Table of Contents
How to generate default routes in EIGRP
There are several ways to generate a default route as an EIGRP route and advertise it to other routers, as follows.
- Redistribute the static default route to EIGRP
- Route summarization
- ip default-network command
In the following sections, we will explain the configuration example of ip default-network command.
Generating EIGRP defaut route by ip default-network command
【Network diagram】
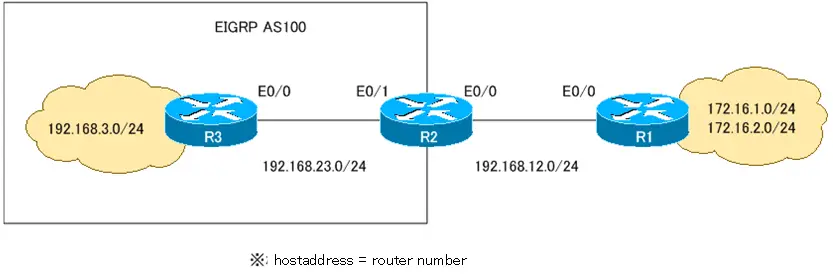
【Condition】
- Allow R2 to advertise the default route to R3 via EIGRP to ensure connectivity for all interfaces.
- On R2 advertise 192.168.12.0/24 as a candidate for the default route to R3.
【Initial configuration】
R1 initial configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.12.2
R2 initial configuration
interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.23.0 no auto-summary
R3 initial configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0 ! router eigrp 100 network 192.168.3.0 network 192.168.23.0 no auto-summary
【Step1:Advertise EIGRP route to R3】
To advertise 192.168.12.0/24 from R2 to R3, also include 192.168.12.0/24 in the EIGRP process on R2. Also, to avoid sending EIGRP packets to R1, specify E0/0 as a passive interface.
R2
router eigrp 100 network 192.168.12.0 passive-interface Ethernet0/0
【Step2:Specify a candidate for the default route】
Use the ip default-network command on R2 to specify 192.168.12.0/24 as a candidate for the default route.
R2
ip default-network 192.168.12.0
【Step3:Verify the candidate default route.】
Look at the routing table of R3 and verify that 192.168.12.0/24, advertised from R2, is a candidate for the default route.
R3
R3#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.23.2 to network 192.168.12.0
D* 192.168.12.0/24 [90/307200] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:33, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.23.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
【Step4:Vefifying communication】
If you execute a ping from R3 to R1, you will see that no response is returned.
R3
R3#ping 172.16.1.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 U.U.U Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) R3#ping 172.16.2.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 U.U.U Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
The reason why the ping from R3 to R1 fails is that the necessary route information does not exist in R2’s routing table. R3 forwards packets destined for R1 to R2 using the default route. R3 will forward them to R2 using the default route, but the packets will be discarded because the route information to route to R1 does not exist in R2’s routing table.
【Step5:Configuring default route on R2】
Configure the static default route as the route information for routing to R1 on R2.
R2
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.12.1
【Step6:Vefifying communication】
When we ping R3 to R1 again, we can confirm that the response is normal.
R3
R3#ping 172.16.1.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/11/24 ms R3#ping 172.16.2.1 source 192.168.3.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.3.3 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/10/16 ms
