Table of Contents
Overview
The aggregate-address command for aggregating BGP routes on Cisco routers has many options. The options are divided into two categories.
- What to do with the attributes of the aggregate route
- How to handle pre-aggregation routes
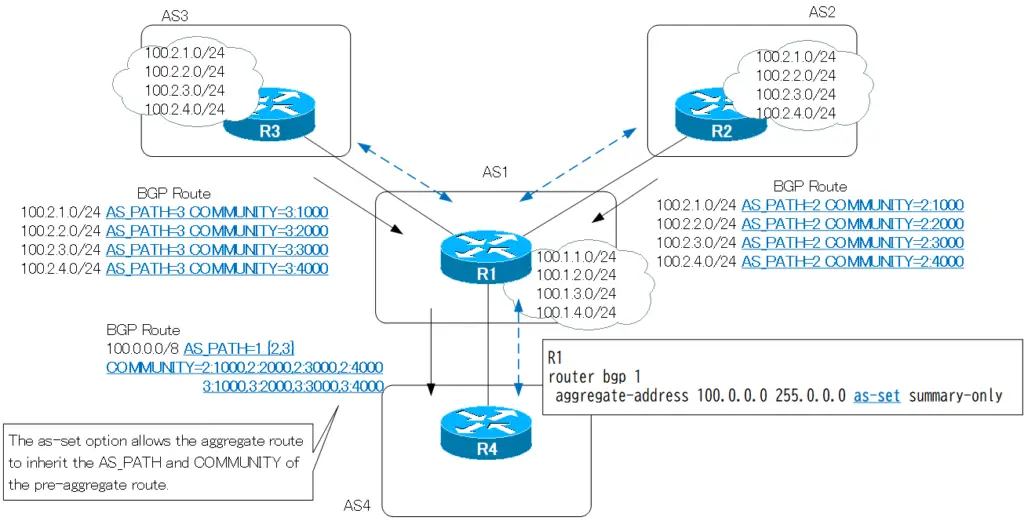
The as-set is an option for “what to do with the attributes of the aggregate route”. The as-set option allows the aggregate route to inherit attributes of the pre-aggregate routes.
aggregate-address command : as-set option
When an aggregated route is generated, the AS_PATH and COMMUNITY attribute information attached to the pre-aggregated route is lost.
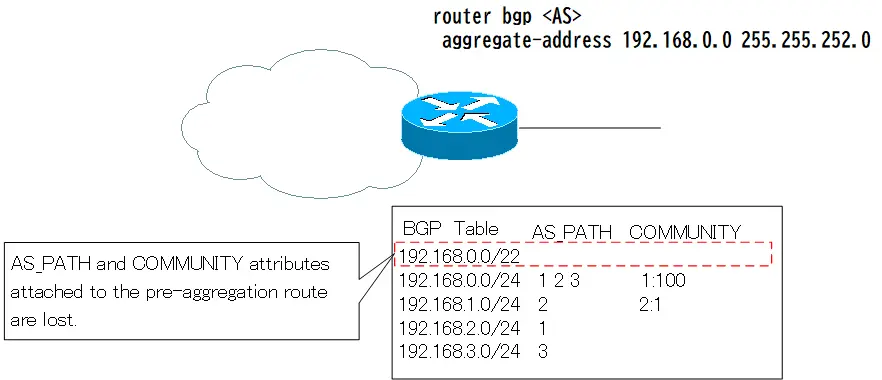
The as-set option allows inheritance of AS_PATH and COMMUNITY attributes added to the pre-aggregate routes.
However, the AS_PATH attribute is of type AS_SET, and the AS number order is lost; AS_SET describes the AS number in { }. The behavior of the as-set option is shown in the following figure.
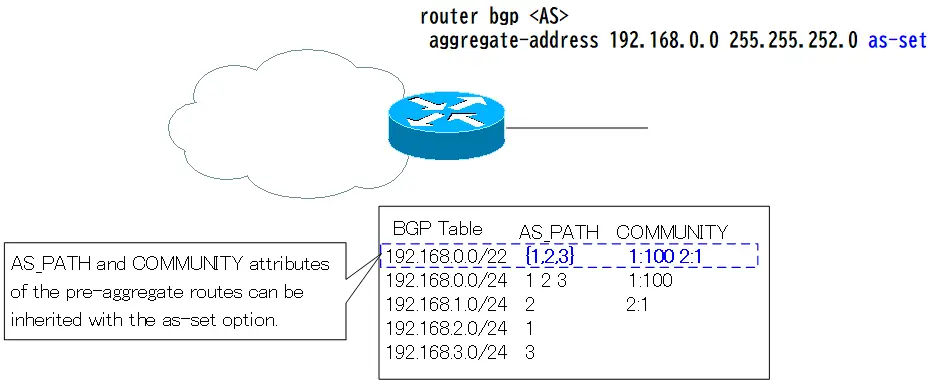
The AS_PATH attribute of the aggregate route will now list the AS numbers of the AS_PATH attributes attached to the four pre-aggregate routes as AS_SET in { }.
And, the COMMUNITY attribute of the aggregate route inherits the COMMUNITY attribute added to the pre-aggregate route as it is.
To configure the as-set option, simply enter the aggregate-address command with as-set appended, without any special arguments.
aggregate-address as-set
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#aggregate-address <network-address> <subnetmask> as-set
<AS>: AS number
<network-address>: Network address of the aggregate route
<subnetmask>: Subnet mask of the aggregate route
aggregate-address as-set option configuration example
Network diagram and initial configuration
Lets consider the as-set option of aggregate-address on R1 in the following network diagram.
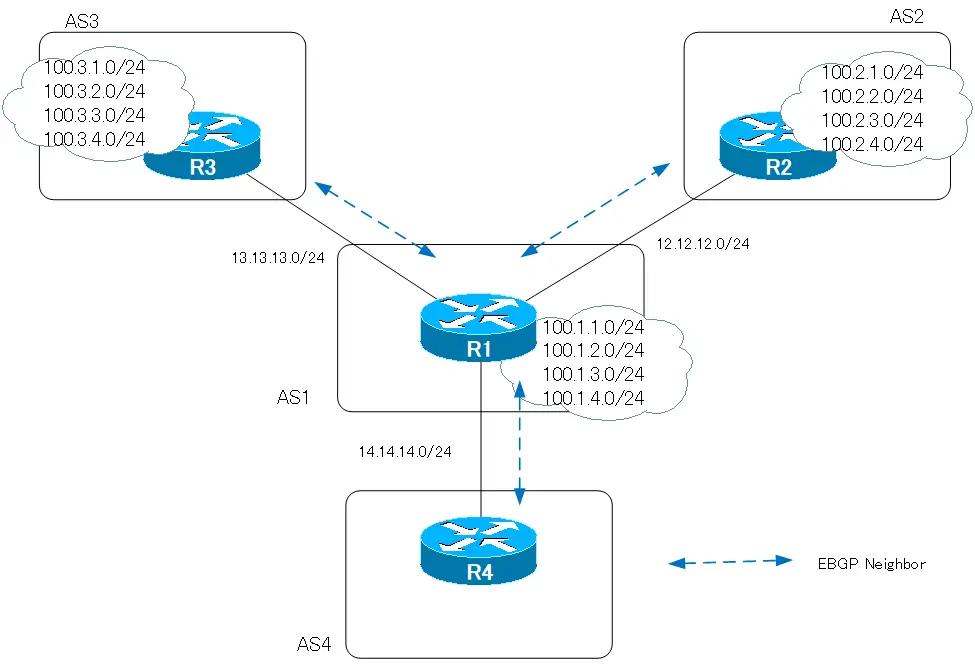
The configurations related to BGP for R1 to R4 before aggregate-address is configured are as follows.
R1 Initial Configuration
On R1, an EBGP neighbor is established with AS2 (R2), AS3 (R3), and AS4 (R4), and 100.1.1.0/24 to 100.1.4.0/24 is advertised with the network command.
