Table of Contents
Overview
This is an example of BGP route summarization configuration using the network command. network command generates known network addresses in the routing table as BGP routes.
Related articles
The BGP network command is explained in the following article.
Please also refer to the following article about BGP route summarization with the network command.
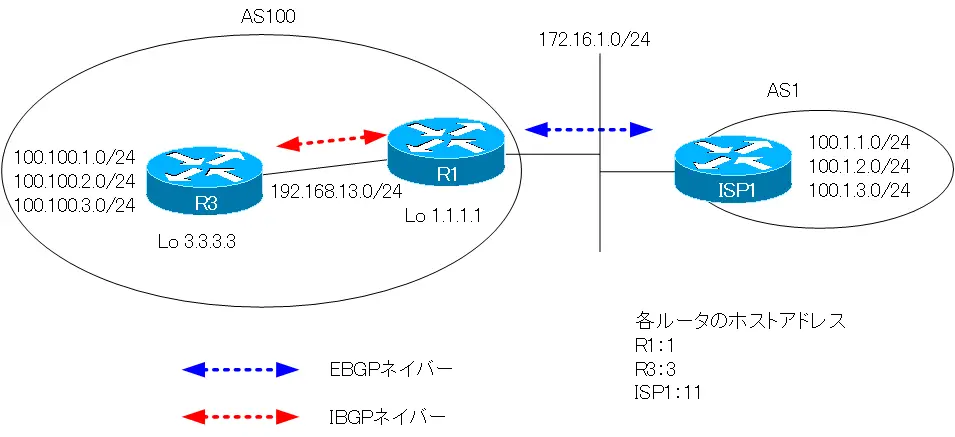
Network Diagram
Configuring and Verifying route summarization using network command
Only network commands for route summarization
First, verify the BGP table and routing table on R1.
R1 BGP Table/Routing Table
R1#show ip bgp
-- omitted --
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
r>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 2.2.2.2 [110/3] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:43, FastEthernet0/1
100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
O 100.100.1.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:43, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.2.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:43, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.3.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:43, FastEthernet0/1
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:44, FastEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
O 192.168.23.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:57:46, FastEthernet0/1
R1 is learning routes in the AS with OSPF. It is also learning 100.100.1.0/24, 100.100.2.0/24, and 100.100.3.0/24 as IBGP routes from R3. To summarize these three routes and advertise to ISP1, configure as follows
Note that the IBGP routes 100.100.1.0/24, 100.100.2.0/24, and 100.100.3.0/24 are in RIB Failure state. This is because they are registered as OSPF routes in the routing table.
Related article
Please also refer to the following article about RIB Failure.
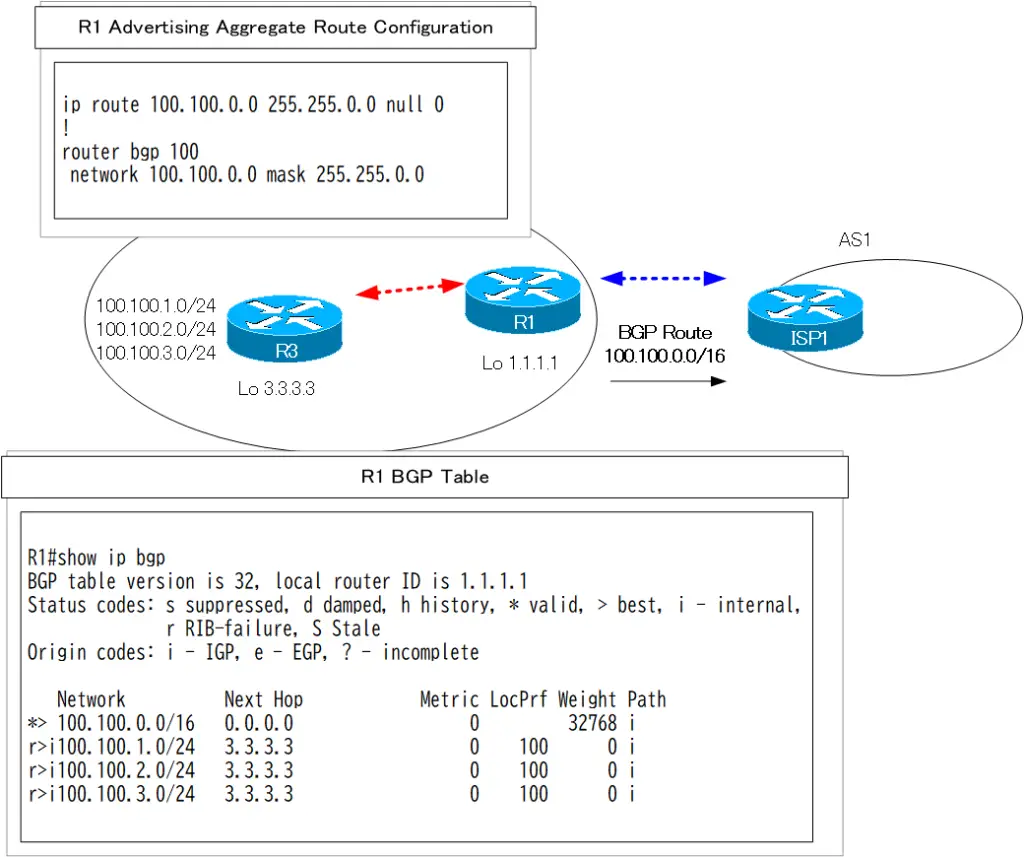
R1 Generate summarized route
router bgp 100 network 100.100.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
However, this network command does not work because there is no 100.100.0.0/16 route in the routing table, and looking at the BGP table, no 100.100.0.0/16 route is generated.
R1 BGP Table
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 31, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
r>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
Add static route destined toward Null0
The network command generates a BGP route for a known network address in the routing table. Network addresses that are not in the routing table cannot be generated as BGP routes on an arbitrary basis. So, to make the network command work, configure a static route with null0 as the output interface.
R1 static route destined toward Null0
ip route 100.100.0.0 255.255.0.0 null 0
If a static route is configured with null0 as the output interface, the route 100.100.0.0/16 is placed in the BGP table and is found to be the best path. Summarized route 100.100.0.0/16 is then advertised to R2.
R1 BGP Table
R1#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 32, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.100.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
r>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation