Table of Contents
Overview
FVRF (Front door VRF) is the logical separating of overlay and underlay networks by VRF. This article describes the concept of FVRF.
What is FVRF(Front door VRF)?
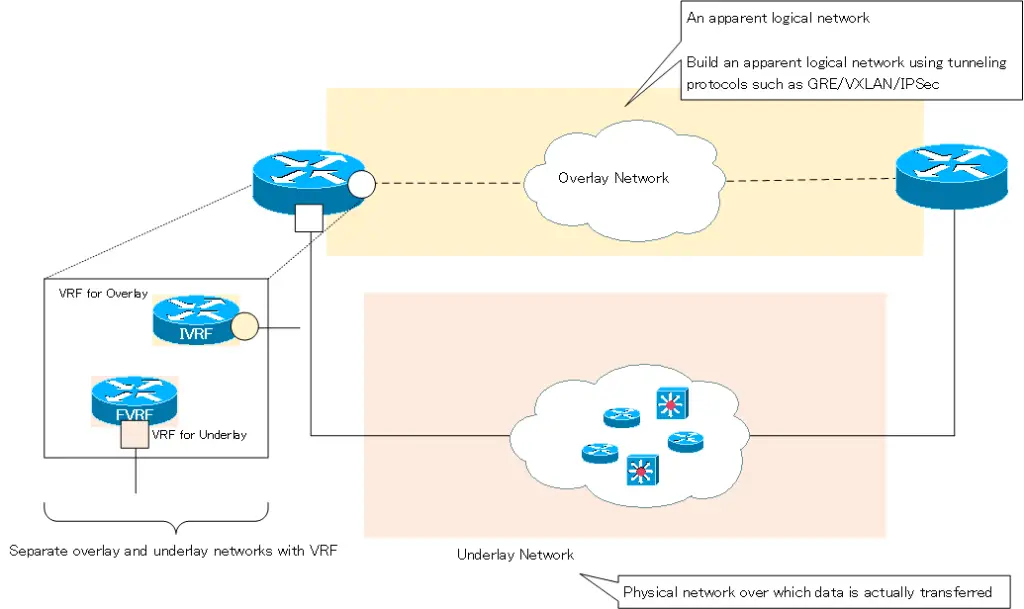
FVRF (Front door VRF) is a logical separation of overlay and underlay networks by VRF. The following two VRFs are used
- FVRF(Front door VRF)
- IVRF(Inside VRF)
FVRF is configured as VRF for underlay network. And IVRF is configured as VRF for the overlay network. The following figure shows how FVRF and IVRF separate the overlay and underlay networks.
Advantages of FVRF
The main advantages of a properly logically separation of the overlay and underlay networks by FVRF/IVRF are considered to be the following.
- Addressing flexibility
- Secure Communications
- Establish stable overlay networks
Addressing flexibility
The overlay and underlay networks are separated by VRF, so addressing can be done freely on each. Overlay and underlay networks can have overlapping address ranges.
In addition, not only one overlay network, but multiple overlays can be stacked. In other words, they can be multi-tenanted. The same address range can be used in an underlay network and an overlay network that is multi-tenanted.
Secure Communications
Because they are separated by VRF, there is no direct communication between the overlay network and the underlay network. When using the Internet as an underlay network, crackers on the underlay network will not be able to attack the overlay network.
If you need to communicate with overlay and underlay networks, you can also flexibly control which networks can communicate through route leaks.
Establish stable overlay networks
If the overlay and underlay networks are not properly separated, the routing table will contain a mixture of underlay and overlay route information. A minor misconfiguration can break the overlay network.
Separating overlay and underlay networks by VRFs allows the effects of any misconfiguration or failure to remain within the respective VRFs.
Disadvantages…
I think the disadvantage of FVRF is that it looks kind of difficult. When I studied about FVRF, I read various books and web pages. Many of them were ” something difficult” because of the sudden DMVPN configurations and so on.
It will be easier to understand if you try to configure FVRF in a simple network diagram. It may seem “difficult,” but when you think about it simply, it’s not so difficult. First, it is easier to understand if you consider a network diagram using point-to-point GRE tunnels as an overlay network. Start with point-to-point GRE tunnels and consider VRF-aware IPSec VTI or DMVPN using FVRF.
- Point-to-point GRE tunnel without FVRF
- Point-to-point GRE tunnel with FVRF
- IPSec VTI with FVRF
- IPSec VTI with FVRF configuration example
- DMVPN with FVRF
- DMVPN with FVRF configuration example part1
- DMVPN with FVRF configuration example part2
Summary
Points
- FVRF (Front door VRF) is the logical separation of overlay and underlay network by VRFs.
- The VRF to be defined as the VRF for the underlay network is called FVRF. The VRF for overlay network is IVRF.
- The following are some of the advantages of using FVRF
- Addressing flexibility
- Secure Communications
- Establish stable overlay networks
Advanced IP Routing
- Overview of Cisco Route-map
- Cisco Route-map Configuration
- GRE Tunnel Interface – Virtual Point-to-Point Connection
- GRE Tunnel Interface Configuration Example
- Overview of VRF/VRF-Lite – Virtually separating the router –
- Cisco VRF Configuration and Verification Commands
- Cisco Layer 3 VPN with VRF-Lite Configuration Example
- What Is FVRF(Front door VRF)?
- Point-to-point GRE Tunnel without FVRF
- Point-to-point GRE tunnel with FVRF (tunnel vrf command)
- IPSec VTI with FVRF
- IPSec VTI with FVRF Configuration Example
- DMVPN with FVRF
- DMVPN with FVRF Configuration Example Part1
- DMVPN with FVRF Configuration Example Part2
