Table of Contents
Overview
This is an example of BGP route filter configuration by filter list (AS_PATH ACL). It is important to know how to represent the AS_PATH attribute in a regular expression.
Related aritcle
The following article describes in detail the commands for configuring and verifying the filter-list (AS_PATH ACL).
Network Diagram
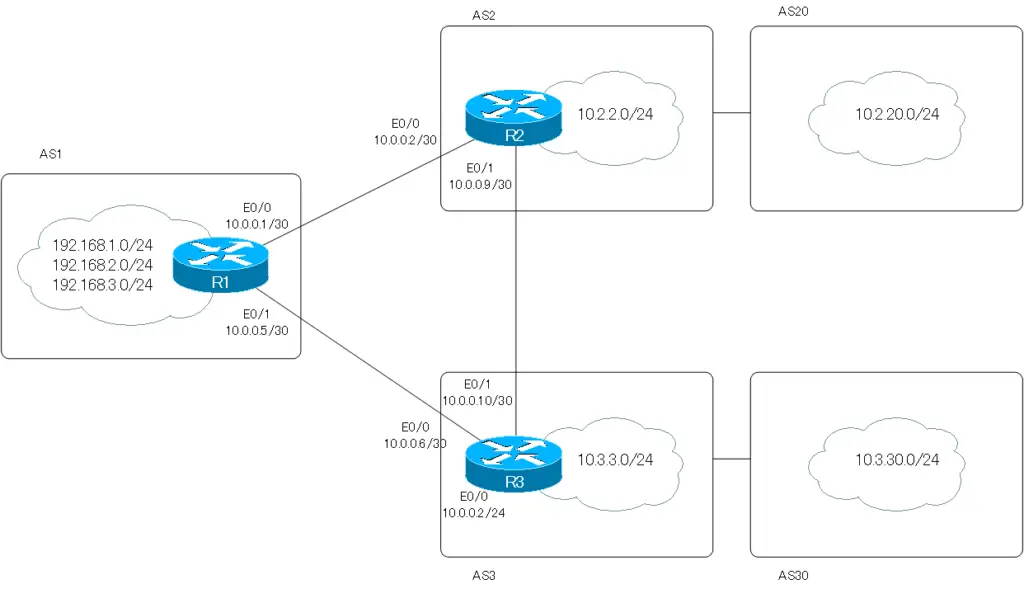
Configuration Conditions
- R1 advertises only BGP routes in its own AS to R2/R3.
- R1 receives only BGP routes generated by AS2 and AS20 from R2.
- R1 must not receive BGP routes generated by AS2 and AS20 from R3.
Initial Configuration
The BGP-related configurations for R1/R2/R3 are as follows.
R1 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.252 ! router bgp 1 bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.1.0 network 192.168.2.0 network 192.168.3.0 neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 2 neighbor 10.0.0.6 remote-as 3
R2 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R2 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.20.2 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.0.0.9 255.255.255.252 ! router bgp 2 bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.2.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 1 neighbor 10.0.0.1 route-map AS_PATH out neighbor 10.0.0.10 remote-as 3 neighbor 10.0.0.10 route-map AS_PATH out ! route-map AS_PATH permit 10 match ip address 1 set as-path prepend 20 ! route-map AS_PATH permit 100 ! access-list 1 permit 10.2.20.0
R3 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R3 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.3.30.3 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 10.3.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.6 255.255.255.252 ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.252 ! router bgp 3 bgp router-id 3.3.3.3 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 10.3.30.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 10.0.0.5 remote-as 1 neighbor 10.0.0.5 route-map AS_PATH out neighbor 10.0.0.9 remote-as 2 neighbor 10.0.0.9 route-map AS_PATH out ! route-map AS_PATH permit 10 match ip address 1 set as-path prepend 30 ! route-map AS_PATH permit 100 ! access-list 1 permit 10.3.30.0
Configuration and Verifycation
Step1: Verify sending and receiving of BGP routes before applying filter-list
Verify BGP routes sent and received before applying the filter-list on R1.
| show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.2 advertised-routes | Displays BGP routes advertised to R2. |
| show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.6 advertised-routes | Displays BGP routes received from R2. |
| show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.2 routes | Displays BGP routes received from R2. |
| show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.6 routes | Displays BGP routes received from R3. |
First, verify the BGP routes advertised from R1 to R2/R3.
R1 BGP routes to be advertised to R2/R3 before applying filter
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.2.2.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.2.20.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 20 i
*> 10.3.3.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 i
*> 10.3.30.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 30 i
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 7
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.6 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.2.2.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.2.20.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 20 i
*> 10.3.3.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 i
*> 10.3.30.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 30 i
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 7
You can see that R1 advertises to R2/R3 other than the BGP route of its own AS.
Note that R1 automatically makes the same Update-Group for EBGP neighbors R2 and R3. Therefore, the BGP routes advertised to R2/R3 are exactly the same. As a result, the received BGP route is sent back to the EBGP neighbor, but the neighbor considers it a loop and discards it.
And the BGP routes received from R2/R3 are as follows
R1 BGP routes received from R2/R3 before applying filter
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.2.2.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.2.20.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 20 i
* 10.3.3.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 2 3 i
* 10.3.30.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 2 3 30 i
Total number of prefixes 4
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.6 routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 10.2.2.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 3 2 i
* 10.2.20.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 3 2 20 i
*> 10.3.3.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 i
*> 10.3.30.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 30 i
Total number of prefixes 4
R1 receives not only BGP routes generated by AS2/AS20 from R2, but also BGP routes generated by AS3/AS30; the same applies to BGP routes received from R3.
Step2: R1 Configure filter-list out
Configure filter-list to limit BGP routes advertised from R1 to R2/R3 to routes in its own AS only.
R1 filter-list out
ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$ ! router bgp 1 neighbor 10.0.0.2 filter-list 1 out neighbor 10.0.0.6 filter-list 1 out
It is possible to filter with distribute-list or prefix-list to satisfy the requirement to advertise only BGP routes in one’s own AS. However, to advertise only BGP routes in your own AS, it is easiest to use filter-list.
To use distribute-list or prefix list, a number of lines of ACLs or prefix-list must be configured, depending on the network address of the BGP route.
On the other hand, the AS_PATH of a BGP route generated by its own AS is empty and can be identified by the regular expression “^$”. Therefore, no matter how many BGP routes or what network addresses are in your AS, you can identify and permit BGP routes generated in your AS with just one line of AS_PATH ACL 1.
Then, just apply AS_PATH ACL 1 on neighbor 10.0.0.2 (R2) and 10.0.0.6 (R3) out.
After applying filter-list, the BGP route must be re-sent.
R1 Resend BGP routes
R1#clear ip bgp 10.0.0.2 out R1#clear ip bgp 10.0.0.6 out
Step3: R1 Verify frefix-list out
Verify the BGP routes to be advertised from R1 to R2/R3.
- show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.2 advertised-routes
- show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.6 advertised-routes
R1 verify filter-list out
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 3
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.6 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 3
You can see that R1 advertises only BGP routes in its own AS to R2/R3.
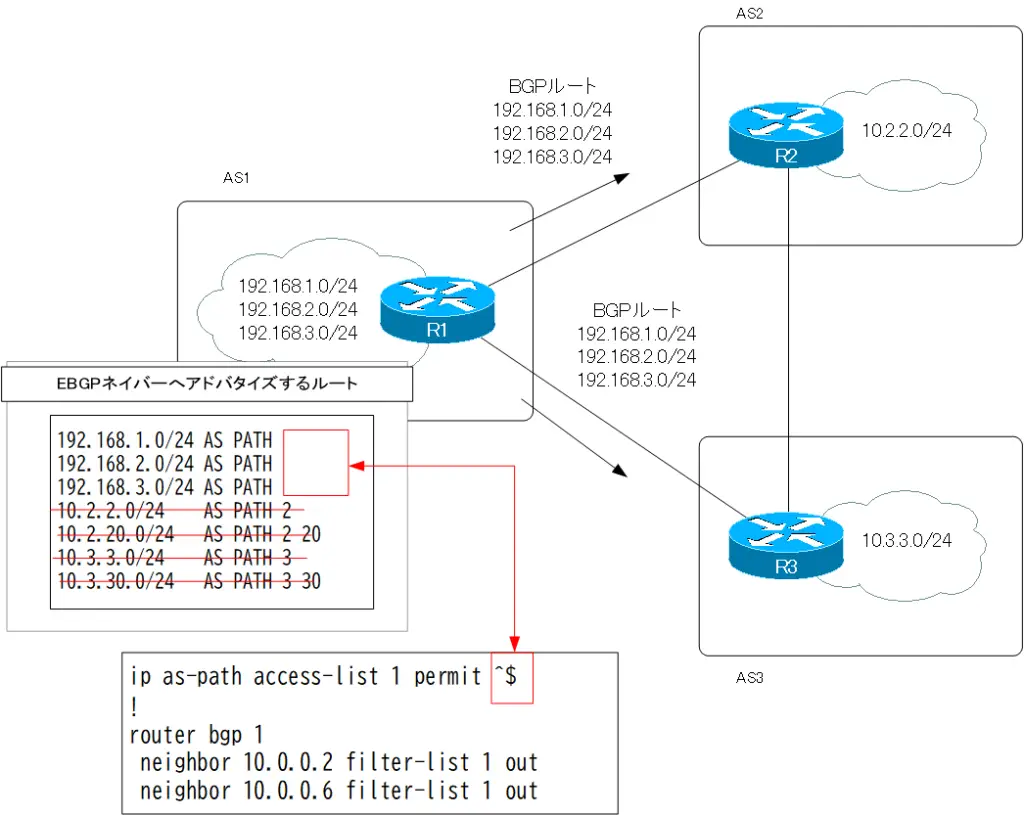
Note that after filtering by the filter-list, the own AS is prepended to AS_PATH. Therefore, AS_PATH of BGP routes received by R2/R3 is “1”.
Step4: R1 Configure filter-list in From R2
Use filter-list to filter incoming BGP routes from R2 on R1.
R1 Configure filter-list in From R2
ip as-path access-list 2 permit _2$|_20$ ! router bgp 1 neighbor 10.0.0.2 filter-list 2 in
R1 limits BGP routes received from R2 to only those generated by AS2 or AS20. That is, AS_PATH ends with 2 or 20. The regular expression is “_2$|_20$”.
AS_PATH ACL 2 identifies and permits BGP routes generated by AS2 or AS20 by this regular expression.Then apply AS_PATH ACL 2 to neighbor 10.0.0.2(R2) in.
After applying filter-list, the BGP route must be re-received from R2.
R1 Receive BGP route again From R2
R1#clear ip bgp 10.0.0.2 in
Step5: R1 Verify prefix-list in From R2
Verify the BGP routes received from R2 on R1 using the show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.2 routes command.
R1 Verify prefix-list in From R2
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.2.2.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.2.20.0/24 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 20 i
Total number of prefixes 2
You can see that the BGP routes received from R2 are limited to only those generated by AS2 or AS20.
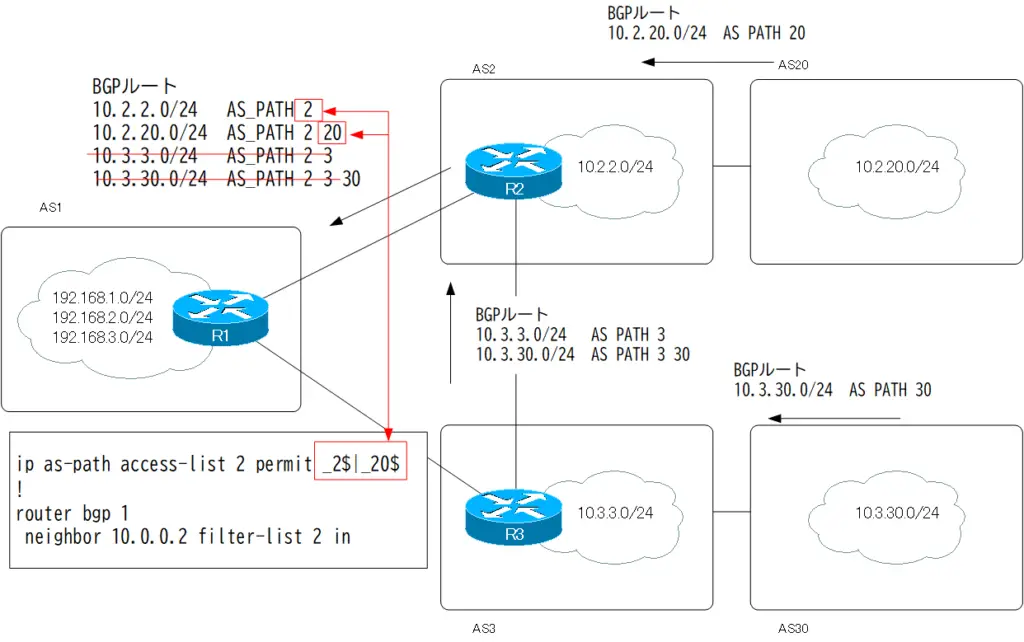
Step6: R1 Configure filter-list in From R3
Use filter-list to filter BGP routes received from R3 on R1.
R1 Configure filter-list in From R3
ip as-path access-list 3 deny _2$|_20$ ip as-path access-list 3 permit .* ! router bgp 1 neighbor 10.0.0.6 filter-list 3 in
No BGP routes generated in AS2 and AS20 are received from R3. AS_PATH ACL 3 to deny BGP routes with AS_PATH ending in 2 or 20. If there is only deny condition, implicit deny will deny everything. To avoid implicit deny, AS_PATH ACL 3 requires “permit . *” condition.. *” is a regular expression for any string, so it matches all AS_PATH attributes.
Then apply AS_PATH ACL 3 to neighbor 10.0.0.6(R3) in.
After applying filter-list, the BGP route must be re-received from R3.
R1 Receive BGP route again From R3
R1#clear ip bgp 10.0.0.6 in
Step7: R1 Verify filter-list in From R3
Verify the BGP routes received from R3 on R1 using the show ip bgp neighbor 10.0.0.6 routes command.
R1 Verify filter-list in From R3
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.6 routes
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.3.3.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 i
*> 10.3.30.0/24 10.0.0.6 0 0 3 30 i
Total number of prefixes 2
R1 is not receiving BGP routes generated by AS2 or AS20 from R3.
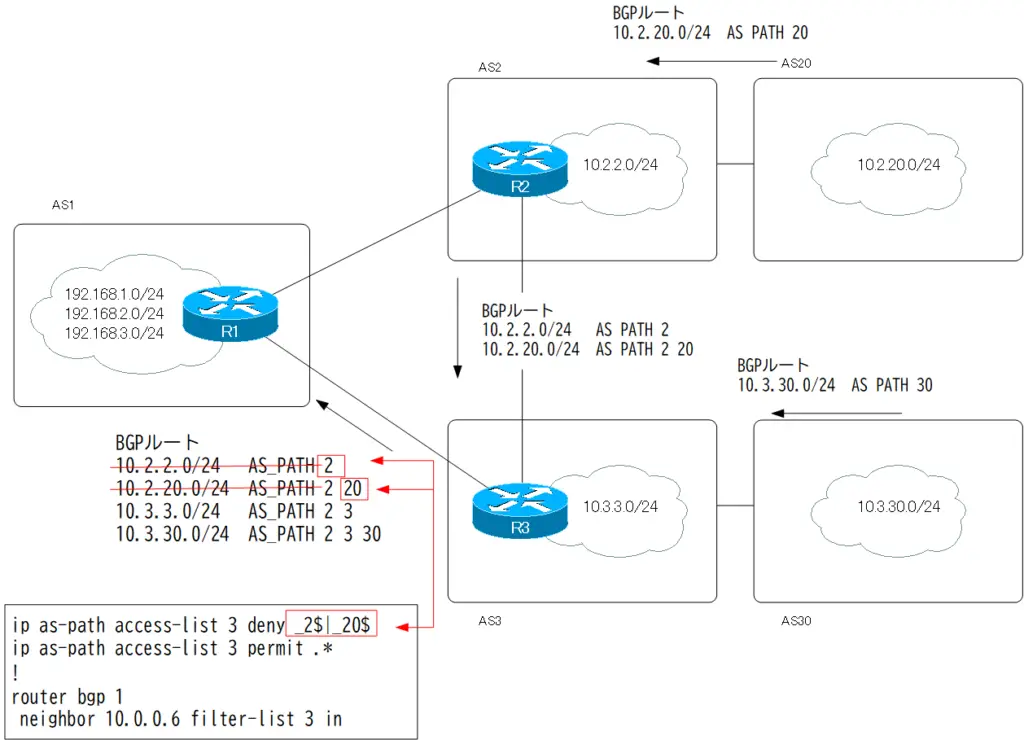
Configuration Summary
The commands related to the filter list for R1, configured from the initial state, are as follows
R1 filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Summary
router bgp 1 neighbor 10.0.0.2 filter-list 2 in neighbor 10.0.0.2 filter-list 1 out neighbor 10.0.0.6 filter-list 3 in neighbor 10.0.0.6 filter-list 1 out ! ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$ ip as-path access-list 2 permit _2$|_20$ ip as-path access-list 3 deny _2$|_20$ ip as-path access-list 3 permit .*
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation
