Table of Contents
Two types of relationships between OSPF routers
In OSPF, there are two types of relationships between routers
- neighbor
- adjacency
To understand how OSPF works, it is important to understand the relationship between these two types of OSPF routers.
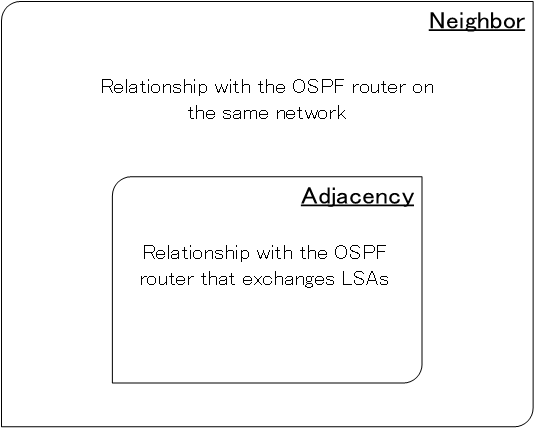
Neighbor
Neighbor is the relationship between OSPF routers on the same network. OSPF first discovers neighbors through Hello packets.
Related article
Neighbor discovery using Hello packets is explained in the following article.
Adjacency
Adjacency is the relationship between OSPF routers that exchange LSAs. Adjacency is a prerequisite for being a neighbor, and a special kind of neighbor is an adjacency.
Network types and neighbor/adjacency
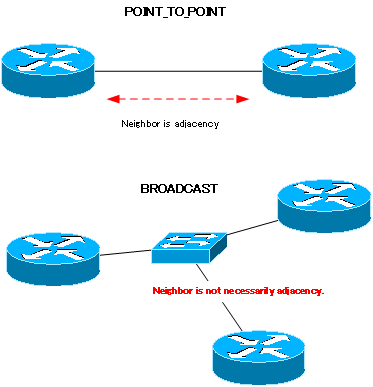
One of the things that gets confusing when thinking about neighbor and adjacency is that neighbor does not necessarily mean adjacency. It depends on the OSPF network type.
The OSPF network type is a classification of OSPF enabled interfaces. The main network types are as follows
- BROADCAST
- POINT_TO_POINT
- NON_BROADCAST
- POINT_TO_MULTIPOINT
The interface on which OSPF is enabled determines the default network type.
| Interface type | OSPF Network type |
| Ethernet | BROADCAST |
| Point-to-point | POINT_TO_POINT |
| Frame Relay/ATM | NON_BROADCAST |
Related article
For more information about OSPF network types, please see the following article.
We rarely use Frame Relay/ATM anymore. Therefore, it is enough to know only BROADCAST and POINT_TO_POINT as network types.
POINT_TO_POINT has only two OSPF routers connected to the same network. Therefore, in POINT_TO_POINT, neighbor is adjacency. On the other hand, BROADCAST will have two or more OSPF routers connected on the same network. Neighbor, i.e., not necessarily adjacency.
DR/BDR Overview
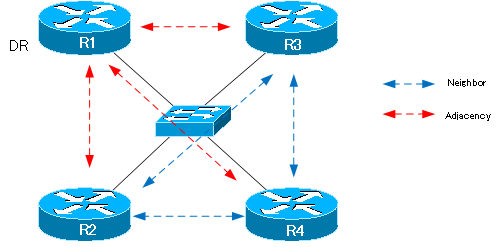
On a BROADCAST network, such as Ethernet, the relationship between DR/BDR is adjacency. DR and BDR are routers that are elected to efficiently synchronize LSDB on networks that are BROADCAST network types such as Ethernet.
Consider the example of four OSPF routers, R1 to R4, connected to the same Ethernet network. If R1 is the DR, the relationship between R1 is neighbor and adjacency; R2 to R4 exchange LSAs with R1. Other than that, they are just neighbors. For example, R2 and R3 are simply neighbors that are OSPF routers connected on the same network; they do not exchange LSAs.
Related article
Summary
Point
- There are two types of relationships between OSPF routers: neighbor and adjacency.
- The neighbor is the relationship between the OSPF routers on the same network.
- Adjacency is the relationship between the routers that exchange LSAs.
- Depending on the network type, the neighbor may not necessarily be the adjacency.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]