R1 Initial Configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 100.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 1 network 100.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.1.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.1.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.1.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 2 neighbor 12.12.12.2 send-community neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 3 neighbor 13.13.13.3 send-community neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 4 neighbor 14.14.14.4 send-community ip bgp-community new-format
R2 Initial Configuration
R2 has established EBGP with AS1 (R1) and advertises routes 100.2.1.0/24 through 100.2.4.0/24 with COMMUNITY. The COMMUNITY of each route is as follows.
100.2.1.0/24 2:1000
100.2.2.0/24 2:2000
100.2.3.0/24 2:3000
100.2.4.0/24 2:4000
R2 Initial Configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 100.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.2.3.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.2.4.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 2 network 100.2.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.2.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.2.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 12.12.12.1 remote-as 1 neighbor 12.12.12.1 send-community neighbor 12.12.12.1 route-map COMMUNITY ip bgp-community new-format ! route-map COMMUNITY permit 10 match ip address 1 set community 2:1000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 20 match ip address 2 set community 2:2000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 30 match ip address 3 set community 2:3000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 40 match ip address 4 set community 2:4000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 1000 ! access-list 1 permit 100.2.1.0 access-list 2 permit 100.2.2.0 access-list 3 permit 100.2.3.0 access-list 4 permit 100.2.4.0
R3 Initial Configuration
R3 has established an EBGP neighbor with AS1 (R1) and advertises routes 100.3.1.0/24 through 100.3.4.0/24 with COMMUNITY. The COMMUNITY of each route is as follows
100.3.1.0/24 3:1000
100.3.2.0/24 3:2000
100.3.3.0/24 3:3000
100.3.4.0/24 3:4000
R3 Initial Configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 100.3.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.3.4.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 100.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 3 network 100.3.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.3.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.3.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 13.13.13.1 remote-as 1 neighbor 13.13.13.1 send-community neighbor 13.13.13.1 route-map COMMUNITY ip bgp-community new-format ! route-map COMMUNITY permit 10 match ip address 1 set community 3:1000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 20 match ip address 2 set community 3:2000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 30 match ip address 3 set community 3:3000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 40 match ip address 4 set community 3:4000 route-map COMMUNITY permit 1000 ! access-list 1 permit 100.3.1.0 access-list 2 permit 100.3.2.0 access-list 3 permit 100.3.3.0 access-list 4 permit 100.3.4.0
R4 Initial Configuration
R4 establishes an EBGP neighbor with AS1 (R1).
R4 Initial Configuration
router bgp 4 neighbor 14.14.14.1 remote-as 4 neighbor 14.14.14.1 send-community ip bgp-community new-format
Advertise aggregate route on R1
R1 aggregates the 100.1.1.0/24 to 100.1.4.0/24 routes of AS1, the 100.2.1.0/24 to 100.2.4.0/24 routes of AS2, and the 100.3.1.0/24 to 100.3.4.0/24 routes of AS3 and advertises them as 100.0.0.0/8. To consider only aggregate routes, add the summary-only option.
R1 Advertise aggregate route
router bgp 1 aggregate-address 100.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 summary-only
With this configuration, R1 generates an aggregate route 100.0.0.0/8 and places it in the BGP table to advertise to other BGP neighbors. Note the attributes of this aggregate route.
R1 show ip bgp 100.0.0.0
R1#sh ip bgp 100.0.0.0 BGP routing table entry for 100.0.0.0/8, version 14 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table) Flag: 0x820 Advertised to non peer-group peers: 12.12.12.2 13.13.13.3 14.14.14.4 Local, (aggregated by 1 100.1.1.1) 0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (100.1.1.1) Origin IGP, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, aggregated, local, atomic-aggregate, best
Looking at the attributes of the aggregate route, AS-PATH and COMMUNITY are missing. The routes advertised from AS2 and AS3 have AS-PATH and COMMUNITY added to them, but the aggregate routes do not have the AS-PATH and COMMUNITY of the pre-aggregate routes.
Verify the attribute of the 100.0.0.0/8 route on R4 as well.
R4 show ip bgp 100.0.0.0
R4#sh ip bgp 100.0.0.0 BGP routing table entry for 100.0.0.0/8, version 40 Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table) Not advertised to any peer 1 , (aggregated by 1 100.1.1.1) 14.14.14.1 from 14.14.14.1 (100.1.1.1) Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
When viewed on R4, the AS-PATH for 100.0.0.0/8 is “1” and there is no COMMUNITY. So the route 100.0.0.0/8 looks like the route generated by AS1. All AS numbers and COMMUNITY of the original route in the range 100.0.0.0/8 are lost.
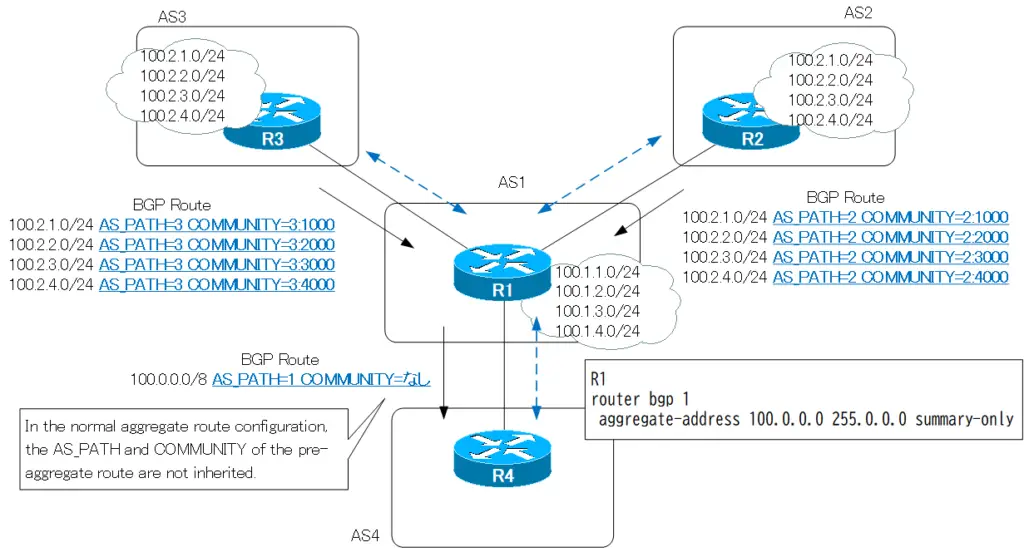
Therefore, as-set is an option that is added to make the aggregate route inherit the AS number and COMMUNITY before the aggregation.
Advertise aggregate route with as-set option on R1
Add the as-set option to the configuration of aggregation on R1.
R1 aggregate-address as-set
router bgp 1 aggregate-address 100.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 as-set summary-only
The key point is how this changes the attribute of the aggregate route 100.0.0.0/8. The BGP table on R1 looks like this
R1 show ip bgp 100.0.0.0
R1#sh ip bgp 100.0.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 100.0.0.0/8, version 27
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x820
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
12.12.12.2 13.13.13.3 14.14.14.4
{2,3}, (aggregated by 1 100.1.1.1)
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (100.1.1.1)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, aggregated, local, best
Community: 2:1000 2:2000 2:3000 2:4000 3:1000 3:2000 3:3000 3:4000
AS2 and AS3, which are the AS numbers of the pre-aggregation routes, are enclosed in { } and attached to the aggregate route. All the COMMUNITY information on the pre-aggregation route are added to the aggregate route. The { } enclosure means that this AS number is included in the pre-aggregation route, although the order is not known.
Verifying the BGP table on R4 shows the following.
R4 show ip bgp 100.0.0.0
R4#sh ip bgp 100.0.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 100.0.0.0/8, version 40
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
1 {2,3}, (aggregated by 1 100.1.1.1)
14.14.14.1 from 14.14.14.1 (100.1.1.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
Community: 2:1000 2:2000 2:3000 2:4000 3:1000 3:2000 3:3000 3:4000
Summary
Points
- AS-SET is an option for “what to do with the attributes of the aggregate route”. It is used to make the aggregate route inherit the AS number and COMMUNITY of the pre-aggregate route.
- Just specify as-set in aggregate-address command.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation
