Table of Contents
Overview
GARP (Gratuitous ARP) is an ARP message sent outside of the normal ARP operation of resolving MAC addresses from IP addresses. This section explains the purpose of GARP and how it works.
What is Gratuitous ARP (GARP)?
Gratuitous ARP (GARP) is an ARP message sent outside of the normal ARP process. GARP is used primarily for two purposes
- Duplicate IP address detection
- Update ARP cache and MAC address table
In the following sections, the GARP mechanism for these two purposes will be explained.
Operation may vary depending on the implementation. The contents of this page have been verified with Cisco routers.
Related articles
For the normal ARP process of resolving MAC addresses from IP addresses, see the following article.
Duplicate IP address detection
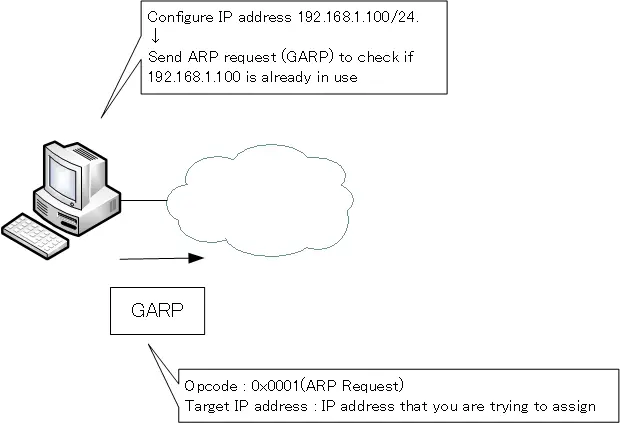
IP addresses must not be duplicated. When assigning a new IP address to an interface, GARP can be used to detect duplicate IP addresses.
An ARP request is sent with the IP address configured on the interface set as the Target IP address. This is a Gratuitous ARP that is sent at a different timing from the normal ARP process. When an ARP reply to this ARP request is returned, it indicates that the IP address is already in use.
Update ARP cache and MAC address table
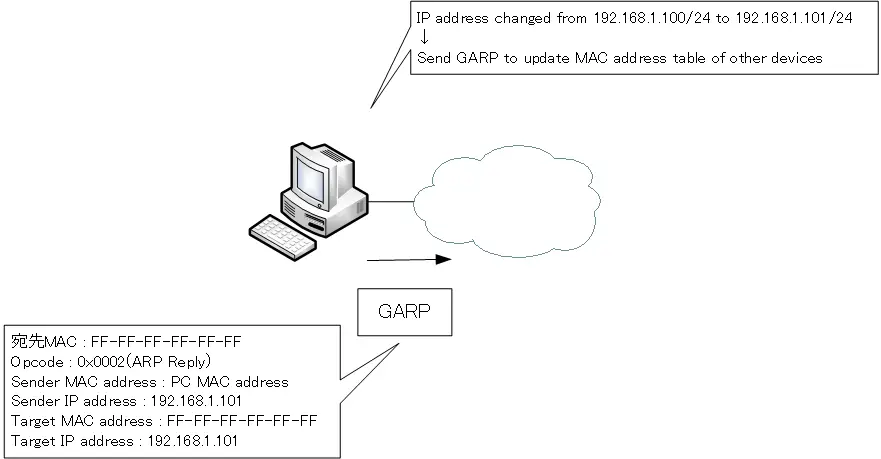
GARP can be used to promptly update the ARP cache of other devices when IP addresses are changed. Broadcast ARP reply so that the ARP caches of other devices can be updated promptly.
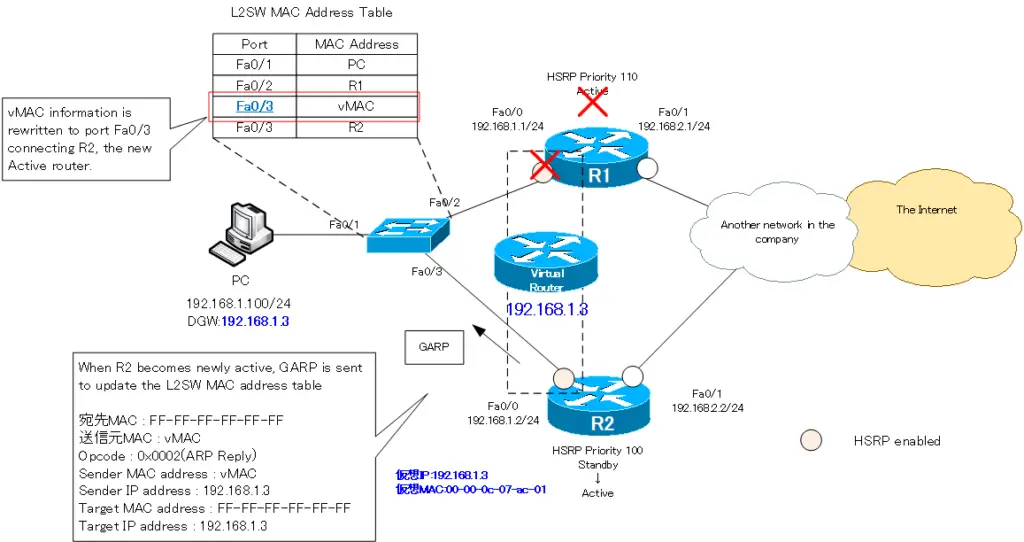
GARP is also sent to update the MAC address table of the intervening Layer 2 switch when switching active/master in HSRP or VRRP. The newly active/master router broadcasts an ARP reply. Its source MAC address is a virtual MAC address, and the virtual MAC address entry is updated in the Layer 2 switch’s MAC address table.
Summary
Points
- GARP (Gratuitous ARP) is an ARP message sent outside the normal ARP operation of resolving MAC addresses from IP addresses.
- GARP is used for the following purposes
- Duplicate IP address detection
- Update ARP cache and MAC address table
TCP/IP
- IP(Internet Protocol) : The Most Important Data Transfer Protocol
- Ping “Will the data be transfered properly?”
- Ping command on Windows OS
- Traceroute : Which router does the data go through?
- ICMP Redirect
- Where’s the Trouble? Ping and Traceroute
- ARP(Address Resolution Protocol)
- ARP Format
- Gratuitous ARP(GARP)
- nslookup command : Verifying DNS name resolution
- DHCP : Automatically Assign IP Address
- Cisco IOS DHCP Server Configuration and Verification Commands
- Cisco Router DHCP Server Configuration Example
- DHCP Relay Agent
- DHCP Relay Agent Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Summary of DHCP Server Placement
- TCP/IP Configuration Summary
- ipconfig command : To verify TCP/IP configurations on Windows OS
- Commands to Verify TCP/IP Configuration On Linux (Ubuntu)
- Web Proxy Server
- FTP : Representative File Transfer Protocol
- TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
- TFTP Client on Windows10/11

