Table of Contents
Overview
The aggregate-address command for aggregating BGP routes on Cisco routers has many options. The options are divided into two categories.
- What to do with the attributes of the aggregate route
- How to handle pre-aggregation routes
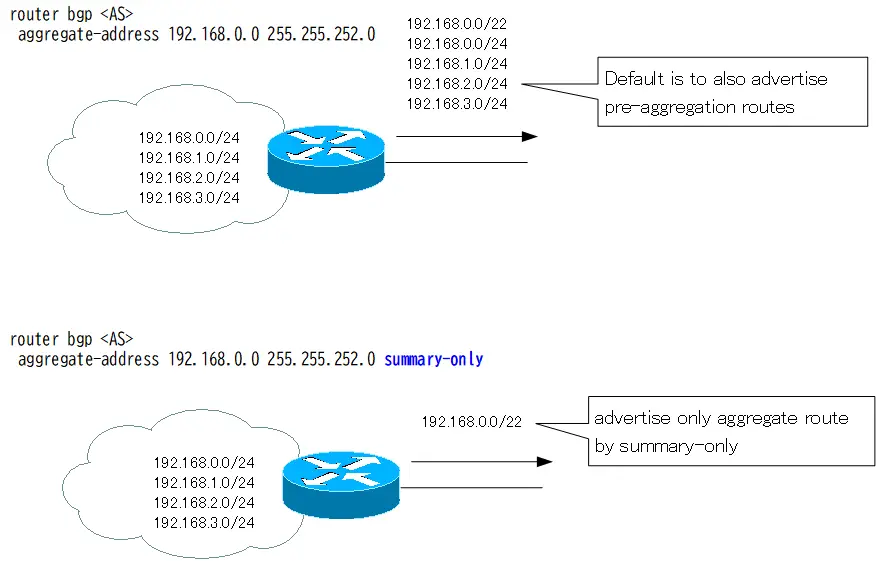
The summary-only option is an option regarding “how to handle routes pre-aggregation”. The option summary-only advertises only aggregate route. This section describes the summary-only option in more detail.
aggregate-address command : summary-only option
If aggregate route is simply generated with the aggregate-address command, all routes within the range of the aggregate route will also be advertised. Normally, aggregating routes results in fewer routes being advertised because only aggregated route is advertised. However, by default, BGP does not reduce the number of routes advertised even after aggregation.
The summary-only option is used when you want to advertise only aggregate route without advertising routes within the range of the aggregate route. By adding the summary-only option, you can advertise “aggregate route only,” as the name implies.
The commands when using the summary-only option are as follows
aggregate-address summary-only
(config)#router bgp <AS>
(config-router)#aggregate-address <network-address> <subnetmask> summary-only
<AS> : AS number
<network-address> : Network address of the aggregate route
<subnetmask> : Subnet mask of the aggregate route
When the summary-only option is configured, the entry for the pre-aggregation route will be displayed as “s” in the BGP table. The “s” stands for suppressed, meaning that the route is not advertised.
Example of BGP table with summary-only configuration
R1#show ip bgp BGP table version is 83, local router ID is 192.168.123.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 123.1.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i s> 123.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Configuration example of aggregate-address summary-only option
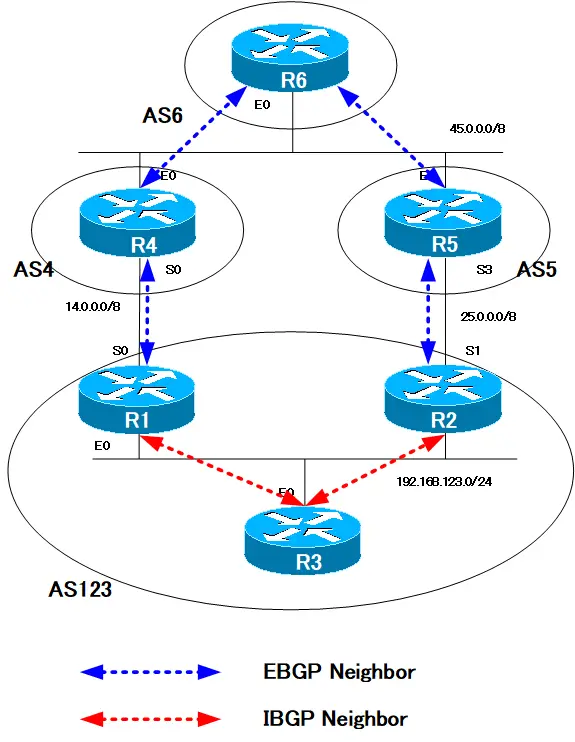
Network diagram and initial configuraiton
Configure the aggregate-address summary-only option on R1 with the following network diagram.
The BGP-related configuration on R1 prior to configuring aggregate-address is as follows.
R1 Initial Configuration
interface Loopback0 ip address 123.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.5.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.6.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.7.1 255.255.255.0 secondary ip address 123.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 123 neighbor 14.0.0.4 remote-as 4 neighbor 192.168.123.3 remote-as 123 network 123.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.5.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 123.1.7.0 mask 255.255.255.0
R1 is configuring BGP neighbors and generating BGP routes 123.1.1.0/24 through 123.1.7.0/24 with the network command. A number of secondary addresses are configured on the Loopback0 interface to advertise routes.
Normal aggregation configuration without summary-only
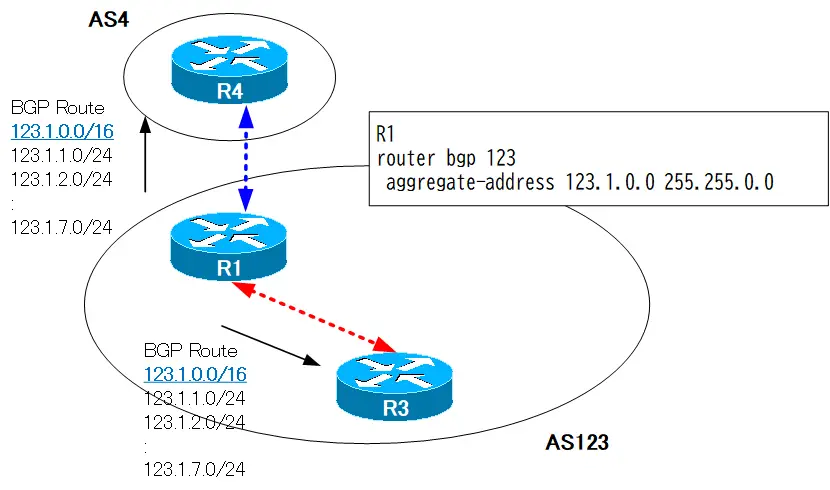
First, configure normal aggregation configuration, i.e., the aggregate-address command without options. Aggregate the 123.1.x.x routes of AS123 and advertise them as 123.1.0.0/16. The router to advertise is R1.
R1 aggregate-address
router bgp 123 aggregate-address 123.1.0.0 255.255.0.0
This command generates an aggregate route, which is placed in R1’s BGP table and advertised to the neighbor. Without the summary-only option, the pre-aggregation routes are advertised together. To verify this, look at the BGP table.
R1 show ip bgp
R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 72, local router ID is 192.168.123.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 123.1.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i *> 123.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.5.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i *> 123.1.7.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
Verifying the BGP table, the aggregate route 123.1.0.0/16 is generated and advertised to the neighbor as the best path. At the same time, the pre-aggregation routes 123.1.1.0/24 to 123.1.7.0/24 are also advertised.
aggregate-address command with summary-only option
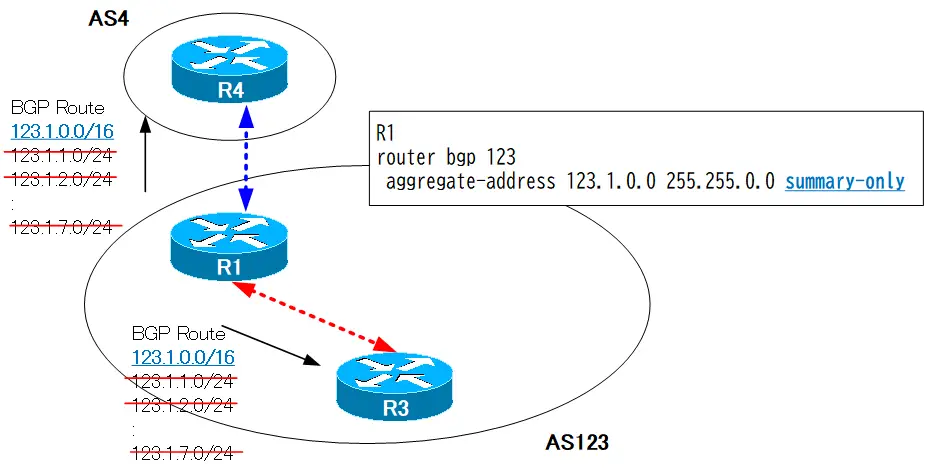
As described above, when aggregate route is generated by the aggregate-address command as usual, all routes before aggregation are also advertised. The summary-only option is used when you want to advertise only aggregate route, without advertising the pre-aggregate route.
R1 aggregate-address summary-only
router bgp 123 aggregate-address 123.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only
This configuration changes the advertisement to only aggregate routes. The BGP table on R1 looks like this.
R1 show ip bgp
R1#sh ip bgp BGP table version is 83, local router ID is 192.168.123.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 123.1.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i s> 123.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.5.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s> 123.1.7.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
The entries for pre-aggregation routes 123.1.1.0/24 through 123.1.7.0/24 are now prefixed with an “s”.The “s” stands for “suppressed.In other words, the pre-aggregation routes are no longer advertised.
Summary
Points
- summary-only is an option for how to handle pre-aggregation routes.
- Summary-only does not advertise pre-aggregation routes, only aggregate route.
How the BGP works
- BGP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- BGP Neighbor Status
- BGP Neighbor Authentication
- BGP Well Known Mandatory Attributes
- Illustration: BGP Best Path Selection
- BGP KEEPALIVE timer/Hold time Configuration
- BGP Route Minimum Advertisement Interval Configuration
- BGP Route Dampening
- BGP Route Filter Overview
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list
- BGP Route Filter : distribute-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list
- BGP Route Filter : prefix-list Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL)-
- BGP Route Filter : filter-list(AS_PATH ACL) Configuration Example
- BGP Route Filter : Route-map
- BGP Route Filter : route-map Configuration Example
- BGP neighbor allowas-in command
- BGP neighbor as-override command
- BGP Route RIB Failure
- BGP Route Administrative Distance Adjustment
- BGP Route Load Balancing
- BGP Auto Summary
- BGP Route Summary : network command
- BGP Route Summarization : network command configuration example
- BGP Route Summary aggregate-address command
- aggregte-address command : summary-only opiton
- aggregte-address command : attribute-map opiton
- aggregte-address command : as-set opiton
- aggregte-address command : advertise-map opiton
- BGP Selective Aggregation Overview
- BGP Selective Aggregation : suppress-map
- BGP Selective Aggregation : unsuppress-map
- BGP local-as
- BGP neighbor remove-private-AS
- bgp fast-external-fallover
- BGP Prefix Limitation