 ip vrf forwarding IVRF ip address 172.16.0.21 255.255.255.0 tunnel vrf FVRF ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding FVRF ip address 10.0.21.21 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip vrf forwarding IVRF ip address 172.18.0.21 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 ! address-family ipv4 vrf IVRF autonomous-system 1 network 172.16.0.0 network 172.18.0.0 exit-address-family eigrp router-id 21.21.21.21 ! router ospf 1 vrf FVRF router-id 21.21.21.21 network 10.0.0.21 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.0.21.21 0.0.0.0 area 0
R12 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname R12 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.17.12.12 255.255.255.0 ip ospf network point-to-point ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.17.0.12 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 network 172.17.0.0 eigrp router-id 12.12.12.12
R22 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname R22 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.18.22.22 255.255.255.0 ip ospf network point-to-point ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 172.18.0.22 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 1 network 172.18.0.0 eigrp router-id 22.22.22.22
UL1 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname UL1 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.11.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
UL2 Configuration Excerpts (Click)
hostname UL2 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.21.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Related article
Initial configuration is the completion phase of the following article.
Configuration and Verification
Step1: ISAKMP policy configuration
Configure a common ISAKMP policy for R11/R21 with the aforementioned IKE Phase1 parameters.
R11/R21 ISAKMP policy
crypto isakmp policy 10 encr 3des hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
Step2: crypto keyring configuration
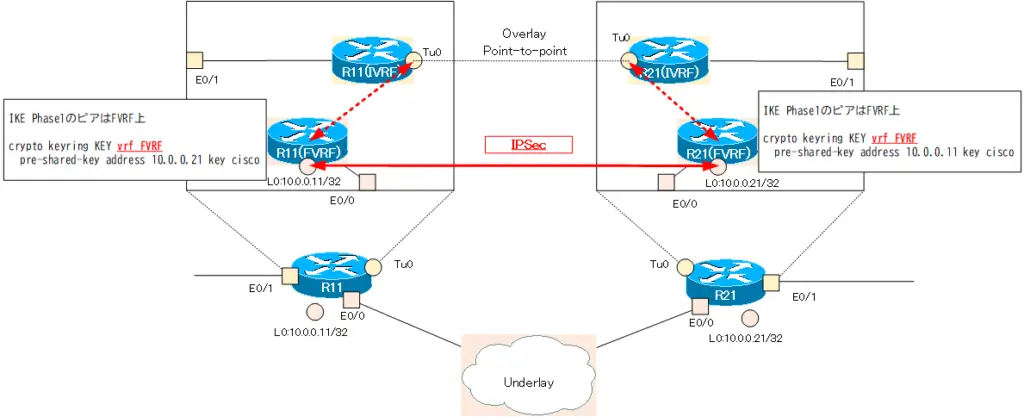
Configure the VPN gateway peer for IPSec communication in R11/R21. IPSec communication is performed over the FVRF of the underlay network. Specify FVRF with crypto keyring vrf command.
R11 crypto keyring
crypto keyring KEY vrf FVRF pre-shared-key address 10.0.0.21 key cisco
R21 crypto keyring
crypto keyring KEY vrf FVRF pre-shared-key address 10.0.0.11 key cisco
Step3: IPSec transform configuration
Configure the transform set to be used for IPSec in IKE Phase2. On R11/R21, configure a common IPSec transform set of the aforementioned parameters.
R11/R21 IPSec transformset
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac mode tunnel
Step4: IPSec profile configuration
Configure a common IPSec profile on R11/R21. The IPSec profile associates an IPSec transform set.
R11/R21 IPSec profile
crypto ipsec profile IPSEC set transform-set TS
Step5: IPSec VTI configuration
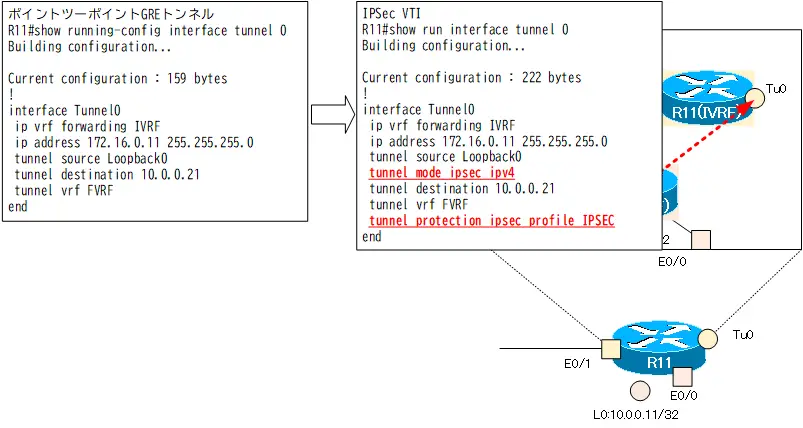
Change the Tunnel0 interface from a point-to-point GRE tunnel to an IPSec VTI. The current Tunnel0 interface configuration for R11 is as follows
R11 show running-config interface tunnel0
R11#show running-config interface tunnel 0 Building configuration... Current configuration : 159 bytes ! interface Tunnel0 ip vrf forwarding IVRF ip address 172.16.0.11 255.255.255.0 tunnel source Loopback0 tunnel destination 10.0.0.21 tunnel vrf FVRF end
To reduce the GRE header overhead, use the tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 command to make it IPSec VTI. Then, the IPSec profile is applied with the tunnel protection command to encrypt all packets handled by Tunnel0 with IPSec.
R11 IPSec VTI
interface Tunnel0 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel protection ipsec profile IPSEC
The IPSec VTI configuration commands for R21 are exactly the same as for R11.
R21 IPSec VTI
interface Tunnel0 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel protection ipsec profile IPSEC
Step6: IPSec VTI verification
Verify that IPSec VTI is working properly by using the following show command.
- show crypto isakmp sa
- show crypto ipsec sa
- show interface tunnel 0
Here is an example of output on R11.
R11 IPSec VTI verification
R11#show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dst src state conn-id status
10.0.0.21 10.0.0.11 QM_IDLE 1001 ACTIVE
IPv6 Crypto ISAKMP SA
R11#show crypto ipsec sa
interface: Tunnel0
Crypto map tag: Tunnel0-head-0, local addr 10.0.0.11
protected vrf: IVRF
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port): (0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0/0/0)
current_peer 10.0.0.21 port 500
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,}
#pkts encaps: 95, #pkts encrypt: 95, #pkts digest: 95
#pkts decaps: 101, #pkts decrypt: 101, #pkts verify: 101
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed: 0
#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed: 0
#send errors 0, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 10.0.0.11, remote crypto endpt.: 10.0.0.21
plaintext mtu 1446, path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu idb Ethernet0/0
current outbound spi: 0x8378E9A7(2205739431)
PFS (Y/N): N, DH group: none
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x9ED7F06A(2664951914)
transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 1, flow_id: SW:1, sibling_flags 80004040, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4263551/3167)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0x8378E9A7(2205739431)
transform: esp-3des esp-md5-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 2, flow_id: SW:2, sibling_flags 80004040, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec): (4263552/3167)
IV size: 8 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:
R11#show interfaces tunnel 0
Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
Internet address is 172.16.0.11/24
MTU 17886 bytes, BW 100 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive not set
Tunnel linestate evaluation up
Tunnel source 10.0.0.11 (Loopback0), destination 10.0.0.21
Tunnel Subblocks:
src-track:
Tunnel0 source tracking subblock associated with Loopback0
Set of tunnels with source Loopback0, 1 member (includes iterators), on interface
Tunnel protocol/transport IPSEC/IP
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel transport MTU 1446 bytes
Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps)
Tunnel protection via IPSec (profile "IPSEC")
~省略~
Tunnel0 of the R11 IPSec VTI is working. Therefore, EIGRP neighbors with R21 on Tunnel0 and the IVRF routing table has been successfully built.
R11 IVRF routing verification
R11#show ip eigrp vrf IVRF neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1) VRF(IVRF)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
1 172.16.0.21 Tu0 14 00:11:31 13 1494 0 14
0 172.17.0.12 Et0/1 11 00:11:48 8 100 0 10
R11#show ip route vrf IVRF
Routing Table: IVRF
~省略~
Gateway of last resort is not set
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.16.0.0/24 is directly connected, Tunnel0
L 172.16.0.11/32 is directly connected, Tunnel0
172.17.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 172.17.0.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1
L 172.17.0.11/32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/1
D 172.17.12.0/24 [90/409600] via 172.17.0.12, 00:11:51, Ethernet0/1
172.18.0.0/24 is subnetted, 2 subnets
D 172.18.0.0 [90/26905600] via 172.16.0.21, 00:11:21, Tunnel0
D 172.18.22.0 [90/27033600] via 172.16.0.21, 00:11:21, Tunnel0
Step7: Communication Verification
Verify that the overlay network communication can be successful; Ping from R12 to R22.
Ping from R12 to R22
R12#ping 172.18.22.22 source 172.17.12.12 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.18.22.22, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 172.17.12.12 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/2 ms
The overlay network is communicating properly; a ping from R12 to R22 captured on R11 E0/1 shows the following.
