Table of Contents
Command Type
There are two main types of commands on Cisco devices
- configuration commands
- exec commands
The configuration command is a command that is added to running-config to configure the IP address and host name of the Cisco device.
You can use the exec command to check the behavior and status of your Cisco devices. ping and traceroute commands to see if they can communicate, and the show command to check the status of your Cisco devices. You can also use the debug command to check the behavior of Cisco devices in real time. However, although the debug command allows you to check the behavior of a Cisco device in detail, it places a heavy load on the device, so you must be careful when using it.
It’s pretty obvious, but it’s important to note that various commands can be classified into these two types. And in order to use the two types of commands properly, you need to understand the modes in the CLI of your Cisco device.
Types of CLI modes
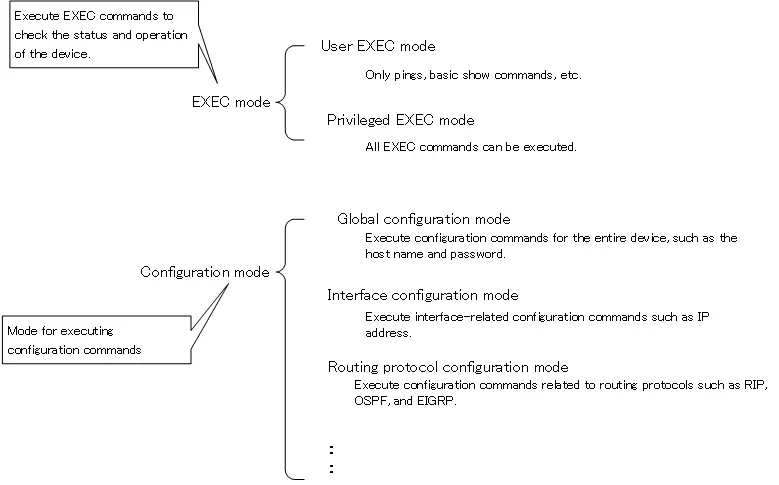
The CLI on Cisco devices offers two modes, depending on the commands that can be executed.
- EXEC mode
- configuration mode
EXEC mode is for executing EXEC commands. Depending on the privileges of the command to be executed, there are two modes: user EXEC mode and privileged EXEC mode.
In user EXEC mode, only a limited number of exec commands, such as ping, can be executed in user EXEC mode. The show running-config command to show running-config cannot be executed in user EXEC mode. Privileged EXEC mode is the so-called administrative privileges and allows all EXEC commands to be executed.
Configuration mode is a mode for executing configuration commands. The configuration mode is further subdivided into the following modes, depending on what configuration commands you want to execute on the Cisco device.
- global configuration mode
- interface configuration mode
- routing protocol configuration mode
- Various other configuration modes
Global configuration mode is the mode in which configuration commands related to the entire Cisco device are executed. For example, commands for setting the hostname and privileged EXEC mode password are executed in global configuration mode. Global configuration mode is also the starting point for all configuration modes.
Interface configuration mode is the mode for executing configuration commands related to the interface, such as setting an IP address for the interface.
And routing protocol configuration mode is the mode for executing configuration commands related to routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP.
Navigating the CLI mode
When you connect the console to a Cisco device and launch the terminal software, the first thing you see is the following
Router con0 is now available Press RETURN to get started.
Press the [Enter] key to log in, initially in user EXEC mode. In user EXEC mode, you will see a “>” at the prompt waiting for a command.
Router>
To go from user EXEC mode to privileged EXEC mode, type “enable”.
Router>enable Router#
You will see a “#” at the prompt, indicating that you are in privileged EXEC mode.
Then type “configure terminal” to go from privileged EXEC mode to global configuration mode.
The prompt will read “(config)#”, indicating that you have entered global configuration mode. You will also see the message “Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.”.
Router#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router(config)#
To go from global configuration mode to interface configuration mode, type “interface “. As an example, to go to interface configuration mode for an interface named FastEthernet0/0, this would look like this
Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)#
From the “(config-if)#” prompt, you can see that we are entering interface configuration mode.
You can also type “router < routing-protocol >” to go from global configuration mode to routing protocol configuration mode.When you move into RIP routing protocol configuration mode, type “router rip”.
Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#
The prompt “(config-router)#” tells you that you are in routing protocol configuration mode.
Entering “exit” from interface configuration mode or routing protocol configuration mode will return you to global configuration mode. Alternatively, you can type “end” to return to privileged EXEC mode.
Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)#exit Router(config)#
Router(config)#router rip Router(config-router)#end Router#
The following diagram summarizes the transition to CLI mode.
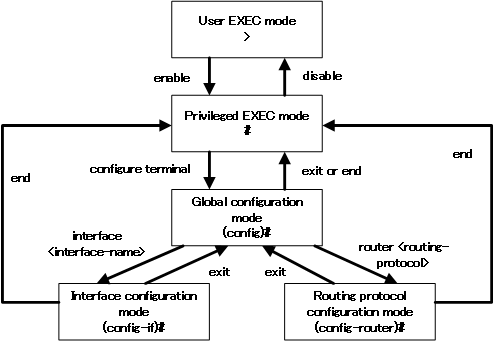
CLI modes are the basis for dealing with Cisco devices. Make sure you understand the meaning and transition of each CLI mode.
Note that it is not necessary to go back to global configuration mode to migrate to configuration mode. For example, you can go directly from interface configuration mode to routing protocol configuration mode as follows
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 R1(config-if)#router rip R1(config-router)#
Cisco Basic
- Preparing for Cisco devices configuration
- Configuration files for Cisco devices
- The configuration steps for Cisco devices
- Basic knowledge of the Cisco CLI: Command types and modes
- Cisco device’s interface
- CLI help and completion
- The main error messages in CLI
- Cisco Deleting a configuration command
- default interface command -Initialize the interface settings-
- Entering commands in batches
- do command – Execute EXEC command from configuration mode –
- interface range command -Batch configuration of multiple interfaces-
- Filtering the display of the show command – displaying only the information you want to see –
- Cisco IOS Name Resolution Configuration
- terminal length command : configuration of the number of lines displayed in the command output
- debug command to verify real-time operation
- Automatically enter privileged EXEC mode upon CLI login
- Configure System Clock
- Saving and managing configuration files
- Version Management of Configuration Files ~archive command
- IOS File System Operations
- Managing Cisco Catalyst Switches :What it means to set an IP address on a switch.
- Remote management by VTY access (Telnet/SSH)
- terminal monitor command to display the log of Telnet/SSH login destination
- Multi-step Telnet Session Suspensions
- Set the minimum number of characters in the password [Cisco]
- Restrict login attempts : login block-for command
- Cisco Initial Configuration Example
- CDP – What are the connected devices? –
- Password recovery for Cisco routers
- Password Recovery for Catalyst Switches