Table of Contents
Summary
This is a configuration example of filtering LSA type 5 in a simple network diagram. We will configure a filter using distribute-list and route-map.
Related article
Please see the following article about the concept of LSA Type 5 filters and command format.
Network Diagram
In the network diagram shown below, perform a LSA type 5 filter.
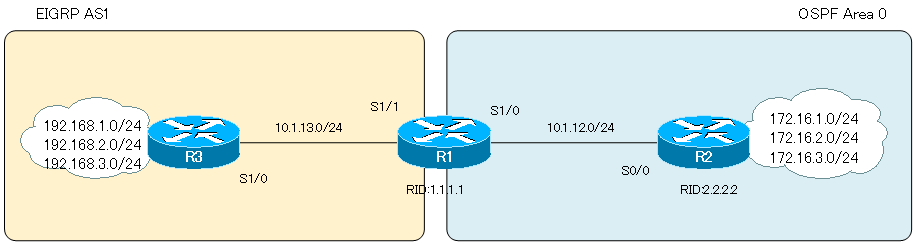
R1 is the ASBR that acts as the boundary between EIGRP and OSPF. Redistribute the EIGRP route information to OSPF on R1. By redistributing, R1 will generate LSA type 5. We will configure the filter at the timing to generate this LSA type 5.
The following is an excerpt from the initial configuration of each router.
R1 Configuration excerpt
hostname R1 ! interface Serial1/0 ip address 10.1.12.1 255.255.255.0 clock rate 64000 no dce-terminal-timing-enable ! interface Serial1/1 ip address 10.1.13.1 255.255.255.0 clock rate 64000 no dce-terminal-timing-enable ! router eigrp 1 network 10.1.13.0 0.0.0.255 no auto-summary ! router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 log-adjacency-changes redistribute eigrp 1 subnets network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
R2 Configuration excerpt
hostname R2 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip ospf network point-to-point ! interface Loopback1 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 ip ospf network point-to-point ! interface Loopback2 ip address 172.16.3.2 255.255.255.0 ip ospf network point-to-point ! router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 log-adjacency-changes network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
R3 Configuration excerpt
! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.2.3 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Loopback2 ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 10.1.13.3 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue ! router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 no auto-summary
If you verify the EIGRP topology table and OSPF LSDB on R1, you will see the following
R1 EIGRP Topology/LSDB summary
R1#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS(1)/ID(10.1.13.1)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 10.1.13.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 20512000
via Connected, Serial1/1
P 192.168.1.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 20640000
via 10.1.13.3 (20640000/128256), Serial1/1
P 192.168.2.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 20640000
via 10.1.13.3 (20640000/128256), Serial1/1
P 192.168.3.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 20640000
via 10.1.13.3 (20640000/128256), Serial1/1
R1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 599 0x80000003 0x00269B 2
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 599 0x80000003 0x00DA14 5
Type-5 AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
10.1.13.0 1.1.1.1 709 0x80000001 0x00ABD8 0
192.168.1.0 1.1.1.1 709 0x80000001 0x000D25 0
192.168.2.0 1.1.1.1 709 0x80000001 0x00022F 0
192.168.3.0 1.1.1.1 709 0x80000001 0x00F639 0
You can see that the route information on the R1 EIGRP topology table has been generated as OSPF LSA type 5. The LSA type 5 generation on R1 is shown in the figure below.
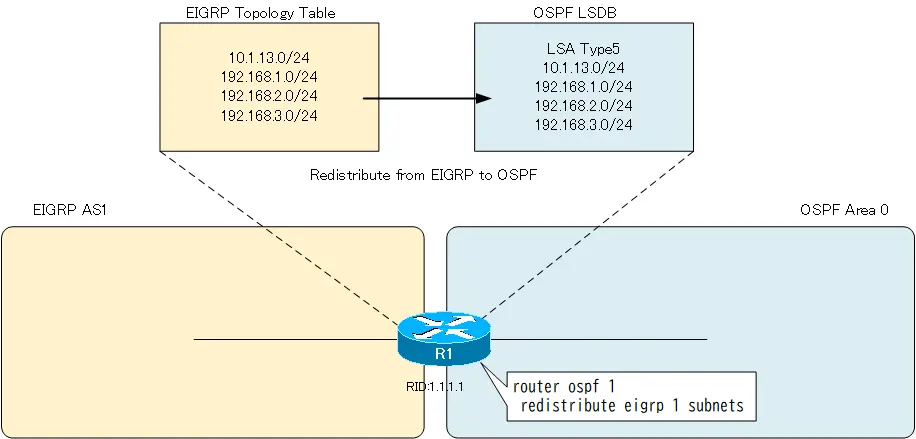
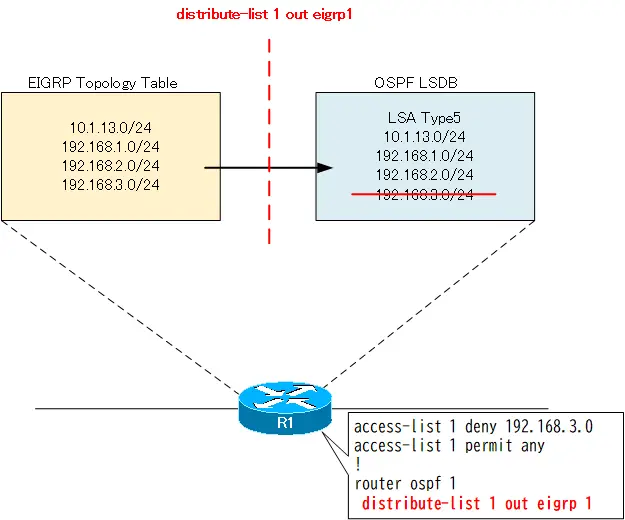
Filter LSA type 5 by distribute-list command
distribute-list(standardACL) configuration
By redistribution from EIGRP to OSPF on R1, LSA type 5 will be generated. At that time, configure the filter that does not generate the next LSA type 5 by using the distribute-list command.
- 192.168.3.0/24
The configuration for R1 is as follows.
R1 Filter LSA type 5 by distribute-list
access-list 1 deny 192.168.3.0 access-list 1 permit any ! router ospf 1 distribute-list 1 out eigrp 1
The OSPF LSDB summary on R1 after the configuration is as follows
R1 LSDB summary after distribute-list configuration
R1#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 315 0x80000002 0x00289A 2
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 315 0x80000003 0x000EE0 5
Type-5 AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
10.1.13.0 1.1.1.1 321 0x80000001 0x00ABD8 0
192.168.1.0 1.1.1.1 319 0x80000001 0x000D25 0
192.168.2.0 1.1.1.1 319 0x80000001 0x00022F 0
You can see that the LSA type 5 for 192.168.3.0/24 is not generated. Also, the show ip protocols command displays the following
R1 show ip protocols
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
-- omitted --
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Redistributed eigrp 1 filtered by 1
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 1.1.1.1
It is an autonomous system boundary router
Redistributing External Routes from,
eigrp 1, includes subnets in redistribution
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
2.2.2.2 110 00:12:16
Distance: (default is 110)
You can see that when redistributing from EIGRP, LSA type 5 is filtering according to access-list 1.
distribute-list(prefix-list) configuration
In the configuration up to this point, standard access-list is used to identify the route, but the following configuration using prefix-list is also possible.
R1 Filter LSA type 5 by distribute-list(prefix-list)
ip prefix-list AAA deny 192.168.3.0/24 ip prefix-list AAA permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ! router ospf 1 no distribute-list 1 out eigrp 1 distribute-list prefix AAA out eigrp 1
In this case, show ip protocols will display the following
R1 show ip protocols (prefix-list)
R1#sh ip protocols
~省略~
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Redistributed eigrp 1 filtered by (prefix-list) AAA
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 1.1.1.1
It is an autonomous system boundary router
Redistributing External Routes from,
eigrp 1, includes subnets in redistribution
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
2.2.2.2 110 00:13:42
Distance: (default is 110)
Filter LSA type 5 by Route-map
You can also apply route-map as an option of the redistribute command to filter the LSA type 5. In the same way as before, on R1, do not generate LSA type 5 for 192.168.3.0/24. The configuration on R1 is as follows
R1 LSA Type5 filter(route-map)
access-list 2 permit 192.168.3.0 ! route-map AAA deny 10 match ip address 2 route-map AAA permit 20 ! router ospf 1 no distribute-list prefix AAA out eigrp 1 redistribute eigrp 1 subnets route-map AAA
After configuration, the LSDB summary on R1 will look like this.
R1 show ip ospf database
R1#sh ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 23 0x80000003 0x00269B 2
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 201 0x80000004 0x000CE1 5
Type-5 AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Tag
10.1.13.0 1.1.1.1 4 0x80000001 0x00ABD8 0
192.168.1.0 1.1.1.1 4 0x80000001 0x000D25 0
192.168.2.0 1.1.1.1 4 0x80000001 0x00022F 0
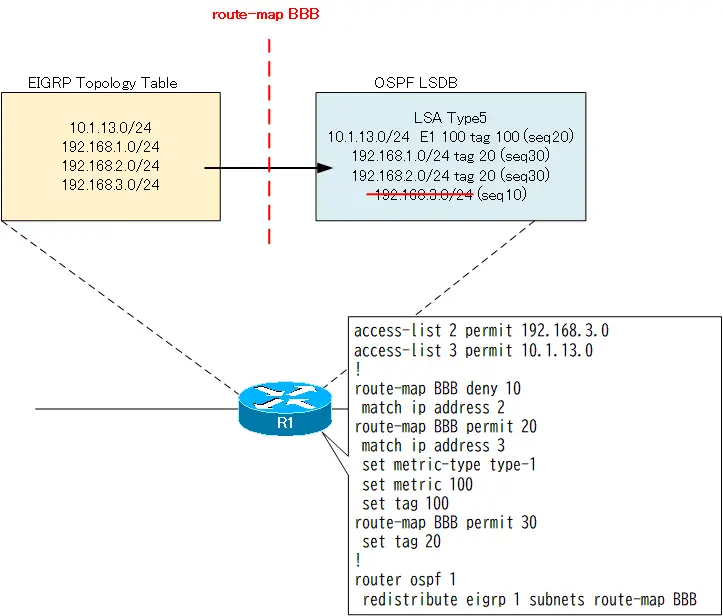
Using route-map allows you to do more than simply filter. For example, when redistributing from EIGRP to generate an LSA type 5, you can tag it or change the metric type or metric value. As an example, the configuration is based on the following conditions
- LSA type 5 for 192.168.3.0/24 is not generated
- 10.1.13.0/24 LSA Type 5 Metric Type E1 Metric 100 Tag 100
- Other LSA type 5 tag 20
The configuration on R1 is as follows.
R1 LSA Type5 filter(route-map) part2
access-list 3 permit 10.1.13.0 ! route-map BBB deny 10 match ip address 2 route-map BBB permit 20 match ip address 3 set metric-type type-1 set metric 100 set tag 100 route-map BBB permit 30 set tag 20 ! router ospf 1 redistribute eigrp 1 subnets route-map BBB
Metric types and metric values are not found in the LSDB summary; look at show ip ospf database external on R1 to see the details of LSA type 5.
R1 show ip ospf database external
R1#show ip ospf database external
OSPF Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Type-5 AS External Link States
LS age: 98
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 10.1.13.0 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0xDBF2
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Metric Type: 1 (Comparable directly to link state metric)
TOS: 0
Metric: 100
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 100
LS age: 85
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.168.1.0 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x76A7
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 20
LS age: 87
Options: (No TOS-capability, DC)
LS Type: AS External Link
Link State ID: 192.168.2.0 (External Network Number )
Advertising Router: 1.1.1.1
LS Seq Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x6BB1
Length: 36
Network Mask: /24
Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path)
TOS: 0
Metric: 20
Forward Address: 0.0.0.0
External Route Tag: 20
You can see that the metric type, metric value, and route tag for LSA type 5 are set as in the conditions given earlier.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]

