VLAN(Virtual LAN)
VLAN (Virtual LAN) is a technology for dividing a network with Layer 2 switches. By using VLANs on Layer 2 switches to divide the network, the logical configuration of the network can be freely decided. In addition, VLANs are not used only with Layer 2/Layer 3 switches. It is also the VLAN settings that determine how virtual servers are connected to the network.
The need to divide the network
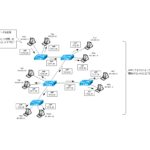
VLAN allow Layer 2 switches to divide an Ethernet network. In this article, I will explain in detail about "Why do we need to divide the network?
Read moreDetails of dividing the network
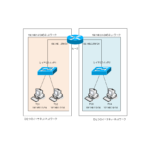
This is a detailed explanation of " dividing a network". Network division is also easier to understand if you think about it based on the OSI reference model hierarchy.
Read moreVLAN Overview

This section summarizes the features of VLAN. In particular, you should have a clear understanding of the implications of VLAN for improving security.
Read moreVLAN behavior
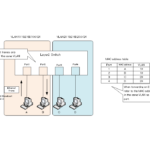
The VLAN is very simple. It divides the network by "forwarding Ethernet frames only between ports of the same VLAN".
Read moreAccess port : Port assigned to only one VLAN
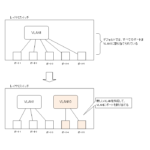
There are two types of ports on a switch: access ports and trunk ports, depending on how the ports and VLANs are assigned. This section explains access ports in detail.
Read moreTrunk port : Port assigned to multiple VLANs
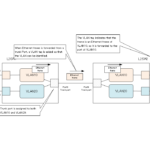
A trunk port is a port that can be assigned to multiple VLANs. When you want to create VLANs across switches, it is efficient to use trunk ports to connect between switches.
Read moreSummary of Trunk Protocols - IEEE802.1Q and ISL
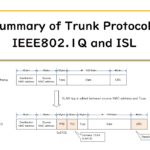
IEEE802.1Q and ISL are trunk protocols to which VLAN information is added when Ethernet frames are forwarded over trunk links.
This section describes the IEEE802.1Q and ISL formats.
Native VLAN
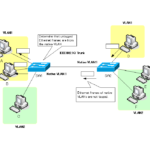
Ethernet frames with native VLANs do not have a VLAN tag added when they are forwarded over the trunk. This section explains how native VLANs work.
Read moreSpecific example of native VLAN mismatch
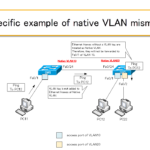
If the native VLAN configuration is mismatched, the VLAN with the unmatched configuration will not be able to communicate.
Let's consider a specific example of a native VLAN mismatch.
Cisco DTP

Cisco Catalyst switches can automatically determine the trunk port/access port according to the opposite port with DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol).
Read moreCisco Configuring and Verifying VLAN
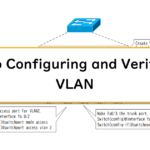
This section describes how to configure and verify VLANs in Cisco.
Let's imagine how VLANs and ports are connected inside the switch by VLAN configuration.
Cisco VLAN Detailed Configuration Example
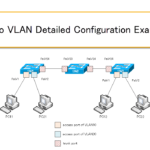
This is an example of VLAN configuration in Cisco. The detailed step-by-step procedure will help you create a separate network with VLANs.
Read moreNotes on deleting VLANs
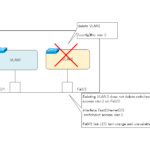
Even if a VLAN is deleted, the configuration of the ports assigned to that VLAN will remain.
This section explains the precautions to be taken when deleting a VLAN.
Voice VLAN - VLAN for connecting IP phones
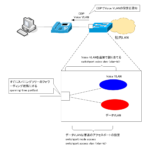
By configuring Voice VLAN, IP phones can be efficiently connected to the corporate network.
This section explains in detail how Voice VLAN works and the configuration commands.
VTP :Synchronize VLAN configuration
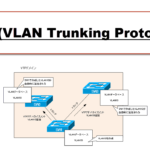
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for synchronizing VLAN configuration between switches.
This section provides an overview of VTP and VTP mode.
VTP pruning - Stopping unnecessary flooding of trunk links
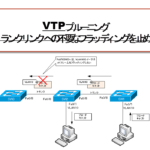
VTP pruning can stop unnecessary flooding of trunk links.
This section explains the how VTP pruning works.
Configuring and Verifying Cisco VTP

Describes the configuration and verification commands for VTP on Cisco Catalyst switches.
Read moreInter VLAN routing overview
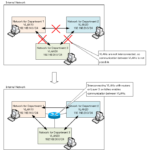
When Layer 2 switches divide a network by VLANs, communication between VLANs becomes impossible, and inter-VLAN routing is used to interconnect VLANs and enable communication between them.
Read moreInter-VLAN routing by router
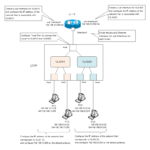
This section is about inter-VLAN routing using routers. There are two ways to connect a router and a Layer 2 switch, one with multiple links per VLAN and the other with a single link.
Read moreInter-VLAN routing by Layer 3 switch
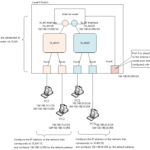
In order to interconnect VLANs (networks) with Layer 3 switches, it is important to know how to configure IP addresses.
There are two ways to configure an IP address on a Layer 3 switch.
Configuring and Verifying Inter-VLAN Routing by Cisco Router
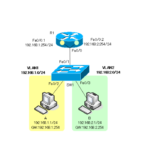
CiscoルータとCatalystスイッチでのVLAN間ルーティングの設定についてです。シンプルなネットワーク構成での具体的な設定例と確認のshowコマンドのログでVLAN間ルーティングの理解を深めましょう。
Read moreCisco Configuring Inter-VLAN routing by Layer3 switch : SVI/routed port
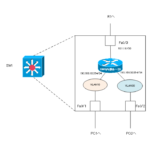
This is the configuration of a Layer 3 switch in Cisco, where the VLAN (network) is connected by configuring the IP address on the SVI or routed port.
Read moreCisco Layer3 Switch Basic Configuration Example
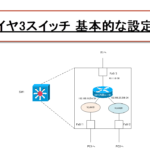
On a Layer 3 switch, configure IP addresses on the SVI/routed ports to interconnect the network (VLAN). Then, enable EIGRP so that it can exchange route information with other routers.
Read moreSummary of Layer 3 Switch Port Concepts - Access Port/Trunk Port/SVI/Routed Port
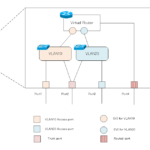
This section summarizes the concept of ports in a Layer 3 switch.
Imagine the association of the virtual router, VLAN, and port inside a Layer 3 switch.
LAN Design pattern : 2-tier and 3-tier
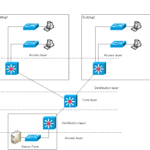
The network of a company's site is mainly consisted of Layer 2 switches and Layer 3 switches.
There are two ways of thinking about designing a LAN: the two-layer model and the three-layer model.