OSPF Router Type
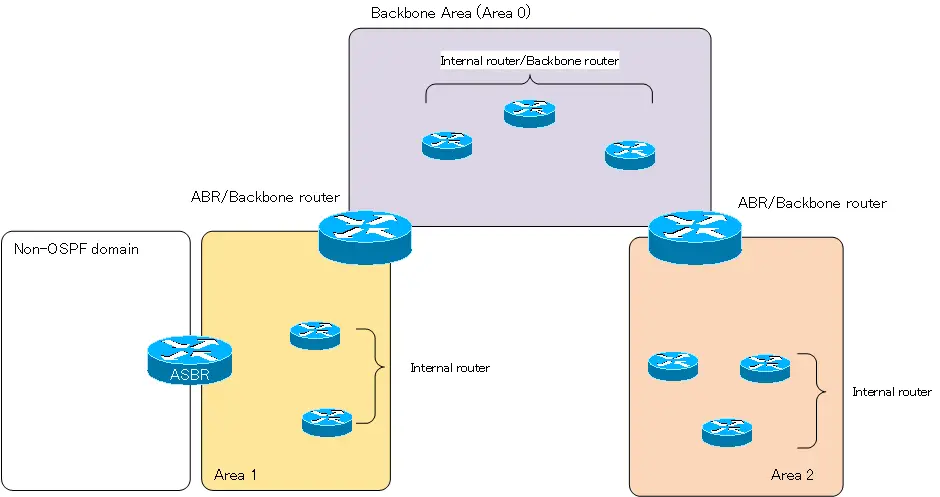
By dividing the OSPF network into areas, the OSPF routers contained in each area and the routers connecting between areas can be classified as follows
- Internal Router
- Backbone router
- Area Border Router : ABR
- Autonomous System Boundary Router : ASBR
Internal Router
A router in which all interfaces belong to the same area is called an internal router. A router whose all interfaces belong to the backbone area is both a backbone router and an internal router.
Backbone router
A router that has at least one interface that belongs to a backbone area is called a backbone router. Area border routers are also backbone routers, as they connect the backbone area to other areas.
Area Border Router : ABR
A router that has interfaces that belong to multiple areas and interconnects the areas is called an area border router (ABR). ABR has a link state database for each area, and exchanges link state information for each area. Each area must, in principle, be adjacent to the backbone area, which means that the ABR maintains separate link-state databases for the backbone area and for the other areas. The ABR is also both an exit and an entrance to an area. The ABR plays a very important role in the advertisement of OSPF route information and the actual packet forwarding.
In addition, ABR can perform route summary.
Related article
Please see the following article about route summary on ABR.
Autonomous System Boundary Router : ASBR
Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) are routers located at the boundary between a network that performs routing with OSPF (OSPF domain) and a network that performs non-OSPF routing such as static routes, RIP/EIGRP/BGP (non-OSPF domain).
ASBRs are routers that are configured to redistribute from non-OSPF routing processes to OSPF. Note that since the communication is bi-directional, the ASBR also needs to redistribute OSPF routes to non-OSPF domains.
Related article
The following article explains more about redistribution.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]