Table of Contents
OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
OSPF DD packets are used to synchronize LSDB between routers in an adjacency relationship. DD packets provide an overview of the LSDB. The DD packet includes a list of LSA headers as an overview of the LSDB. When DD packets are exchanged between routers in an adjacency, they will know which LSAs they do not have with each other.

OSPF DD Packet Format
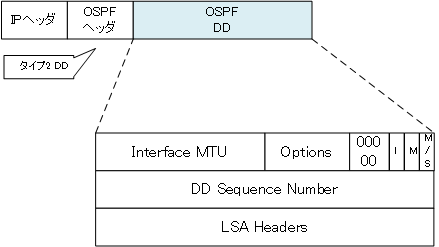
Type 2 of the OSPF header indicates that it is a DD packet; the format of a DD packet is as follows
Related Article
The OSPF header is explained in the following article.
Interface MTU(16bits)
Interface MTU (16 bits) is the MTU size of the interface that outputs DD packets. DD packets may be larger in size and may be split. If the neighbor and MTU size do not match, DD packets may not be exchanged properly. So, If the MTU sizes do not match, the neighbor will get stuck in the ExStart state.
Options(8bits)
Options (8 bits) indicate the various capabilities of the OSPF router. 5 bits following Options are fixed at “00000”.
I-bit
The I in I-bit stands for Initial. Only the first DD packet in a series of DD packet exchanges has I-bit=1.
M-bit
The M in M-bit stands for More, and M-bit=1 indicates that there is more to the DD packet. M-bit = 1 indicates that there is more to the DD packet, and M-bit = 0 at the end of a series of DD packet exchanges.
M/S-bit
MS-bit means Master/Slave; the router that starts exchanging DD packets is the Master. M/S-bit=1 indicates that the router is the Master router. The router with the larger router ID is the Master router.
DD Sequence Number(32bits)
The DD Sequence Number (32 bits) ensures that DD packets are received; the router that serves as the Master determines a unique initial value and increments the sequence number in subsequent DD packet exchanges.
LSA Headers
A list of LSA headers for all LSAs in the LSDB of the router generating the DD packet.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]