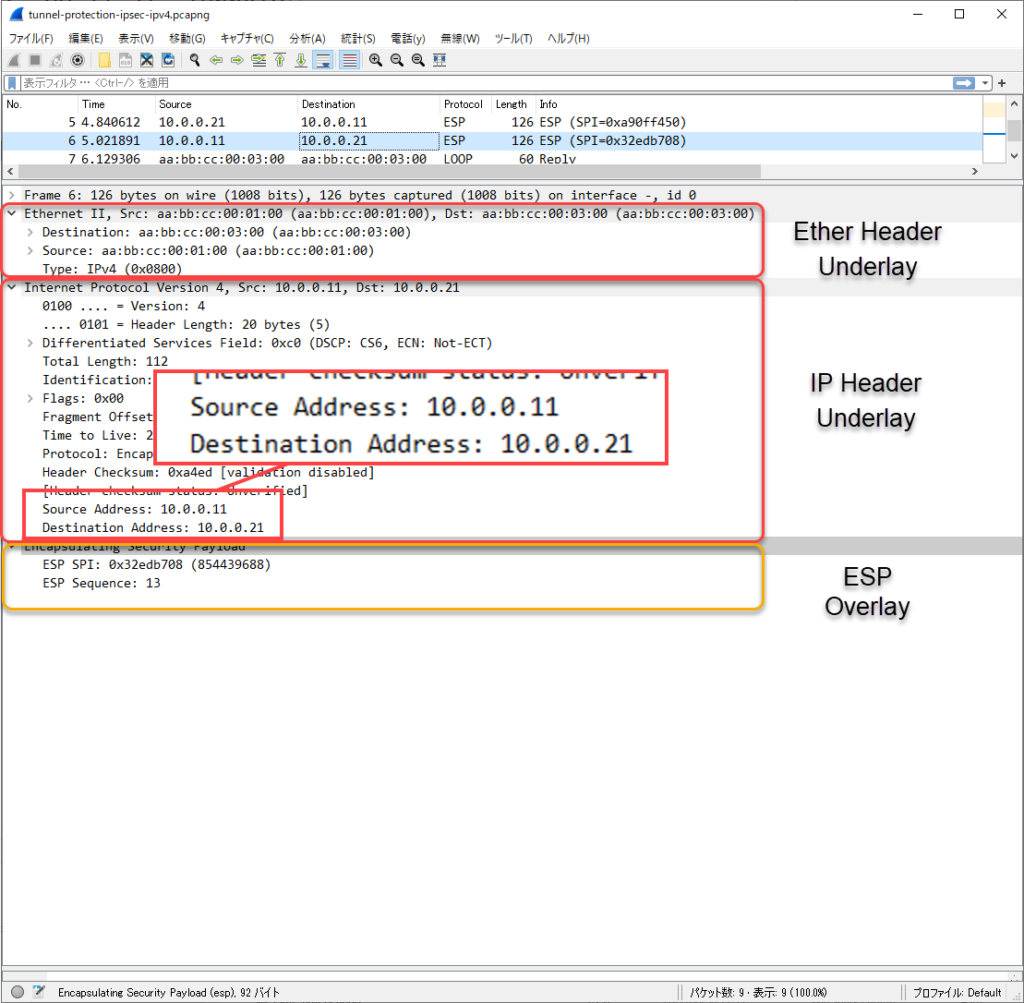
オーバーレイネットワークのデータは、IPSec(ESP)で暗号化されていることがわかります。
Configuration command summary
This is a summary of the configuration commands configured on R11/R21 from the initial configuration state.
R11 Configuration command summary
crypto keyring KEY vrf FVRF pre-shared-key address 10.0.0.21 key cisco ! crypto isakmp policy 10 encr 3des hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 ! crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac mode tunnel ! crypto ipsec profile IPSEC set transform-set TS ! interface Tunnel0 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel protection ipsec profile IPSEC
R21 Configuration command summary
crypto keyring KEY vrf FVRF pre-shared-key address 10.0.0.11 key cisco ! crypto isakmp policy 10 encr 3des hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 ! crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac mode tunnel ! crypto ipsec profile IPSEC set transform-set TS ! interface Tunnel0 ip vrf forwarding IVRF tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel protection ipsec profile IPSEC
Advanced IP Routing
- Overview of Cisco Route-map
- Cisco Route-map Configuration
- GRE Tunnel Interface – Virtual Point-to-Point Connection
- GRE Tunnel Interface Configuration Example
- Overview of VRF/VRF-Lite – Virtually separating the router –
- Cisco VRF Configuration and Verification Commands
- Cisco Layer 3 VPN with VRF-Lite Configuration Example
- What Is FVRF(Front door VRF)?
- Point-to-point GRE Tunnel without FVRF
- Point-to-point GRE tunnel with FVRF (tunnel vrf command)
- IPSec VTI with FVRF
- IPSec VTI with FVRF Configuration Example
- DMVPN with FVRF
- DMVPN with FVRF Configuration Example Part1
- DMVPN with FVRF Configuration Example Part2


