Table of Contents
Overview
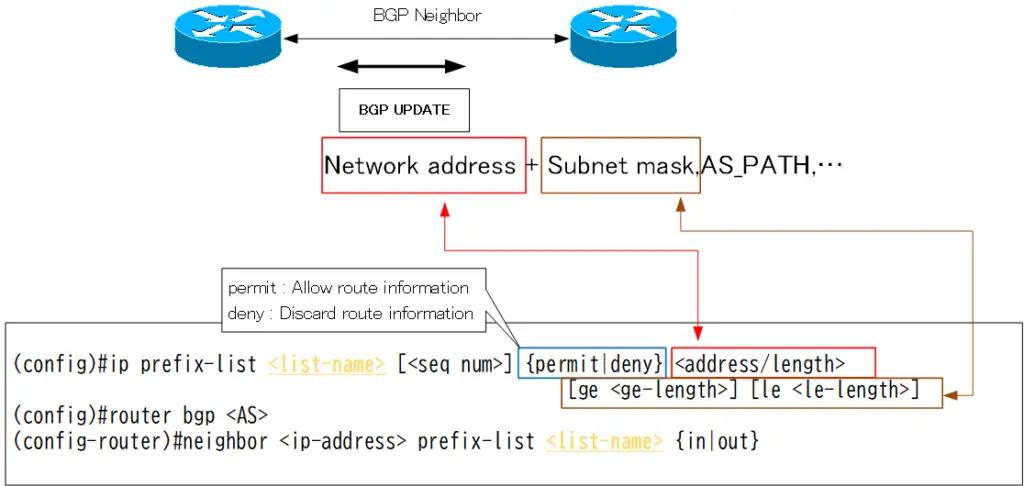
This section describes the configuration and verification commands for the BGP route filter using prefix-list. The prefix-list identifies BGP routes to be filtered by network address and subnet mask.
Flow of Configuring prefix-list
The configuration flow for filtering BGP routes using prefix-list is as follows
- Identify route information to be filtered by prefix-list
- Applying prefix-list to a specific neighbor
- Re-sent/Re-recieve BGP routes
Configuration Commands for prefix-list
The commands to create prefix list and apply it to BGP neighbor are as follows.
BGP route filter prefix-list
(config)#ip prefix-list <list-name> [<seq num>] {permit | deny} <address/length> [ge <ge-length>] [le <le-length>]
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#neighbor <ip-address> prefix-list <list-name> {in|out}
<list-name> : prefix-list name
<seq-num> : sequence number. 5 units by default
<address/length> : bit pattern of network address
<ge-length> : subnetmask length
<le-length> : subnetmask length
<AS> : AS number
<ip-address> : neighbor IP address
The prefix-list identifies BGP routes by referencing network address and subnet mask of the route information. It then decides how to handle the identified route information by permit or deny.
“permit” means to allow route information. That is, if it is applied out, BGP routes are advertised; if it is applied in, BGP routes are received. “deny” means discard route information. That is, if it is applied out, the corresponding BGP route is not advertised; if it is applied in, the corresponding BGP route is not received. Also, remember that there is an “implicit deny” at the end of the prefix-list.
Note also how “any” is configured in prefix-list. The “any (all)” configuration in prefix-list is as follows.
0.0.0.0/0 le 32
This configuration means that any bit pattern in the network address is acceptable and the subnet mask is /32 or less. In other words, it represents all network address and subnet mask combinations.
Related article
See also the following article about prefix-list.
Re-send/Re-recieve BGP routes
Simply applying prefix-list to a neighbor does not make the route filter work. BGP routes must be re-sent/received. Re-send or re-receive, depending on the direction in which prefix-list is applied. Use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode.
Re-send/Re-recieve BGP routes
#clear ip bgp <ip-address> {in|out}
<ip-address> : Neighbor IP address
Verifycation Commands for prefix-list
The following table summarizes the main show commands for verifying BGP route filtering by prefix-list.
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
| #show ip prefix-list | Verify prefix-list to identify BGP routes. |
| #show ip neighbor | Verify the prefix-list applied to the BGP neighbor. |
| #show ip bgp | Verify the BGP table. |
| #show ip bgp neighbor advertised-routes | Verify BGP routes to be advertised to the specified BGP neighbor. |
| #show ip bgp neighbor routes | Verify BGP routes received from the specified BGP neighbor. |
show ip prefix-list
Use the show ip prefix-list command to verify the prefix-list for identifying BGP routes.
show ip prefix-list
R1#show ip prefix-list ip prefix-list FROM_R2: 2 entries seq 5 deny 172.16.1.0/24 ge 28 seq 10 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ip prefix-list TO_R2: 1 entries seq 5 permit 192.168.1.0/24
show ip bgp neighbor
To verify the prefix-list applied to a BGP neighbor, use the show ip bgp neighbor command.
show ip bgp neighbor
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 | include prefix filter Incoming update prefix filter list is FROM_R2 Outgoing update prefix filter list is TO_R2
show ip bgp
Use the show ip bgp command to display the BGP table and verify that the intended filters are in place. However, it is difficult to see the entire BGP table, so please filter the display of the BGP table.
show ip bgp
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 192.168.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.1.0/25 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 172.16.1.128/26 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
show ip bgp neighbor advertised-routes
The show ip bgp neighbor advertised-routes command displays the BGP routes advertised to the specified neighbor.
shwo ip bgp neighbor advertised-routes
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 192.168.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Total number of prefixes 1
show ip bgp neighbor routes
The show ip bgp neighbor routes command displays BGP routes received from the specified neighbor.
show ip bgp neighbor routes
R1#show ip bgp neighbors 10.0.0.2 routes
BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 192.168.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.1.0/25 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
*> 172.16.1.128/26 10.0.0.2 0 0 2 i
Total number of prefixes 2
Summary
Points
- The configuration flow for filtering BGP routes using prefix-list is as follows
- Identify route information to be filtered by prefix-list
- Applying distribute-list to a specific neighbor
- Re-sent/Re-recieve BGP routes
- The prefix-list identifies routes to be filtered by reference to network address and subnet mask.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation