Table of Contents
Overview
Adjusting the Administrative Distance of BGP routes allows BGP routes to be preferred over routes by other routing processes. This section describes how to adjust the administrative distance for BGP routes.
How to Adjust Administrative Distance of BGP Routes
The default administrative distance for BGP routes are as follows
- EBGP Route : 20
- IBGP Route : 200
Adjusting the Administrative Distance of BGP routes allows BGP routes to be preferred over routes by other routing processes. There are three main ways to adjust the administrative distance of BGP routes
- distance command
- distance bgp command
- BGP backdoor
Related article
Please also refer to the following article about Administrative Distance.
distance command
To change the administrative distance of BGP routes, use the following configuration.
BGP distance command
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#distance <AD-value> <neighbor-address> <wildcard-mask> <ACL>
<AS>:AS number
<AD-value>: Administrative distance value
<neighbor-address>: Neighbor IP address
<wildcard-mask>: Wildcard mask for neighbor IP address
<ACL>: ACL number
The <neighbor-address> and <wildcard-mask> allow you to change the administrative distance of routes received from a specific neighbor. Note that if <neighbor-address> and <wildcard-mask> are specified as 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255, it means “any”.
Also, by associating an access list number at the end, only the administrative distance of the route permitted in the access list can be changed.
distance command configuration example
Configure the distance command with the following network diagram.
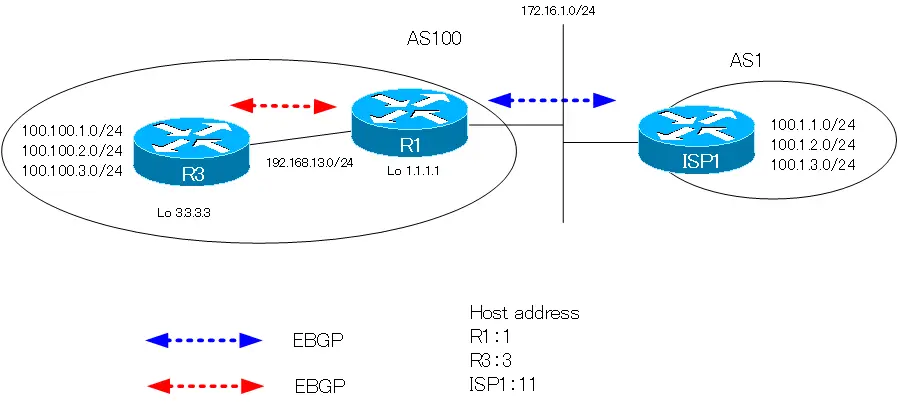
First, verify the BGP table and routing table on R1.
R1 BGP Table/Routing Table
R1#show ip bgp
-- omitted --
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.3.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
r>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
O 100.100.1.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:03:43, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.2.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:03:43, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.3.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:03:43, FastEthernet0/1
B 100.1.1.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 01:34:59
B 100.1.3.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 01:34:59
B 100.1.2.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 01:34:59
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 01:35:01, FastEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
100.100.1.0/24, 100.100.2.0/24, and 100.100.3.0/24 are learned by both IBGP and OSPF. OSPF routes are placed on the routing table by the administrative distance. On the BGP table, the best path is marked with “r” because it is not on the routing table. The “r” means RIB-Failure status.
Related article
The following article describes in detail the “r” (RIB-Failure) BGP routes on the BGP table.
100.1.1.0/24, 100.1.2.0/24, and 100.1.3.0/24 are learned by EBGP; since they are EBGP routes, the Administrative Distance is 20, which is the default.
From this state, R1 changes the administrative distance as follows
- Change the administrative distance of 100.100.1.0/24 received from R3 to 90
- Change the Administrative Distance of the route received from ISP1 to 100
R1 is configured as follows.
R1 Change administrative distance
access-list 1 permit 100.100.1.0 ! router bgp 100 distance 90 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 1 distance 100 172.16.1.11 0.0.0.0
After configuration, the BGP table and routing table on R1 will change as follows.
R1 BGP Table/Routing Table(After Administrative Distance Change)
R1#show ip bgp
-- omitted --
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.3.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
B 100.100.1.0 [90/0] via 3.3.3.3, 00:00:06
O 100.100.2.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.3.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1
B 100.1.1.0 [100/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
B 100.1.3.0 [100/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
B 100.1.2.0 [100/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:09, FastEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
With the Administrative Distance of 100.100.1.0/24 now 90, the 100.100.1.0/24 route is changed to BGP route. 100.100.1.0/24 is no longer marked with an “r” in the BGP table as well.
Also, administrative distance of 100.1.1.0/24, 100.1.2.0/24, and 100.1.3.0/24 has changed to 100.
distance bgp command
To change the administrative distance of BGP routes, there is also the distance bgp command. The syntax for the distance bgp command is as follows.
distance bgp command
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#distance bgp <external> <internal> <local>
<AS>:AS number
<external>: Administrative distance value for EBGP route
<internal>: Administrative distance value for IBGP route
<local>: Administrative distance value for locally generated route
The distance bgp command changes the administrative distance for each BGP route category, such as EBGP routes, IBGP routes, and locally generated BGP routes.
distance bgp command configuration example
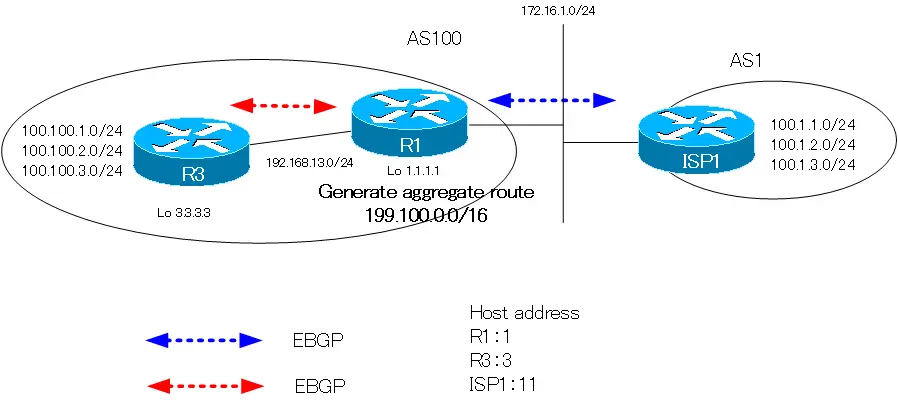
Configure the distance bgp command on R1 in the figure. R1 generates an aggregated route 192.1.0.0/16. The BGP and routing tables on R1 are as follows.
R1 BGP Table/Routing Table
R1#show ip bgp
-- omitted --
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.3.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
r>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
r>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
*> 199.1.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i
s> 199.1.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
O 100.100.1.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.2.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1
O 100.100.3.0 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:06, FastEthernet0/1
B 100.1.1.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
B 100.1.3.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
B 100.1.2.0 [20/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:08, FastEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 199.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback1
B 199.1.0.0/16 [200/0] via 0.0.0.0, 00:00:08, Null0
100.100.1.0/24, 100.100.2.0/24, and 100.100.3.0/24 are learned by both IBGP and OSPF. OSPF routes are placed on the routing table by the administrative distance. On the BGP table, the best path is marked with “r” because it is not on the routing table. The “r” means RIB-Failure status.
100.1.1.0/24, 100.1.2.0/24, and 100.1.3.0/24 are learned by EBGP; since they are EBGP routes, the Administrative Distance is 20, which is the default.
Also, the aggregate route 199.1.0.0/16 generated by R1 has an administrative distance value of 200.
From here, use the distance bgp command on R1 to change the administrative distance as follows
- Administrative distance value for EBGP route:50
- Administrative distance value for IBGP route:80
- Administrative distance value for aggregate route:30
R1 distance bgp
router bgp 100 distance bgp 50 80 30
The BGP and routing tables on R1 after configuring distance bgp are as follows.
R1 BGP Table/Routing Table(After configuring distance bgp)
R1#show ip bgp
-- omitted --
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 100.1.1.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.2.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*> 100.1.3.0/24 172.16.1.11 0 0 1 i
*>i100.100.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
*>i100.100.2.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
*>i100.100.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 i
*> 199.1.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i
s> 199.1.1.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R1#show ip route
-- omitted --
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
100.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 6 subnets
B 100.100.1.0 [80/0] via 3.3.3.3, 00:00:06
B 100.100.2.0 [80/0] via 3.3.3.3, 00:00:06
B 100.100.3.0 [80/0] via 3.3.3.3, 00:00:06
B 100.1.1.0 [50/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:06
B 100.1.3.0 [50/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
B 100.1.2.0 [50/0] via 172.16.1.11, 00:00:07
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/2] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:08, FastEthernet0/1
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 172.16.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 199.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback1
B 199.1.0.0/16 [30/0] via 0.0.0.0, 00:00:08, Null0
IBGP routes are preferred over OSPF for 100.100.1.0/24, 100.100.2.0/24, and 100.100.3.0/24 due to the Administrative Distance value for IBGP routes being changed to 80, and they are now in the routing table. The “r” on the table has also disappeared.
Also, the EBGP route’s administrative distance value is now 50 and the aggregate route’s administrative distance value is now 30.
BGP Backdoor
There is also BGP backdoor functionality to change the Administrative Distance value of a particular EBGP route. BGP backdoors sets the Administrative Distance value for a particular EBGP route to 200.
BGP backdoor can be used when IGP is used across ASes and IGP route are preferred over EBGP route. To configure BGP backdoor, add backdoor as an option at the end of the network command as follows
BGP Backdoor
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#network <address> {mask <subnetmask>} backdoor
<AS>:AS number
<address>: Network address
<subnetmask>: Subnet mask
This changes the Administrative Distance value of the EBGP route for the specified network address/subnet mask to 200.
Summary
Points
- Adjusting the Administrative Distance of BGP routes allows BGP routes to be preferred over routes by other routing processes.
- There are three main ways to adjust the administrative distance of BGP routes
- distance command
- distance bgp command
- BGP backdoor
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation