How the BGP works
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a routing protocol mainly used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide Internet access services. A key feature of BGP is its ability to scale to handle vast amounts of Internet route information, allowing for flexible control over optimal route decisions.
This section describes how BGP works and how to configure it on network devices such as Cisco routers.
BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
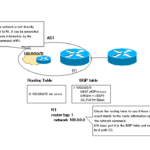
The basic configuration process for BGP consists of the following three steps
1. Enable the BGP routing process
2. Configuring the Neighbor
3. Generating BGP routes
BGP Neighbor Status

The states of BGP neighbors are Idle/Conect/Active/OpenSent/OpenConfirm/Established. This section describes the states of these BGP neighbors.
Read moreBGP Neighbor Authentication

BGP neighbor authentication allows you to establish a neighbor only with a legitimate BGP router.
This section describes the configuration commands for neighbor authentication and a simple configuration example.
BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
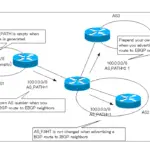
There are various path attributes added to the BGP route. Well Known Mandatory attributes are always added to a BGP route.
Read moreIllustration: BGP Best Path Selection

When multiple BGP routes are received for the same network address, the best path (optimal route) is determined and registered in the routing table.
In what order the path attributes of the BGP routes are evaluated to determine the best path is illustrated in detail.
BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
BGP neighbors are basically maintained by exchanging KEEPALIVE messages periodically; this section describes the timer settings related to KEEPALIVE messages.
Read moreBGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration

BGP applies triggered updates that send routes when there is some kind of change. The minimum advertisement interval slightly delays the advertisement of BGP routes when changes occur.
This section describes the commands for configuring the minimum advertisement interval for BGP routes.
BGP Route Dampening
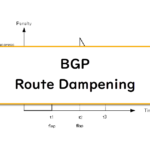
Route dumping is the feature that reduces the impact of BGP route flap. This section explains how BGP route dampening works and the configuration commands in Cisco IOS.
Read moreBGP Route Filter Overview
It is possible to filter when advertising and receiving route information to and from a specified neighbor with BGP. "How to identify the route information" is important in route filtering with BGP.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : distribute-list

This section describes the commands for configuring and verifying the BGP route filter using distribute-list. The distribute-list identifies the BGP route information with ACL to be allowed or denied.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example

This is an example of BGP route filter configuration using distribute-list. BGP routes to be filtered are identified with both standard and extended ACLs.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : prefix-list

This section describes the configuration and verification commands for the BGP route filter using prefix-list. The prefix-list identifies BGP routes to be filtered by network address and subnet mask.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example

The following is an example of configuring BGP route filter with prefix-list. Configure the same conditions with prefix-list as with distribut-list filter.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-

This section describes the commands for configuring and verifying the filter-list.
The filter-list identifies the BGP routes to be filtered by AS_PATH ACL.
BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example

This is an example of BGP route filter configuration by filter list (AS_PATH ACL). It is important to know how to represent the AS_PATH attribute in a regular expression.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : Route-map
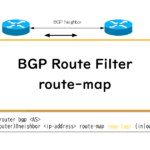
This section describes the configuration and verification commands for BGP route filtering using route-map. The route map allows you to identify BGP routes to filter by reference to standard/extended ACLs, prefix lists, AS_PATH ACLs, etc. In addition to filters, additional path attributes can be set for BGP routes.
Read moreBGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
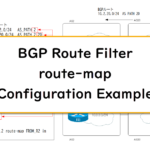
This is an example of BGP route filter configuration with route-map. Route-maps allow you to flexibly identify BGP routes to filter by referencing standard/extended ACLs, prefix-lists, and AS_PATH ACLs in the match condition.
Read moreBGP neighbor allowas-in command

The neighbor allowas-in command disables AS_PATH loop prevention for BGP routes received from a specific neighbor.
Read moreBGP neighbor as-override command

The neighbor as-override command rewrites the AS_PATH attribute of a BGP route to advertise to a specific neighbor. This section describes the neighbor as-override command.
Read moreBGP Route RIB Failure
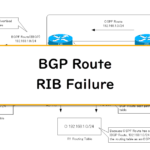
If the best-path BGP route is not registered in the routing table, the route is placed in RIB Failure status.This section describes RIB Failure of BGP route.
Read moreBGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment

Adjusting the Administrative Distance of BGP routes allows BGP routes to be preferred over routes by other routing processes. This section describes how to adjust the administrative distance for BGP routes.
Read moreBGP Route Load Balancing
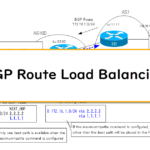
Packets destined to a network learned by BGP (BGP route) can also be load balanced.This section describes two methods for load balancing BGP routes.
Read moreBGP Auto Summary

This section describes BGP auto-summary, which is different from auto-summary with RIP/EIGRP.
Read moreBGP Route Summary : network command

The network command can be used to generate BGP routes for known network addresses in the routing table.
This section describes the generation of BGP aggregate route by the network command.
BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example

This is an example of BGP route summarization configuration using the network command. network command generates known network addresses in the routing table as BGP routes.
Read moreBGP Route Summary aggregate-address command

The aggregate-address command can be used to generate BGP aggregate routes.
This section describes the aggregate-address command and the conditions for the command to work.
aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton

The summary-only option is an option regarding "how to handle routes pre-aggregation". The option summary-only advertises only aggregate route. This section describes the summary-only option in more detail.
Read moreaggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton

The attribute-map is an option for "what to do with the attributes of the aggregate route". The attribute-map allows attributes to be added to the aggregate route.
Read moreaggregte-address command : as-set opiton

The as-set is an option for “what to do with the attributes of the aggregate route”. The as-set option allows the aggregate route to inherit attributes of the pre-aggregate routes.
Read moreaggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton

This section describes advertise-map, an option of the aggregate-address command that generates BGP aggregate routes.
Read moreBGP Selective Aggregation Overview

When BGP aggregates routes, not only the aggregated route is advertised, but also the individual routes before the aggregation. Selective Aggregation allows control over which pre-aggregation routes are advertised along with the aggregate route.
Read moreBGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map

This section describes the suppress-map option of the aggregate-address command for selective aggregation. suppress-map option allows you to determine the pre-aggregation routes that are not advertised.
Read moreBGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map

The unsuppress-map allows you to determine which pre-aggregation routes to advertise along with the aggregation routes for each neighbor.
Read moreBGP local-as
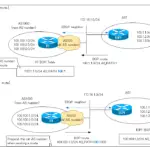
local-as allows you to establish a BGP neighbor for a specific EBGP neighbor with an AS other than the original AS number and exchange routes.
This section describes the operation of BGP local-as and the configuration commands.
BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
Use the neighbor remove-private-AS command to remove private AS number from the AS_PATH of BGP route. This section describes the neighbor remove-private-AS command.
Read morebgp fast-external-fallover

bgp fast-external-fallover is a feature that immediately drops the neighbor if the interface used for the BGP connection goes down.
Read moreBGP Prefix Limitation

If a large amount of route information (prefix) is sent due to a neighbor's misconfiguration, for example, the load on the router may increase and have an adverse effect on the router. Therefore, the neighbor maximum-prefix command is used to limit the number of route information received from BGP neighbors.
Read more