Table of Contents
Overview
This section covers commands for configuring and verifying VRRP with Cisco IOS. In addition to basic configuration, it covers configuration commands for tracking interfaces.
Related article
The following article explains in detail how VRRP makes the default gateway redundant.
Basic VRRP Configuration
The configuration procedures and commands for VRRP are very similar to those for HSRP; the basic VRRP configuration is as follows
- Configure virtual router ID and virtual IP address
- Configure VRRP priority
The commands for each procedure are explained in the following sections.
Configure virtual router ID and virtual IP address
VRRP is enabled on the interface that, like HSRP, acts as the default gateway. Configure the virtual router ID and virtual IP address with the following commands
(config-if)#vrrp <virtual-router-id> ip <ip-address>
<virtual-router-id> : Virtual Router ID. 1~255
<ip-address> : IP address of Virtual router
The virtual router ID and the IP address of the virtual router should be configured the same on each router as for HSRP.
Note that for Layer 3 switches, this is configured in the SVI/routed port interface configuration mode.
Configure VRRP priority
The master router is determined by priority. Configure higher VRRP priority for the router you want to be the master router. To configure VRRP priority, use the following command in interface configuration mode.
(config-if)#vrrp <virtual-router-id> priority <priority>
<virtual-router-id> : Virtual Router ID. 1~255
<priority> : VRRP priority. 1~255
Extended object tracking (local interface) configuration
As with HSRP, the state of the local interface can be tracked to switch master routers. However, the configuration is to define the object tracking configuration. Define a local interface as the object to be monitored.
To monitor the state of the local interface as extended object tracking for VRRP, follow the steps below.
- Definition of the object that determines the interface to be monitored
- Decrement value of priority when object is down
Definition of the object that determines the interface to be monitored
First, define the object that determines the interface to be monitored. Enter the following command in global configuration mode
(config)#track <object-id> interface <interface-name> line-protocol
<object-id> : object ID
<interface-name> : interface name to be monitored
Decrement value of priority when object is down
Associate VRRP with an object. At that time, configure how many priorities are decremented when the object is down. Enter the following command in interface configuration mode for an interface with VRRP enabled
(config-if)#vrrp <virtual-router-id> track <object-id> [decrement <priority>]
<virtual-router-id> : 仮想ルータID
<object-id> : Associated object number
<priority> : Decrement value of priority
After decrement, it can be omitted. In VRRP, preempt is enabled by default, so there is no need to explicitly enable preempt.
Related article
For more information on configuring extended object tracking to monitor routing table status, please see the following article.
VRRP verification commands
The following commands are mainly used to verify VRRP operation.
| show command | Contents |
|---|---|
| #show vrrp brief | Verify summary information such as master router, backup, and virtual IP addresses. |
| #show vrrp | In addition to the information that can be verified with show vrrp brief, detailed information including VRRP timers and virtual MAC addresses are also available. |
| #show track | Verify information on monitored objects when performing extended object tracking. |
VRRP Configuration Example
VRRP is used to provide redundant default gateways for R1/R2 in the following network diagram.
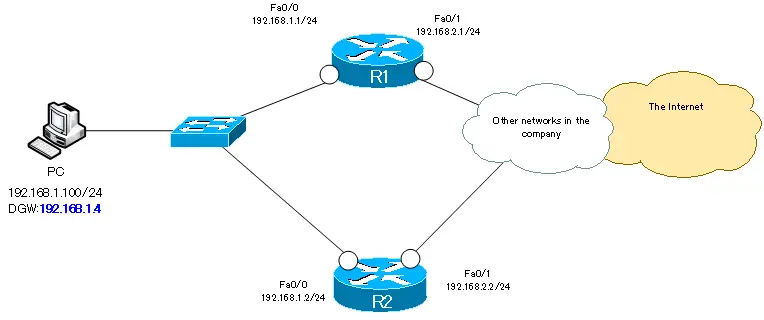
- Specify 192.168.1.4 as the default gateway for the PC
- R1 to act as master router
- Switch active router to R2 when R1 Fa0/1 is down
Configuration
Basic Configuration
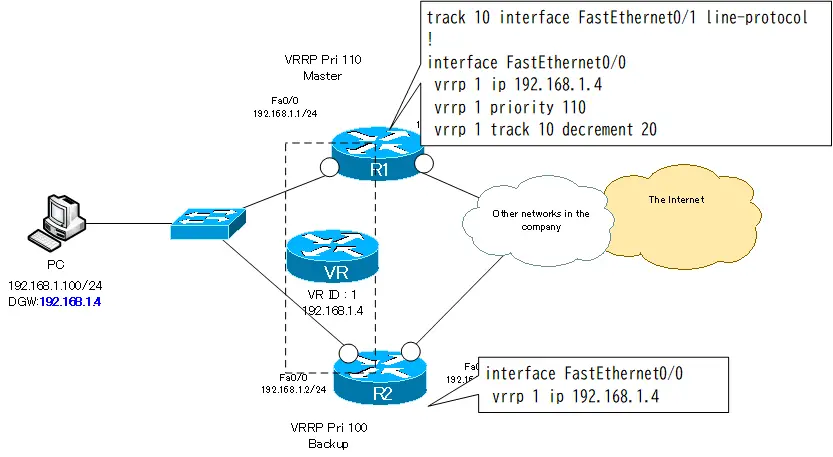
Since the default gateway of the PC is 192.168.1.4, we use 192.168.1.4 as the IP address of the virtual router. The virtual router ID is configured as 1. To make R1 the master router, the Priority is assigned to 110, which is greater than the default.
R1
interface FastEthernet0/0 vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.4 vrrp 1 priority 110
R2
interface FastEthernet0/0 vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.4
Extended Object Tracking Configuration(Monitoring R1 Fa0/1)
Also, define an object to monitor R1 Fa0/1 on R1 and associate it with VRRP. If the object goes down, reduce the priority by 20 so that R2 has a larger priority.
R1
track 10 interface FastEthernet0/1 line-protocol ! interface FastEthernet0/0 vrrp 1 track 10 decrement 20
Verification
show vrrp brief
The output of the show vrrp brief command on R1 appears as follows
R1
R1#show vrrp brief Interface Grp Pri Time Own Pre State Master addr Group addr Fa0/0 1 110 3570 Y Master 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.4
From the output of show vrrp brief, we can see that R1 is the master router for virtual router ID 1. The IP address of the virtual router is 192.168.1.4.
show vrrp
For more detailed VRRP status, verify the show vrrp command; the display on R1 is shown below.
R1
R1#show vrrp
FastEthernet0/0 - Group 1
State is Master
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.4
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 110
Track object 10 state Up decrement 20
Master Router is 192.168.1.1 (local), priority is 110
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.570 sec
From the output of show vrrp, we can see that the virtual MAC address is “00-00-5e-00-01-01”. And the object with object number 10 is being tracked, and its current state is “Up”.
Also, the interval between VRRP Advertisement transmissions is 1 second. If the next VRRP Advertisement does not arrive within 3.570s, the master router is considered down.
show track
The show track command on R1 displays the following
R1
R1#show track
Track 10
Interface FastEthernet0/1 line-protocol
Line protocol is Up
1 change, last change 00:19:39
Tracked by:
VRRP FastEthernet0/0 1
We can see that it is monitoring the status of Fa0/1. We can also see that it is associated with VRRP virtual router ID 1 on Fa0/0.
Switching the master router
Verify the behavior of object tracking on R1. After shutting down the monitored Fa0/1, the show track and show vrrp commands should look like this
R1
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1
R1(config-if)#shutdown
R1(config-if)#do show track
Track 10
Interface FastEthernet0/1 line-protocol
Line protocol is Down (hw admin-down)
2 changes, last change 00:00:15
Tracked by:
VRRP FastEthernet0/0 1
R1(config-if)#do show vrrp
FastEthernet0/0 - Group 1
State is Backup
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.4
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 90 (cfgd 110)
Track object 10 state Down decrement 20
Master Router is 192.168.1.2, priority is 100
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.570 sec (expires in 3.306 sec)
When R1 Fa0/1 is shutdown, object 10 becomes Down and R1’s VRRP priority decreases by 20. As a result, R1 is the backup router because it has a smaller priority than R2.
IP Routing Basic
- Router – The central device that performs routing
- Dividing Network with router
- Layer3 Switch Overview
- Measuring the distance to the destination network -Administrative Distance and Metric
- Equal Cost Multi Path Load Balancing
- Cisco Static Route Configuration
- Example of Cisco Static Route Configuration Step by Step
- RIP Split horizon
- RIP Timers
- RIP Route Poisoning – Quickly remove unnecessary route information
- Cisco RIP Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Cisco RIP Configuration Example
- Generating a default route in RIP – Redistribution of static route
- Passive-Interface ~Stops Routing Protocols from Sending Packets
- Default Gateway Redundancy Overview
- How the Cisco HSRP works
- Configuring and Verifying Cisco HSRP
- How VRRP works
- Configuring and Verifying commands for VRRP [Cisco]