Table of Contents
Overview
This section describes the configuration and verification commands for BGP route filtering using route-map. The route map allows you to identify BGP routes to filter by reference to standard/extended ACLs, prefix lists, AS_PATH ACLs, etc. In addition to filters, additional path attributes can be set for BGP routes.
Related articles
To understand BGP route filtering using route-map, you must understand route filtering using standard/extended ACL, prefix-list, and AS_PATH ACL referenced in route maps. Please also see the following articles。
Flow of Configuring route filter using route-map
The configuration flow for filtering BGP routes using route-map is as follows.
- Identify route information to be filtered by route-map
- Applying route-map to a specific neighbor
- Re-sent/Re-recieve BGP routes
Configuration Commands for BGP route filter using route-map
Create a route map to filter and apply to a specific BGP neighbor. The configuration commands are as follows
BGP route filter route-map
(config)#route-map <mat-tag> {permit | deny} [<seq-num>]
(config-route-map)#match <condition>
(config-route-map)#set <action>
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#neighbor <ip-address> route-map <map-tag> {in|out}
<map-tag> : Arbitrary route-map name
permit | deny : Specify permit or deny
<seq-num> : Sequence number. If omitted, “10.”
<condition> : Condition
<action> : Additional Processes
<AS> : AS number
<ip-address> : BGP neighbor IP address
is the name of the route-map. Decide on route-map name that is easy to understand and not too long.is the order of processing. Processing is performed in the order of decreasing .
permit | deny to permit or deny BGP routes. Then, match identifies the BGP routes to be filtered. Standard/extended ACLs, distribute-lists, and AS_PATH ACLs can be referenced.Other conditions can also be configured; if match is omitted, it is all.
In addition, set sets additional actions for the permitted BGP routes. It mainly sets path attributes.
In the following sections, we will look at the permit | deny, match, and set configurations in more detail.
permit | deny
How BGP routes are handled is the permit|deny behind the . Make sure you understand this properly. The permit|deny of standard/extended ACLs, prefix-list, and AS_PATH ACL only mean whether they match the route-map match condition. BGP routes that meet the match condition are processed as permit | deny after <map-tag>.
“permit” means to allow route information. That is, if it is applied out, BGP routes are advertised; if it is applied in, BGP routes are received. “deny” means discard route information. That is, if it is applied out, the corresponding BGP route is not advertised; if it is applied in, the corresponding BGP route is not received.
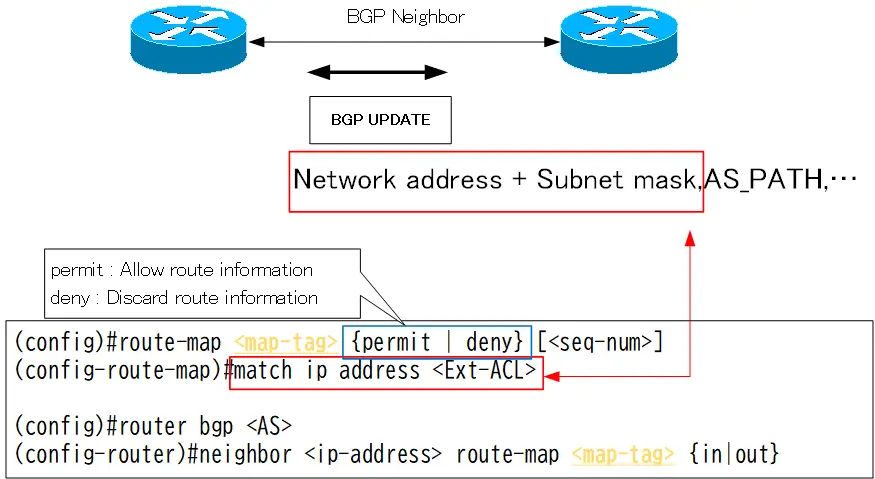
match condition std/ext ACL
The configuration for referencing standard/extended ACLs in the route-map’s match condition is as follows.
route-map match condition std/ext ACL
(config)#route-map <mat-tag> {permit | deny} [<seq-num>]
(config-route-map)#match ip address {<ACL-num> | <ACL-name>}
<ACL-num> : Referenced ACL number
<ACL-name> : Referenced ACL name
If it is a standard ACL, only the network address of the BGP route is checked.
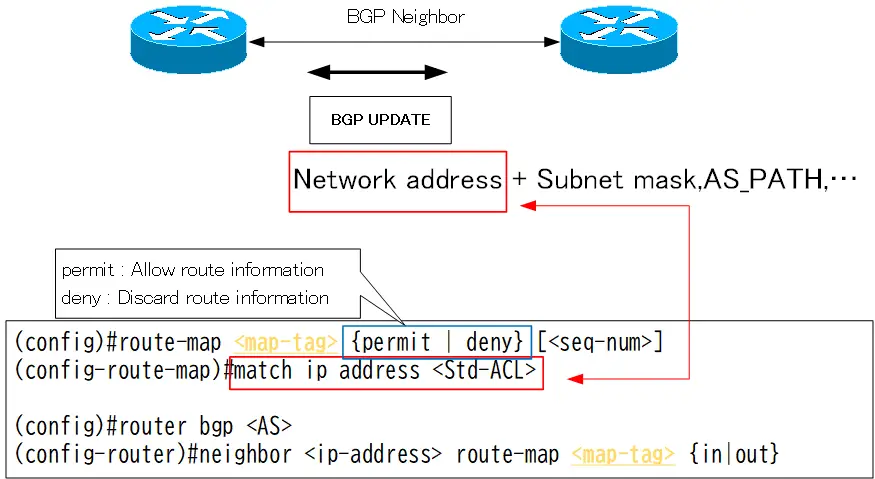
If it is an extended ACL, check the network address + subnet mask of the BGP route.
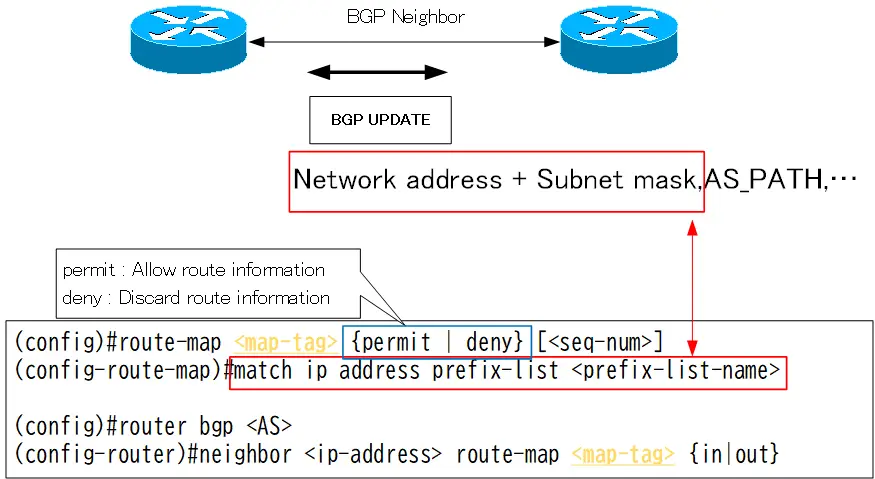
match condition prefix-list
The configuration for referencing prefix-list in the route-map’s match condition is as follows.
route-map match condition prefix-list
(config)#route-map <mat-tag> {permit | deny} [<seq-num>]
(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list <prefix-list-name>
<prefix-list-name> : Referenced prefix-list name
Referring to the prefix list, the network address + subnet mask of the BGP route is checked.
