Table of Contents
Overview
In principle, the DHCP server and client must be on the same network; this section summarizes how to place the DHCP server.
DHCP server and client placement
The following restrictions apply to DHCP server and client placement
In principle, the DHCP server and DHCP client should be connected to the same network.
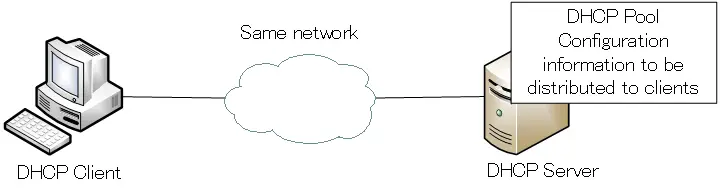
The reason for this restriction is that DHCP exchanges are essentially broadcast-based. At first, the DHCP client does not know its own IP address. Naturally, it does not know the IP address of the DHCP server.
Broadcast is used to communicate with a DHCP server, although the IP address is not known. Broadcast can be used to send data to a host whose IP address is not known. The DHCP client does not know the IP address of the DHCP server, but broadcasts DHCP messages to all hosts on the same network. Then, if a DHCP server exists on the same network, the DHCP server will be able to receive DHCP messages.
A company’s internal network will rarely consist of only one network. Multiple networks, such as for each department, are interconnected by routers/Layer 3 switches. You need to consider the placement of DHCP server that distributes IP addresses to DHCP clients connected on various networks.
Related article
The following article explains how DHCP works.
3 Options for DHCP Server Placement
There are 3 possible options for the placement of DHCP server.
- Place DHCP servers on each network
- Router/Layer 3 switch as DHCP server
- Place single DHCP server (DHCP Relay Agent)
Of these options for DHCP server placement, the most common are option2. and option3. It is unlikely that DHCP servers placement as in option1.
In the following sections, we will look at each DHCP server placement in a little more detail.
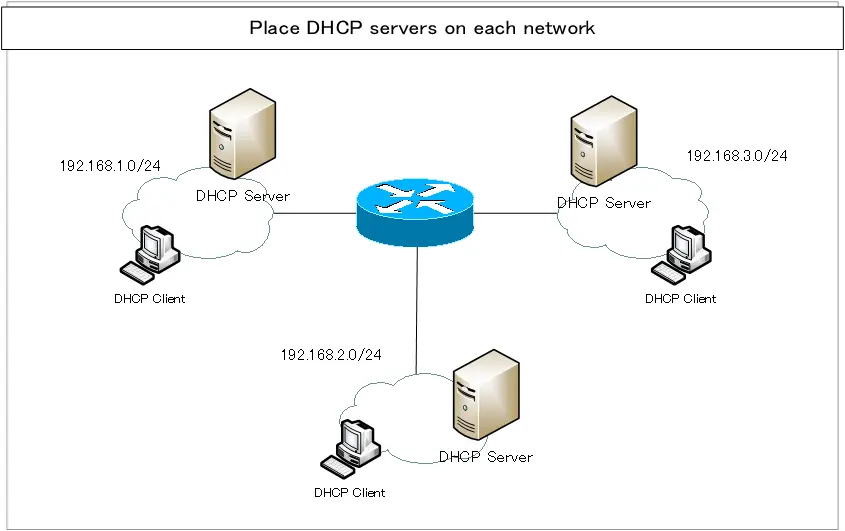
Place DHCP servers on each network
In principle, the DHCP server and DHCP client should be connected to the same network.
The DHCP server placement adheres to this constraint. A DHCP server is placed on each network where DHCP clients reside. Naturally, many DHCP servers must be placed; building DHCP servers is not difficult, but it can be very tedious when there are many of them.
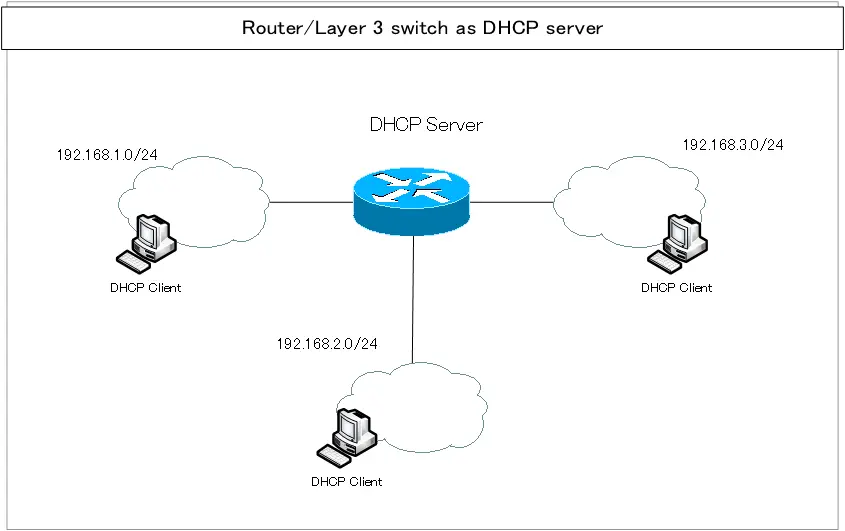
Router/Layer 3 switch as DHCP server
Routers/Layer 3 switches interconnect networks; the network to which the DHCP client is connected is interconnected to other networks by routers/Layer 3 switches. From the point of view of the DHCP client, the router/Layer 3 switch (default gateway) is always the same network. Therefore, the router/Layer 3 switch is the DHCP server. That way, you are following the constraints of DHCP server placement. It is rare that a router/Layer 3 switch does not have DHCP server functionality.
However, not all networks of DHCP clients are interconnected with only one router/Layer 3 switch. Multiple routers/Layer 3 switches may have to act as DHCP servers.
In a home network for individual users or a small SOHO network, a router is usually used as a DHCP server. Also, when tethering is enabled on a smartphone and it is used as a mobile router, the smartphone (mobile router) is the DHCP server.
Related article
The following article describes the commands for configuring a Cisco router/Layer 3 switch as a DHCP server.
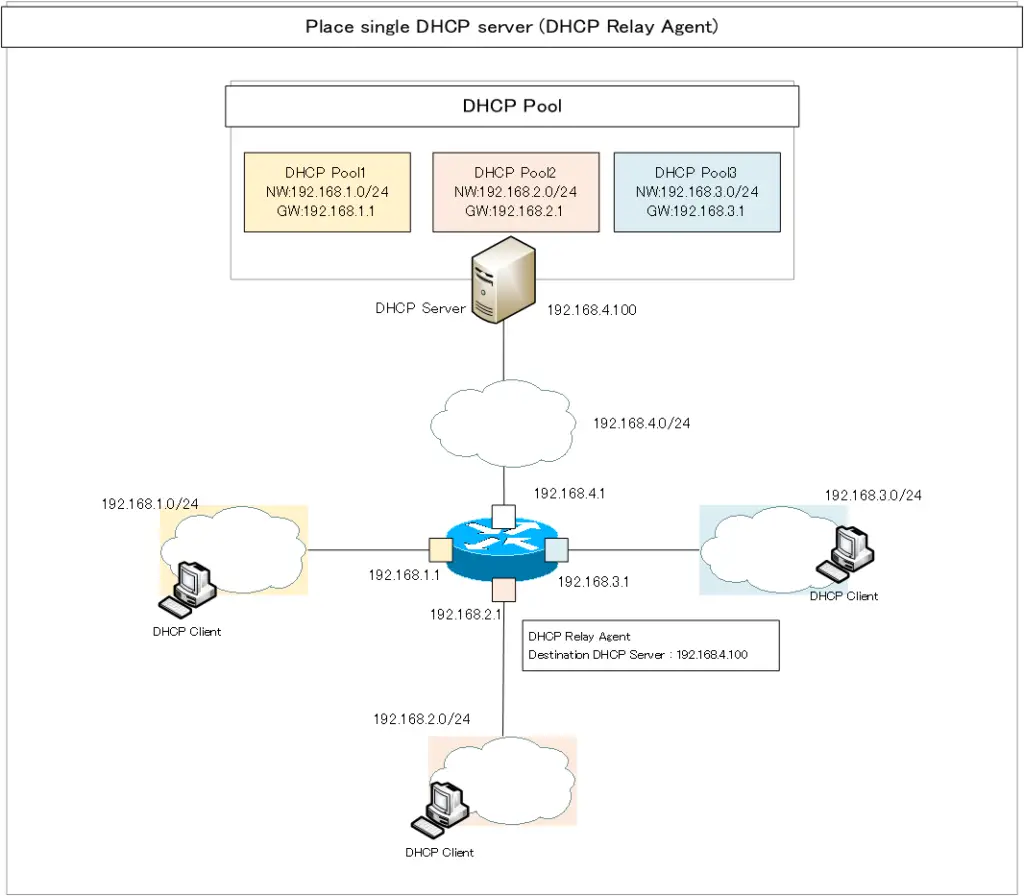
Place single DHCP server (DHCP Relay Agent)
Building and deploying many DHCP servers is tedious. Therefore, a single DHCP server can distribute IP addresses to DHCP clients on multiple networks. To do this, create a DHCP pool for each network you wish to distribute to the DHCP server.
However, as mentioned in the introduction, there is a restriction that, in principle, the DHCP server and DHCP client must be connected on the same network. To circumvent this restriction, additionally, a DHCP relay agent is required.
In most cases, the router/Layer 3 switch connecting the DHCP client’s network will be the DHCP relay agent. The DHCP Relay Agent unicasts DHCP messages broadcast from DHCP clients to the DHCP server.
Related article
The following article describes the DHCP Relay Agent.
Summary
ポイント
- In principle, the DHCP server and DHCP client are connected to the same network
- There are three options for DHCP server placement.
- Place DHCP servers on each network
- Router/Layer 3 switch as DHCP server
- Place single DHCP server (DHCP Relay Agent)
TCP/IP
- IP(Internet Protocol) : The Most Important Data Transfer Protocol
- Ping “Will the data be transfered properly?”
- Ping command on Windows OS
- Traceroute : Which router does the data go through?
- ICMP Redirect
- Where’s the Trouble? Ping and Traceroute
- ARP(Address Resolution Protocol)
- ARP Format
- Gratuitous ARP(GARP)
- nslookup command : Verifying DNS name resolution
- DHCP : Automatically Assign IP Address
- Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuration and Verification Commands
- Cisco Router DHCP Server Configuration Example
- DHCP Relay Agent
- DHCP Relay Agent Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Summary of DHCP Server Placement
- TCP/IP Configuration Summary
- ipconfig command : To verify TCP/IP configurations on Windows OS
- Commands to Verify TCP/IP Configuration On Linux (Ubuntu)
- Web Proxy Server
- FTP : Representative File Transfer Protocol
- TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
- TFTP Client on Windows10/11