Table of Contents
Overview of local-as
local-as allows a BGP neighbor to establish a BGP neighbor and exchange routes with an AS other than the original AS number for a specific EBGP neighbor. Local-as allows for a smooth transition between old and new AS numbers, for example, when you want to change the AS numbers due to ISP consolidation, but the neighbor has not yet been configured.
The following figure shows an overview of local-as.
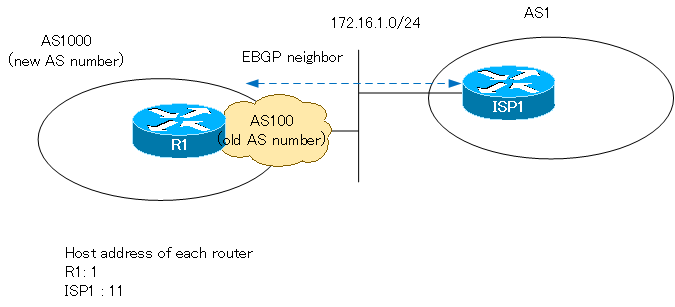
R1 in this figure assumes that we have changed the AS number from AS100 to AS1000. However, ISP1 has not yet been able to handle the change in R1’s AS number and has set R1’s AS number as 100. R1 can behave as if it were AS100 to ISP1 with local-as.
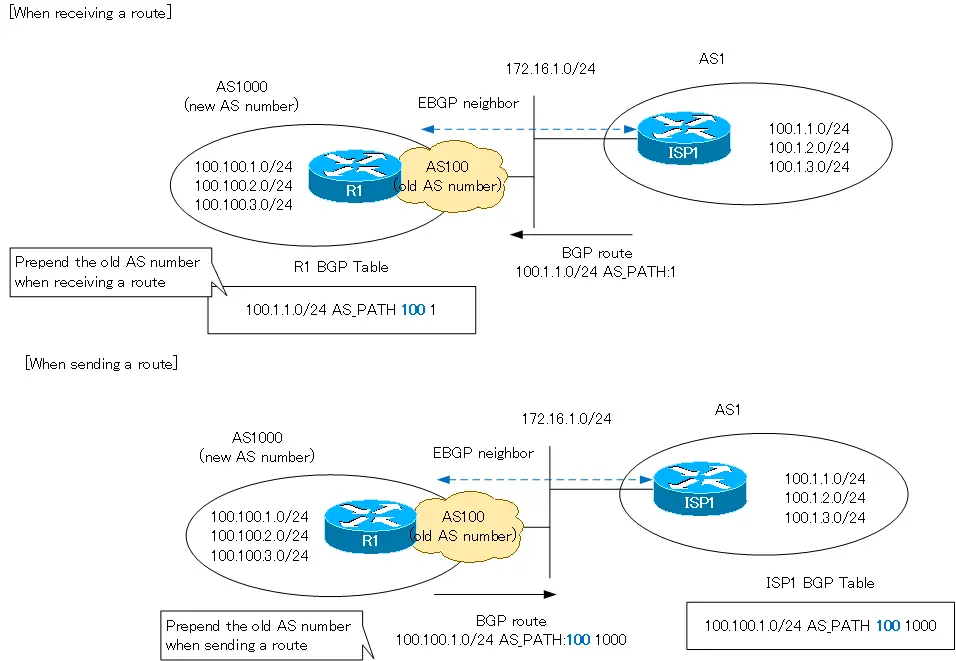
AS_PATH attribute in the local-as configuration.
When emulating other AS numbers by local-as, the route’s AS_PATH attribute looks like this
- Receiving a route : [old AS number] to be prepended to AS_PATH.
- Sending a route : AS_PATH is prepended with [old AS number] [new AS number].
Configuration of local-as
To configure lobal-as, use the following command in BGP’s configuration mode.
Router(config)#router bgp <AS-num1>
Router(config-router)#neighbor <ip-address> local-as <AS-num2>
<AS-num1> : AS number
<ip-address> : neighbor IP address
<AS-num2> : AS number to pretend to be a neighbor
Example of local-as configuration
Let’s look at an example configuration for local-as.
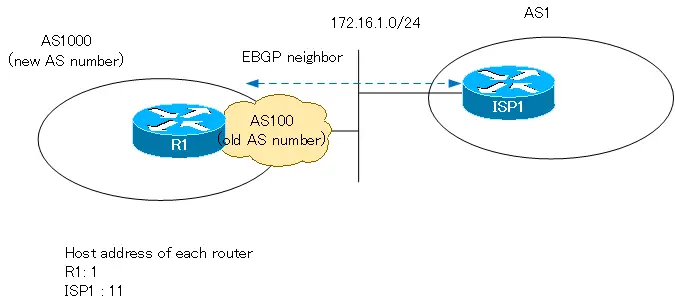
The ISP1 in this figure recognizes the AS number of R1 as 100 and configures BGP as shown below.
ISP1 BGP configuration
router bgp 1 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 100.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.1.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.1.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 172.16.1.1 remote-as 100 no auto-summary
In R1, the AS number is actually changed to AS1000, but it is configured in local-as to be AS100 for ISP1.
R1 local-as configuration
router bgp 1000 neighbor 172.16.1.11 remote-as 1 neighbor 172.16.1.11 local-as 100 network 100.100.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.100.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 100.100.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0
When you verify the BGP neighbor on R1, it has successfully established a neighbor with ISP1.
R1 neighbor verification
R1#show ip bgp summary -- omitted -- Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 172.16.1.11 4 1 8 8 7 0 0 00:03:49 3
And, if you look at the BGP table in R1, it looks like this
R1 BGP table
R1#show ip bgp -- omitted -- Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 100.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 100 1 i *> 100.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 100 1 i *> 100.1.3.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 100 1 i *> 100.100.1.0/24 192.168.13.3 2 32768 i *> 100.100.2.0/24 192.168.13.3 2 32768 i *> 100.100.3.0/24 192.168.13.3 2 32768 i
You will see that the route received from ISP1 has an additional AS number prepended to the route that you specified in local-as.
And if you look at the BGP table for ISP1, it looks like this
ISP1 BGP table
ISP1#show ip bgp -- omitted -- Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 100.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 100.1.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 100.1.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 100.100.1.0/24 172.16.1.1 2 0 100 1000 i *> 100.100.2.0/24 172.16.1.1 2 0 100 1000 i *> 100.100.3.0/24 172.16.1.1 2 0 100 1000 i
The AS_PATH attribute of the route to be received from R1 at ISP1 is now “100 1000” and the AS number specified in local-as is additionally prepended.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation