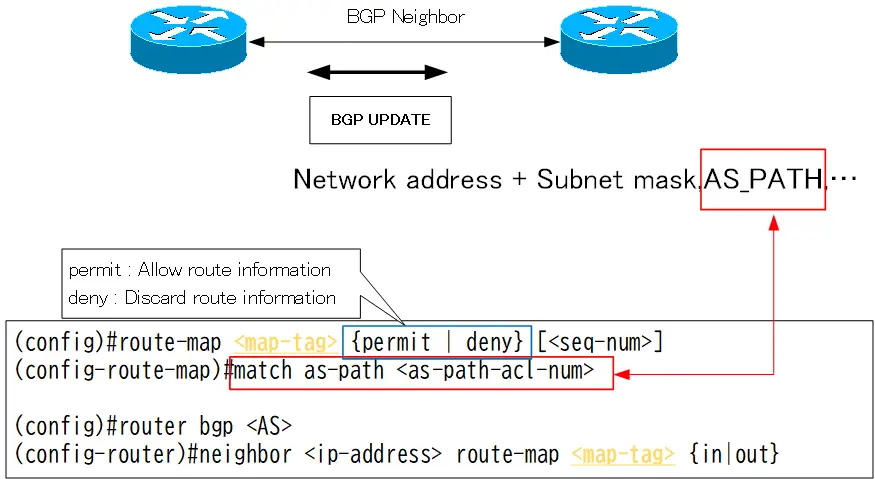
match condition AS_PATH ACL
The configuration for referencing AS_PATH ACL in the route-map’s match condition is as follows.
route-map match condition AS_PATH ACL
(config)#route-map <mat-tag> {permit | deny} [<seq-num>]
(config-route-map)#match as-path <as-path-acl-num>
<as-path-acl-num> : AS_PATH ACL number
AS_PATH ACLs are referenced to check the AS_PATH attribute of the BGP route.
set <action>
In addition to filtering BGP routes, additional path attributes can be set by configuring set . set <action> sets the path attribute of the permitted BGP routes
The main set associated with the set of BGP path attributes is summarized in the table below.
| set <action> | Overview |
|---|---|
| set weight | Set WEIGTH. |
| set local-preference | Set LOCAL_PREF. |
| set origin | Set ORIGIN. |
| set ip next-hop | Set NEXT_HOP. |
| set metric | Set MED. |
| set as-path prepend | Prepend to AS_PATH. |
| set community | Set COMMUNITY. |
| set extcommunity | Set extended COMMUNITY. |
Implicit deny
There is an implicit deny in route-map as well as in the standard/extended ACL, prefix-list, and AS_PATH ACL. Note that if there is only a condition for a sequence of deny, all BGP routes will eventually be denied by implicit deny.
Re-send/Re-recieve BGP routes
Simply applying route-map to a neighbor does not make the route filter work. BGP routes must be re-sent/received. Re-send or re-receive, depending on the direction in which filter-list is applied. Use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode.
Re-send/Re-recieve BGP routes
#clear ip bgp <ip-address> {in|out}
<ip-address> : Neighbor IP address
Verifycation Commands for BGP route filter using route-map
The following table summarizes the main show commands for verifying BGP route filtering by route-map.
| Commands | Overview |
|---|---|
| #show route-map | Verify the route-map to identify BGP routes. Also verify the standard/extended ACLs, prefix-list, and AS_PATH ACLs referenced in the route-map. |
| #show ip protocols | Verify the route-map applied to the BGP neighbor. |
| #show ip bgp | Verify the BGP table. |
| #show ip bgp neighbor advertised-routes | Verify the BGP routes to be advertised to the specified BGP neighbor. |
| #show ip bgp neighbor routes | Verify BGP routes received from the specified BGP neighbor. |
Summary
Point
- The configuration flow for filtering BGP routes using route-map is as follows.
- Identify route information to be filtered by route-map
- Applying route-map to a specific neighbor
- Re-sent/Re-recieve BGP routes
- Identify BGP routes to filter by referencing standard/extended ACLs, prefix-lists, AS_PATH ACLs, etc. in route-map match conditions.
- How BGP routes that meet the match condition are treated is permit | deny after .
Related article
The following article provides a detailed configuration example of BGP route filter using route-map.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation