Table of Contents
VTP Overview
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for synchronizing VLAN configuration between switches. Cisco maintains VLAN configuration information in a VLAN database. VTP is a protocol that synchronizes the VLAN database between switches, so that when a VLAN is created on one switch, it is automatically created on the other switches.
There are two major steps in the VLAN configuration process.
- Create VLAN
- Port assignment
Related article
For more information on the VLAN configuration and verification commands, please refer to the following article.
Using VTP can simplify the step 1. There is no need to create VLANs on each switch. Note that VTP not only creates VLANs, but also synchronizes VLAN name changes and VLAN deletions between switches. The range in which VLAN configuration is synchronized by VTP is called the VTP domain. In order to synchronize VLAN configuration between switches using VTP, it is assumed that the switches are connected by trunk links.
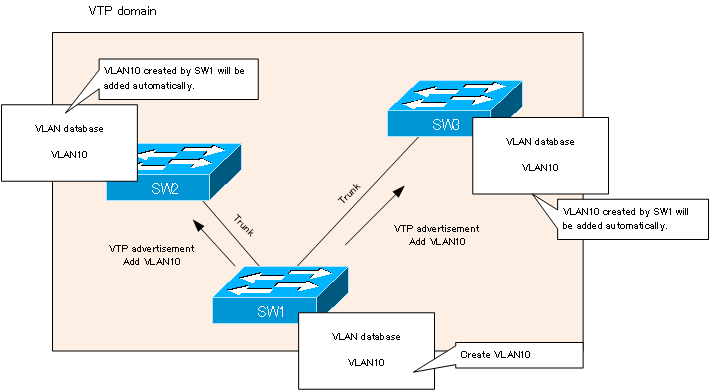
Note that VTP only synchronizes the VLAN configuration. You still need to configure the access port or trunk port on each switch to assign ports to VLANs.
VTP Mode
There are three modes of operation for VTP
- Server(default)
- Client
- Transparent
The operation of each mode of VTP can be summarized in the table below.
| Create, modify, and delete VLANs | Generating Advertisement | Forwarding Advertisements | synchronization | |
| Server | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Client | × | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Transparent | ○ | × | ○ | × |
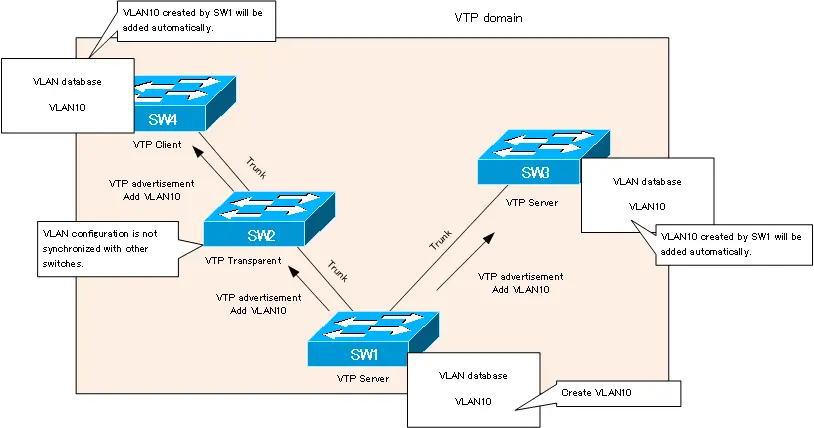
VTP Server mode
A switch in VTP server mode can create, modify, and delete VLANs common to a VTP domain. When any VLAN configuration is changed, a VTP advertisement is generated and sent to other switches. VTP advertisements are also sent at regular intervals (default 300 seconds).
When it receives a VTP advertisement from another switch, it synchronizes the VLAN configuration and forwards to other switch.
VTP Client mode
A switch in VTP client mode cannot create VLANs by itself. The client mode is used to synchronize the VLAN configuration with the VLAN configurationof the switch in the server mode; when a VTP advertisement is received, the VLAN configuration is synchronized and forwarded to other switch.
VTP Transparent mode
The VTP transparent mode switch is a mode that deviates from the original purpose of VTP. The VLAN configuration is not synchronized with other switches. A switch in VTP transparent mode can create , change , delete VLAN locallyWhen using VLAN numbers after 1006, you need to set VTP transparent mode.. Switches in VTP transparent mode will not keep VLAN configuration information in the VLAN database, but will keep the VLAN configuration commands on running-config and startup-config. When using VLAN IDs after 1006, you need to configure VTP transparent mode.
When a VTP advertisement is received from another switch, it is further forwarded to another switch. Therefore, even if there is a switch in transparent mode in between, it will not affect the synchronization of the VLAN configuration of the other switches.
Configuration revision number
The parameter that indicates the newness of the VLAN configuration for VTP advertisement is the configuration revision number. Each time the VLAN database is changed by the VTP server, such as creating, changing, or deleting VLAN, the configuration revision number is increased by one. The higher the configuration revision number, the more newer the VLAN configuration is.
Note that the VTP transparent mode switch does not have a VLAN database, so the configuration revision number is meaningless and the value is 0.
When adding a new switch to an existing network, a large configuration revision number can cause problems. When an existing switch synchronizes with the VLAN database of a newly added switch, the VLANs that are originally required may be deleted. When you add a new switch, put it in transparent mode and clear the configuration revision number.
VLAN(Virtual LAN)
- The need to divide the network
- Details of dividing the network
- VLAN Overview
- VLAN behavior
- Access port : Port assigned to only one VLAN
- Trunk port : Port assigned to multiple VLANs
- Summary of Trunk Protocols – IEEE802.1Q and ISL
- Native VLAN
- Specific example of native VLAN mismatch
- Cisco DTP
- Cisco Configuring and Verifying VLAN
- Cisco VLAN Detailed Configuration Example
- Notes on deleting VLANs
- Voice VLAN – VLAN for connecting IP phones
- VTP :Synchronize VLAN configuration
- VTP pruning – Stopping unnecessary flooding of trunk links
- Configuring and Verifying Cisco VTP
- Inter VLAN routing overview
- Inter-VLAN routing by router
- Inter-VLAN routing by Layer 3 switch
- Configuring and Verifying Inter-VLAN Routing by Cisco Router
- Cisco Configuring Inter-VLAN routing by Layer3 switch : SVI/routed port
- Cisco Layer3 Switch Basic Configuration Example
- Summary of Layer 3 Switch Port Concepts – Access Port/Trunk Port/SVI/Routed Port
- LAN Design pattern : 2-tier and 3-tier