Table of Contents
Overview
Selective aggregation means that when routes are aggregated in BGP, some pre-aggregation routes are selected and advertised together with the aggregated routes, rather than all or nothing, where all pre-aggregation routes are sent or none at all.
This section describes the suppress-map option of the aggregate-address command for selective aggregation. suppress-map option allows you to determine the pre-aggregation routes that are not advertised.
aggregate-address command : suppress-map option
Selective aggregation with the suppress-map option is considered on the basis that all default pre-aggregation routes are advertised. The suppress-map option allows you to stop some of the pre-aggregation routes from being advertised along with the aggregation routes.
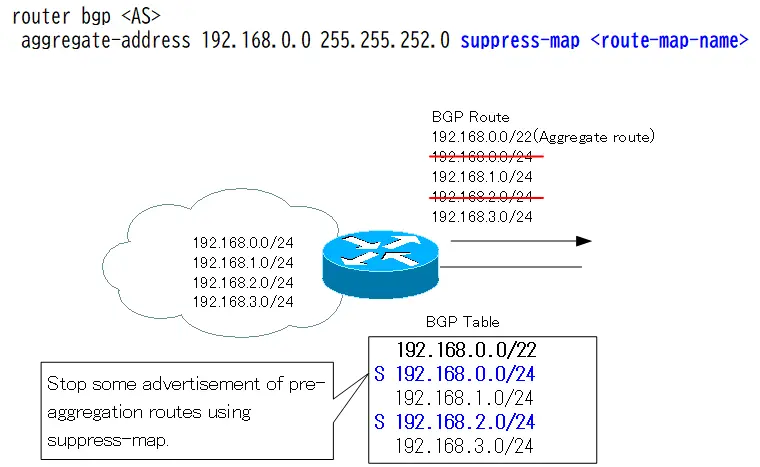
The syntax of the support-map command is as follows.
aggregate-address suppress-map
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#aggregate-address <network-address> <subnetmask> suppress-map <route-map-name>
<AS>: AS number
<network-address>: Network address of the aggregate route
<subnetmask>: Subnet mask of the aggregate route
<route-map-name>: route-map name
Note that the route map is specified after suppress-map, but it is easy to get confused with the route map configuration suppress-map is an option to “stop” the pre-aggregation routes. Therefore, the pre-aggregation routes that are permit in the route-map after suppress-map are no longer advertised. Conversely, pre-aggregation routes that you want to advertise along with the aggregation route are configured to be denied in the route-map.
Selective aggregation with suppress-map configuration example
Consider the specific configuration in “Figure: Selective Aggregation with suppress-map”. Generate an aggregate route that aggregates the following four BGP routes.
- 192.168.0.0/24
- 192.168.1.0/24
- 192.168.2.0/24
- 192.168.3.0/24
Aggregating these four routes with the longest subnet mask is “192.168.0.0/22”. Along with this aggregate route, “192.168.1.0/24” and “192.168.3.0/24” are also advertised. In other words, stop advertising 192.168.0.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 of the pre-aggregation route. The configuration of the suppress-map is as follows.
suppress-map configuration example
access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 access-list 1 permit 192.168.2.0 ! route-map SUPP-MAP permit 10 match ip address 1 ! router bgpaggregate-address 192.168.0.0 255.255.252.0 suppress-map SUPP-MAP
The routes matching the sequence 10 match condition in the route-map “SUPP-MAP” are 192.168.0.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24. Since the route map SUPP-MAP is specified in suppress-map, 192.168.0.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24 advertisements will be suppressed.
The route map “SUPP-MAP” still has an implicit deny any at the end.192.168.1.0/24と192.168.3.0/24. Therefore, the advertisement of these two pre-aggregation routes will not be suppressed and will be advertised to the neighbor along with the aggregate route.
set action is not required for route-map specified the suppress-map.
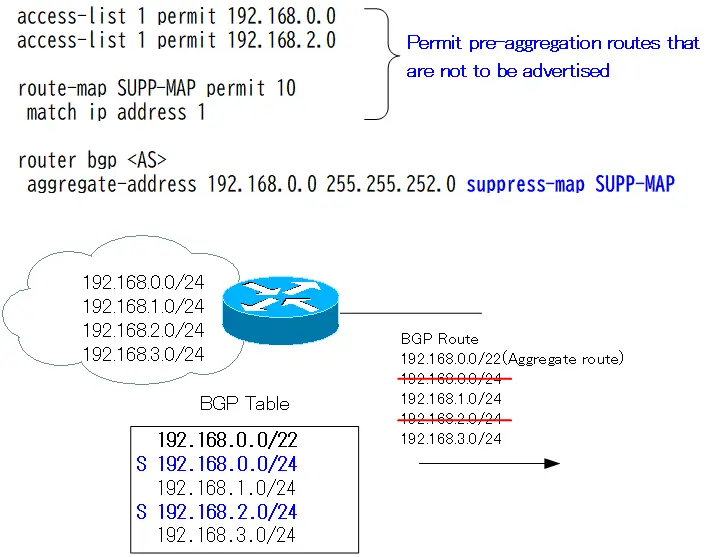
And note the BGP table when suppress-map is configured. If you suppress the advertisement of a particular pre-aggregation route with suppress-map, the BGP table will be a mixture of “*(valid)” and “s(suppressed)”.
BGP table when suppress-map is configured
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 100.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.0.0/22 0.0.0.0 32768 i
s> 192.168.0.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
s> 192.168.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Summary
Points
- suppress-map is an option to the aggregate-address command to perform selective aggregation. suppress-map performs selective aggregation for all neighbors.
- Specify a route-map after suppress-map. Routes that are permited in the route map are not advertised as suppressed.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation