Table of Contents
How to generate a default route in OSPF
OSPF can also generate default route like other routing protocols such as RIP and EIGRP. As shown in the following figure, default route is often used to route packets destined for the Internet.
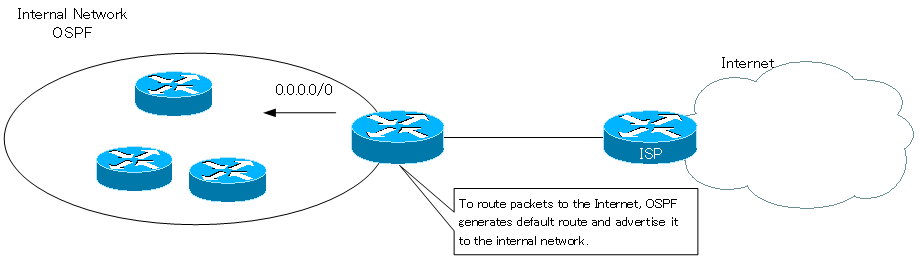
In addition to routing to the Internet, default route is also generated to ensure reachability from the stub area to the external network. To generate default route in OSPF, the following methods are available
- default-information originate command
- Make the area as a stub area
In the following sections, we will explain how to generate default route in OSPF.
default-information originate command
In RIP and EIGRP, the default route can be generated by configuring it as a static route and redistributing it. However, with OSPF, the default route cannot be generated in this way. When static routes are redistributed to OSPF, the default route is not subject to redistribution. To generate a default route in OSPF, use the default-information originate command. The command syntax is as follows
(config)#router ospf <process>
(config-router)#default-information originate [always] [metric <metric>] [metric-type {1|2}]
The default-information originate command causes the router to generate a default route with LSA type 5. Also, the metric type is 2 and the metric is 1. The metric value and metric type can be changed by specifying options.
However, there is a condition for generating a default route. The condition is that the default route must already exist in the routing table. To generate an OSPF default route even when there is no default route in the routing table, add the “always” option.
- Generate 0.0.0.0/0 with LSA type 5 and advertise it to other OSPF routers
- The default route must already exist in the routing table.
Example of default-information originate
Verify the default-information originate configuration in the following network diagram.
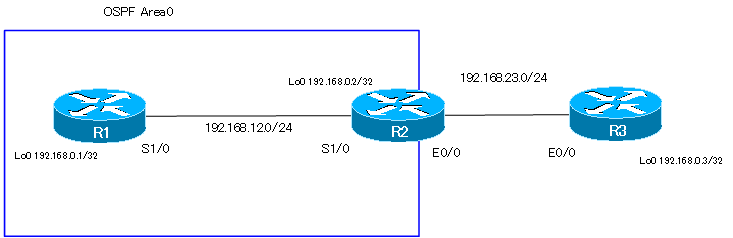
Configure R2 in this network diagram as follows to generate the default route.
R2 Generate default route
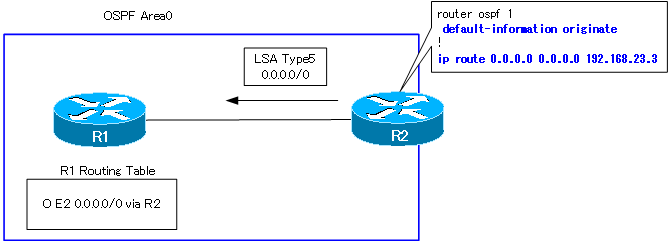
router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 log-adjacency-changes network 192.168.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 default-information originate ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.23.3
After configuring the default route statically, the default-information originate command will cause R2 to generate LSA type 5, which represents the default route. the LSA type 5 of R2 is as follows
R2 show ip ospf database external
R2#show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 1)
Type-5 AS External Link States
LS age: 88
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 0.0.0.0 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 2.2.2.2
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0xFCAC
Length: 36
Network Mask: /0
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 1
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 1
Then, the default route with R2 as the next hop will appear in the routing table of R1. Since it is an external route and metric type 2, it will be coded “O E2”.
R1 show ip route
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.12.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 192.168.12.0 is directly connected, Serial1/0
192.168.0.0/32 is subnetted, 2 subnets
C 192.168.0.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 192.168.0.2 [110/65] via 192.168.12.2, 00:03:56, Serial1/0
O*E2 0.0.0.0/0 [110/1] via 192.168.12.2, 00:03:56, Serial1/0
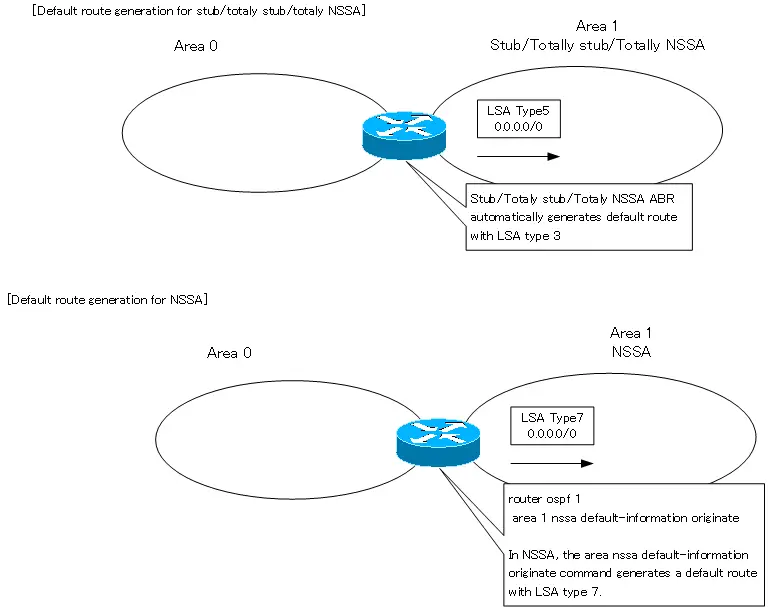
Generate default route by stub area
The ABR of the stub area will generate a default route. ABRs in the Totally Stub area and Totally NSSA also automatically generate default routes. The default route generated by ABR in stub, Totally Stub, and Totally NSSA is LSA type 3.
Note that NSSA’s ABR does not automatically generate the default route; you must explicitly configure the area nssa default-information originate command in order for NSSA to generate the default route. And in this case, the default route will be generated with LSA type 7.
The following figure shows the generation of a default route in a stub area.
Related article
The generation of default routes in the stub area is explained in the following article.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]
