Table of Contents
Overview
The network command can be used to generate BGP routes for known network addresses in the routing table. This section describes the generation of BGP aggregate route by the network command.
Related article
Please also refer to the following article regarding the BGP network command.
Two methods for BGP route aggregation
BGP allows manual aggregation at arbitrary boundaries as well as at class boundaries in 8-bit increments. Aggregation is basically manual aggregation; the following methods are available to perform BGP route aggregation on Cisco routers.
- network command
- aggregate-address command
Basically, aggregation is done with the aggregate-address command. In case you are interested, here is an introduction to configuring the aggregation with the network command.
Related article
Aggregation of BGP routes using the aggregate-address command is described in the following article.
Aggregation using network command
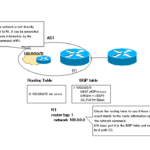
The network command is used to generate BGP route. In order for the network command to generate a BGP route, there must be an exact match of the route information in the routing table. The key point is that it must be an exact match. For example, suppose the routing table contains the following route information.
- 192.168.0.0/24
- 192.168.1.0/24
- 192.168.2.0/24
- 192.168.3.0/24
Trying to generate route information for 192.168.0.0/22 by aggregating these four routes, the network command is configured as follows.
router bgp <AS> network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.252.0
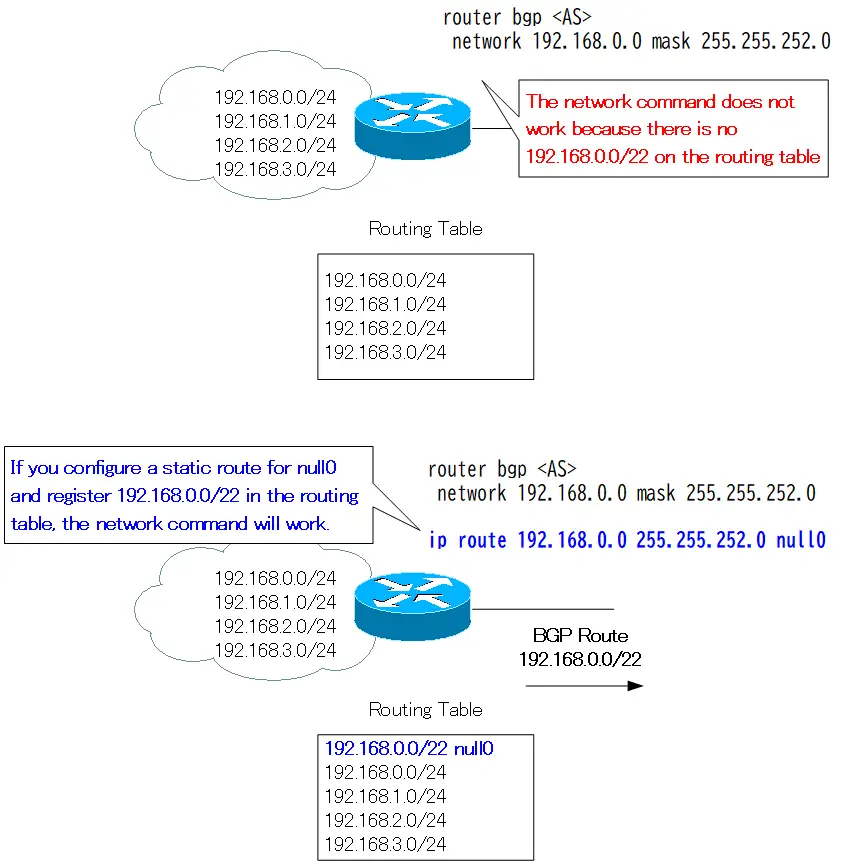
However, no aggregate route is generated with this configuration. This is because the route information specified by the network command, 192.168.0.0/22, does not exist in the routing table. The idea is to register matching route information in the routing table so that the network command will work.
The network command will work if you additionally configure a static route with null0 as the output interface as follows.
ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 null0
The reason null0 is used as the output interface is to prevent loops of packets destined for networks that are included in the range of the aggregate route but do not actually exist.
Problems with configuring aggregation using the network command
As you can see, the network command can also be used to configure aggregate route, but there are some problems.
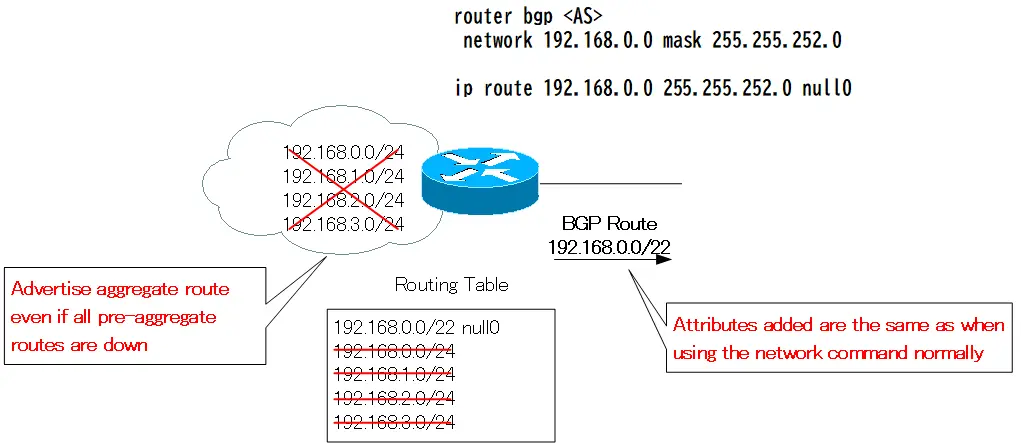
- Always advertise the aggregate route
- Aggregate route attributes are not flexible
Static route with null0 as the output interface is always present in the routing table. Thus, even if all the pre-aggregation networks are down, the network command will always be enabled and the aggregate route will be advertised to the neighbor.
Also, since the aggregate route is generated by the network command, the attribute is the same as the route generated by the network command normally, and cannot be configured flexibly.
On the other hand, if you generate aggregate route with the aggregate-address command, it will stop advertising the aggregate route if all pre-aggregate routes are down. It is also possible for the aggregate route to inherit attributes added to the pre-aggregate route by configuring the options of the command.
Summary
Point
- Aggregate route generation can also be done with the network command for generating BGP routes.
- To generate an aggregated route with the network command, configure a static route for the aggregate route with Null0 as the output interface and then use the network command.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation