Table of Contents
Overview
The neighbor as-override command rewrites the AS_PATH attribute of a BGP route to advertise to a specific neighbor. This section describes the neighbor as-override command.
What is neighbor as-override command ?
The neighbor as-override command rewrites the AS_PATH attribute of BGP route. When advertising a BGP route to a specific neighbor, the AS number at the beginning of AS_PATH is rewritten to its own AS number.
The primary case for using the neighbor as-override command is when connecting between sites via MPLS-VPN. When using MPLS-VPN to connect between sites and using BGP between PE and CE, the AS numbers of the CE routers may be the same. Then the BGP route will be invalid due to loop prevention by AS_PATH.
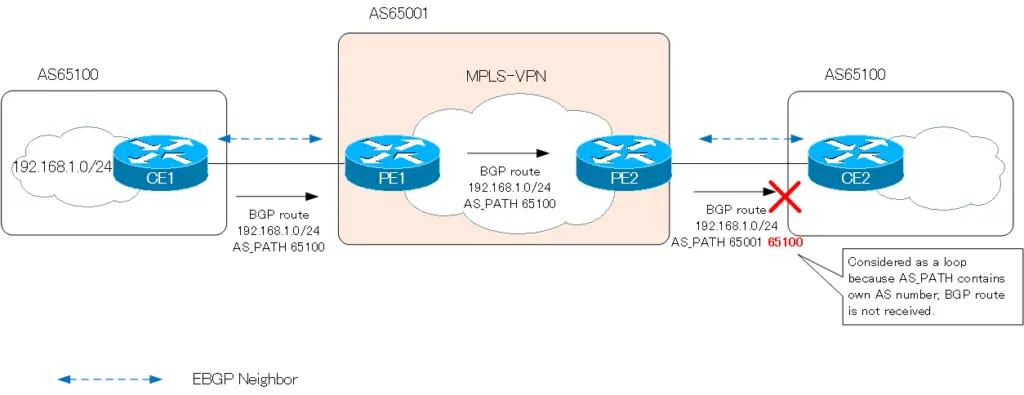
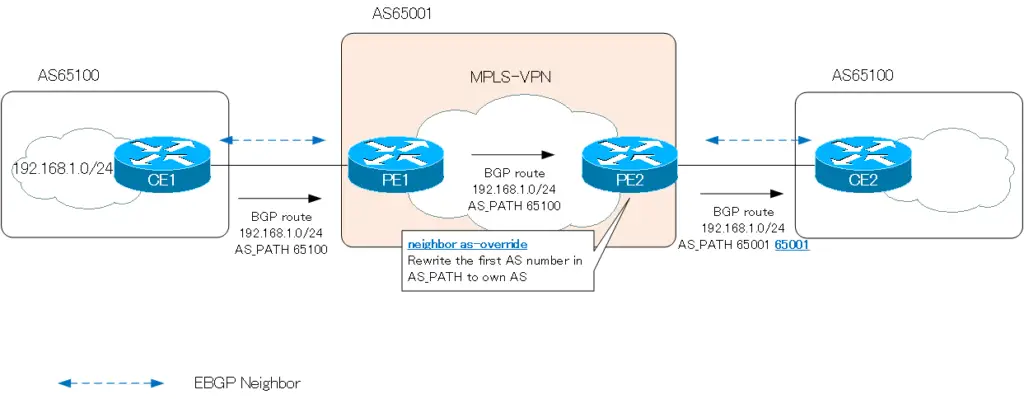
So, use the neighbor-as-override command on the PE router. In the following figure, PE2 configures the neighbor-as-override command for CE2. The AS_PATH attribute attached to the BGP route 192.168.1.0/24 is “65100”; the PE2 router rewrites this to its own AS number “65001”. And because the CE2 router is an EBGP neighbor, PE2 router’s AS number is added (prepended) to the AS_PATH of the BGP route 192.168.1.0/24 and becomes “65001 65001”.
Since the AS_PATH does not contain its own AS number, the CE2 router can successfully receive the BGP route 192.168.1.0/24.
Related article
Instead of neighbor as-override, neighbor allowas-in can also be configured. neighbor allowas-in command is explained in the following article.
neighbor as-override Command and Verification commands
Command Format
The neighbor as-override command is configured in BGP IPv4 VRF configuration mode; it cannot be configured directly under BGP configuration mode. VRF must also be configured beforehand.
neighbor as-override
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf <vrf-name>
(config-router-af)#neighbor <ip-address> as-override
<AS> : AS number
<vrf-name> : VRF name
<ip-address> : Neighbor IP address
When advertising a BGP route to a specified neighbor, the first AS number in AS_PATH is rewritten to its own AS. Processed before the AS_PATH prepend when advertising a BGP route to an EBGP neighbor.
Related article
Please also see the following article about VRF.
Verifycation Command
If the neighbor details are viewed with the show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf neighbor command, it can be verified that the neighbor as-override command has been configured.
show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf neighbor
R1#show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf AAA neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.1.2.2, vrf AAA, remote AS 65100, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 2.2.2.2
BGP state = Established, up for 00:42:45
Last read 00:00:44, last write 00:00:44, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
Route refresh: advertised and received(old & new)
Address family IPv4 Unicast: advertised and received
Message statistics:
InQ depth is 0
OutQ depth is 0
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 2 2
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 4 2
Keepalives: 48 48
Route Refresh: 0 0
Total: 54 52
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
For address family: VPNv4 Unicast
Translates address family IPv4 Unicast for VRF AAA
BGP table version 9, neighbor version 9/0
Output queue size: 0
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
1 update-group member
Overrides the neighbor AS with my AS before sending updates
~省略~
neighbor as-override Configuration Example
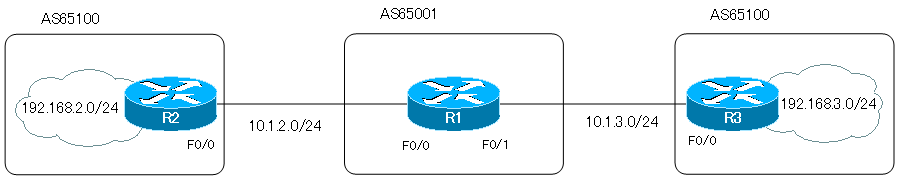
Network Diagram
Consider the following network diagram for the neighbor as-override command.
初期設定
Here is an excerpt of the initial configuration for each router: R1 defines VRF “AAA”; R1-R2 and R1-R3 establish BGP neighbors; R2 advertises 192.168.1.0/24 via BGP; R3 advertises 192.168.3.0/24 via BGP.
R1 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R1 ! ip vrf AAA rd 65001:1 route-target export 65001:1 route-target import 65001:1 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding AAA ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip vrf forwarding AAA ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 65001 no synchronization bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes no auto-summary ! address-family ipv4 vrf AAA neighbor 10.1.2.2 remote-as 65100 neighbor 10.1.2.2 activate neighbor 10.1.2.2 as-override neighbor 10.1.3.3 remote-as 65100 neighbor 10.1.3.3 activate neighbor 10.1.3.3 as-override no synchronization exit-address-family
R2 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R2 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 65100 no synchronization bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.2.0 neighbor 10.1.2.1 remote-as 65001 no auto-summary
R3 Initial Configuration(Click)
hostname R3 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 192.168.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.1.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 65100 no synchronization bgp router-id 3.3.3.3 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.3.0 neighbor 10.1.3.1 remote-as 65001 no auto-summary
Configuration and Verifycation
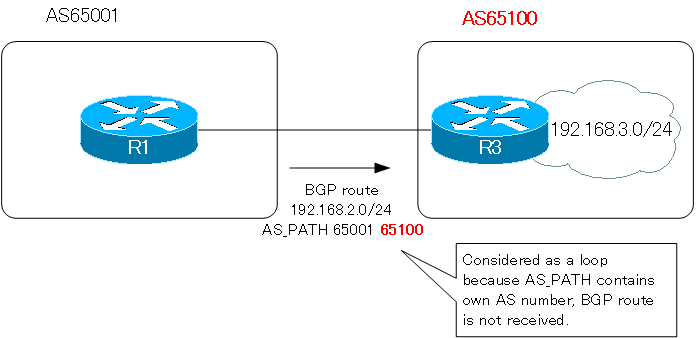
Step1:Verify loop prevention by AS_PATH
Verify that if the AS_PATH attribute contains its own AS number, BGP route is considered a loop.Enable debugging of BGP UPDATE messages on R3 and receive BGP routes again.
R3 Verify loop prevention by AS_PATH
R3#debug ip bgp updates BGP updates debugging is on for address family: IPv4 Unicast R3#clear ip bgp * in R3# *Mar 1 00:25:46.339: BGP(0): 10.1.3.1 rcv UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.1.3.1, origin i, originator 0.0.0.0, path 65001 65100, community , extended community *Mar 1 00:25:46.343: BGP(0): 10.1.3.1 rcv UPDATE about 192.168.3.0/24 -- DENIED due to: AS-PATH contains our own AS; *Mar 1 00:25:46.347: BGP(0): 10.1.3.1 rcv UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop 10.1.3.1, origin i, originator 0.0.0.0, path 65001 65100, community , extended community *Mar 1 00:25:46.351: BGP(0): 10.1.3.1 rcv UPDATE about 192.168.2.0/24 -- DENIED due to: AS-PATH contains our own AS; R3#undebug all All possible debugging has been turned off
The BGP route 192.168.2.0/24, which is considered a loop, is not received and is not in the BGP table.
R3 show ip bgp
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 4, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
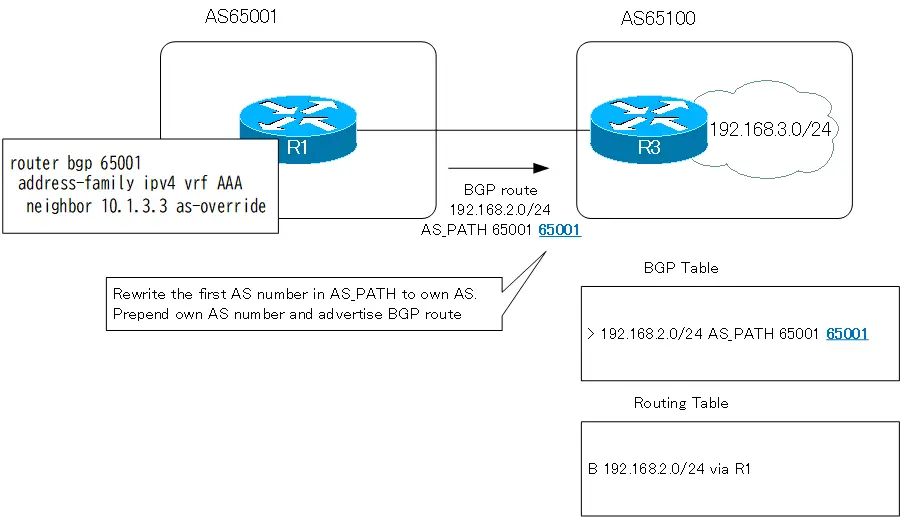
Step2:R1 configure neighbor as-override
On R1, configure the neighbor as-override command for neighbor R3: when advertising a BGP route from R1 to R3, the leading AS number “65100” is rewritten to its own AS number “65001”.
R1 neighbor as-override
router bgp 65001 address-family ipv4 vrf AAA neighbor 10.1.3.3 as-override
Step3:R3 Verify BGP route
R3 receives the BGP route 192.168.2.0/24 and makes it the best path. Then, R3 registers BGP route 192.168.2.0/24 in the routing table.
R3 Verify BGP route
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.2.0 10.1.3.1 0 65001 65001 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R3#show ip route
~省略~
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.1.3.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
B 192.168.2.0/24 [20/0] via 10.1.3.1, 00:01:09
C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
Step4:R1 Configure neighbor as-override
Configure the neighbor as-override command for R2 in the same way.
R2 neighbor as-override
router bgp 65001 address-family ipv4 vrf AAA neighbor 10.1.2.2 as-override
Step5:Verify Communication
Now communication is possible in the network between distant ASes with the same AS number. verify the BGP table and routing table of R2/R3.
R2/R3 BGP Table and Routing Table
R2#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0 10.1.2.1 0 65001 65001 i
R2#show ip route bgp
B 192.168.3.0/24 [20/0] via 10.1.2.1, 00:00:22
R3#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 7, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.2.0 10.1.3.1 0 65001 65001 i
*> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R3#show ip route bgp
B 192.168.2.0/24 [20/0] via 10.1.3.1, 00:00:48
Then verify that communication is possible between 192.168.2.0/24 and 192.168.3.0/24. Ping from R2 to R3.
Ping from R2 to R3
R2#ping 192.168.3.3 source 192.168.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 192.168.2.2 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/18/20 ms
Summary
Points
- The neighbor as-override command rewrites the AS number at the beginning of AS_PATH to its own AS number when advertising a BGP route to a specific neighbor.
- Enter the following command in configuration mode for the VRF address family of BGP
- (config-router-af)#neighbor <ip-address> as-override
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation



