Table of Contents
Problems with large-scale OSPF network
OSPF is a type of IGPs that is used within an AS (Autonomous System), and let’s imagine that the OSPF network within the AS becomes larger and larger, for example, with dozens to hundreds of routers. In such a very large network, the following problems can be considered.
- The number of LSAs flowing on the network will increase, overwhelming the network bandwidth
- The link state database gets larger
- Routing table gets larger
- Increased impact of changes in the network
- Increased memory and CPU load on routers
The number of LSAs flowing on the network will increase, overwhelming the network bandwidth
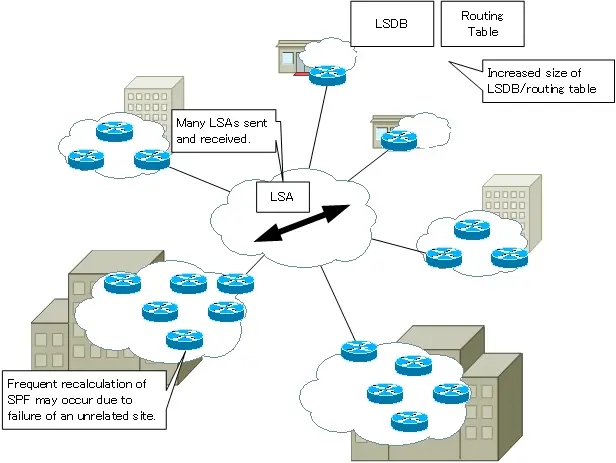
In OSPF, each router exchanges link state advertisement(LSA). Of course, the more routers and the more networks a router has, the more LSAs it will have. Then, the exchange of LSAs will overwhelm the bandwidth of the network considerably.
The link state database gets larger
The increase in the number of LSAs not only overwhelms the bandwidth of the network, but also increases the size of the link state database maintained by each router.
Routing table gets larger
Furthermore, since the routing table is calculated from the link state database according to the SPF algorithm, the size of the routing table will inevitably increase as the size of the link state database increases. Not only that, but it also increases the time required for the SPF algorithm to calculate the routing table.
Increased impact of changes in the network
When there is a change in the network, the router that detects the change must send the change information to other OSPF routers to keep the link state database synchronized across the network. Therefore, a change in one part of the network can affect the entire network. If a situation arises where a certain part of a large network repeatedly goes up and down, each time the LSA is flooded, it will result in a situation where the SPF calculation in the routing table from the link state database will be frequent.
Increased memory and CPU load on routers
SPF calculation places a considerable load on the router’s CPU, so it may become overwhelmed with SPF calculation alone and be unable to perform other processes. A large network consists of a number of sites. In most cases, a network outage in one site has no effect on communications in other sites. However, in a single area, a downed network in one site may cause SPF calculations to be performed on OSPF routers in all sites. During this time, no packets can be routed.
OSPF area division
In order to solve the various problems that can occur in such a large OSPF network, a concept called “area” is very important. By dividing the OSPF network into appropriate areas, OSPF can support large networks.
By dividing the area, LSDB synchronization is maintained with OSPF routers in the same area. And the OSPF router has a detailed understanding of the network diagram in LSDB. By dividing the area, there is a different level of detail to understand the network diagram inside and outside the area. Inside the area, the network diagram will be very detailed. On the other hand, outside the area, only the network address will be known, not the detailed network diagram.
LSAs that describe details in an area are advertised only in the area. This reduces the LSA traffic to be exchanged and also reduces the size of the LSDB and routing table. Then, for changes outside the area, the SPF will not be calculated to reduce the impact of changes in less relevant areas.
Related article
For more information about OSPF areas, please see the following article.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]