Table of Contents
What is Virtual-link?
OSPF virtual link is a virtual area 0 point-to-point link. Virtual link is configured between two ABRs. And the area that the two ABRs that are configuring the virtual link belong to in common is called transit area.
Virtual-link is used in the following cases.
- Virtually connect to area 0
- Integrating Discontinuous Backbone Areas
In the following sections, we will discuss the use of virtual-link.
Usage of Virtual Link : Virtually connect to area 0
The OSPF area must be in two layers, with the backbone area (area 0) at the center. All areas should be connected to area 0. It is an illegal area layout to connect more areas beyond the area other than area 0.
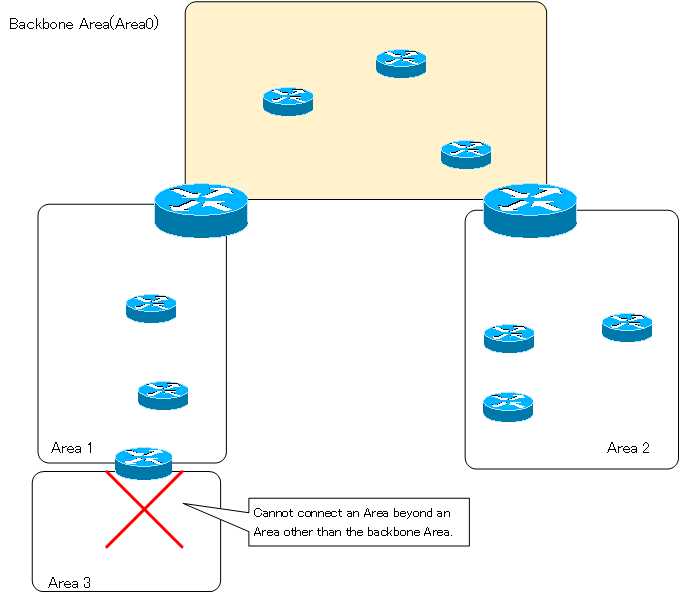
If you are forced to take a illegal area layout where there are areas that cannot be physically connected to Area 0, you can use virtual-link to virtually connect to Area 0.
The following figure shows a virtual connection to Area 0 via a virtual-link.
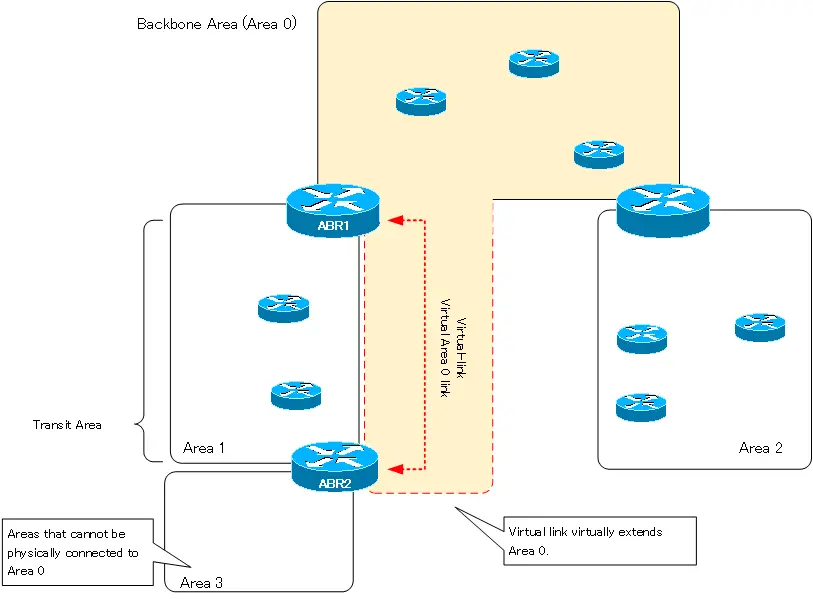
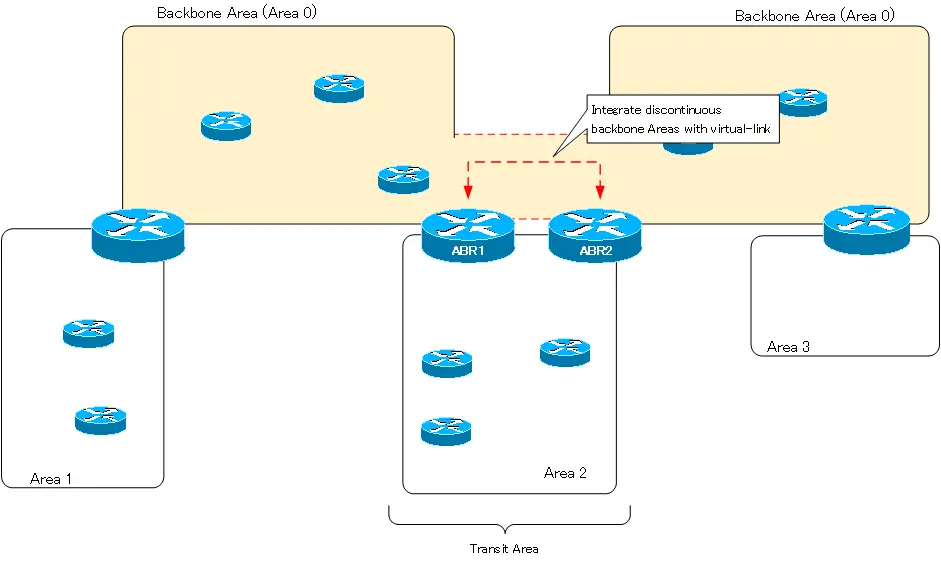
Area 3 is an area that cannot be physically connected to Area 0. The route information of the networks in Area 3 that are not connected to the backbone area will not be advertised to the OSPF domain. Virtual-link is used to ensure that the route information of Area 3 networks can be learned successfully.
Configure a virtual link between ABR1 and ABR2 in the figure; Area 1, to which ABR1 and ABR2 commonly belong, is the transit area of the virtual-link. Then ABR1 and ABR2 will be connected by a virtual area 0 point-to-point link. In other words, Area 0 is extended and Area 3 can be considered as connected to Area 0.
However, the use of virtual-link in such an area layout should be considered as a temporary solution. Eventually, it is better to integrate Area 3 into Area 1 so that the virtual link is not needed.
Usage of Virtual Link : Integrating Discontinuous Backbone Areas
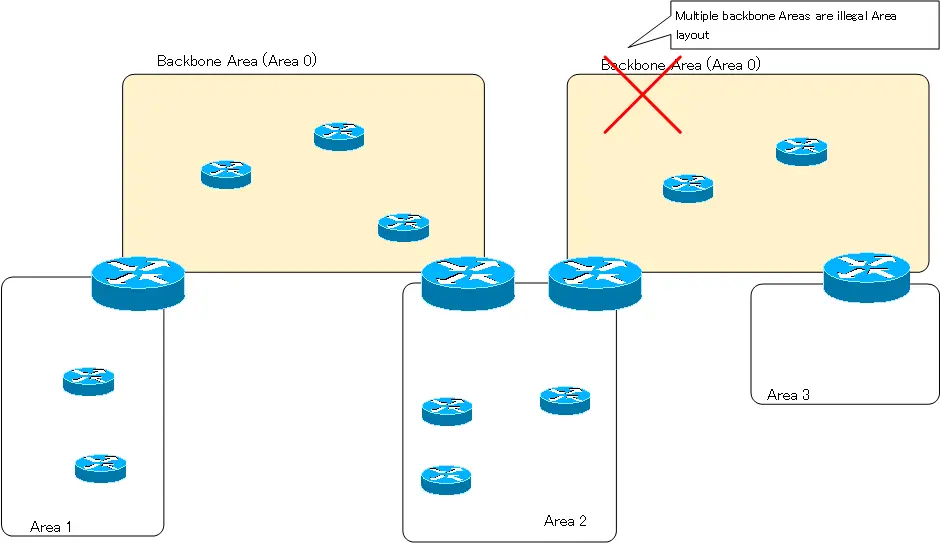
An area layout in which multiple backbone areas (area 0) exist in discontinuity is also an illegal area layout.
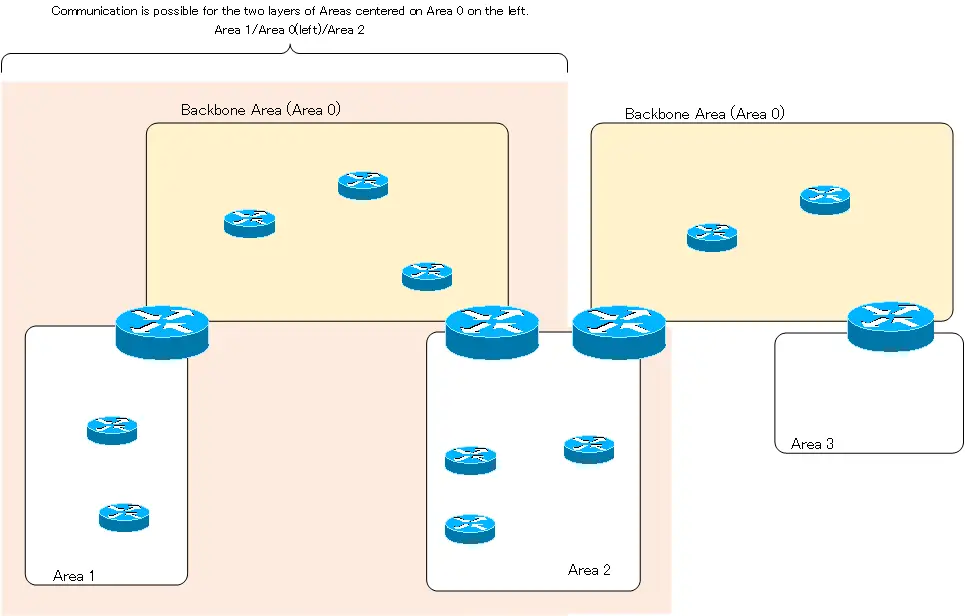
If these backbone areas are discontinuous, communication will be possible in a two-tier area centered on each backbone area. However, the entire OSPF network will not be able to communicate. There is no problem between the two tiered areas with the backbone area on the left. Area 1-Area 0 (left)-Area 2 is reachable. Also, Area 2 – Area 0 (right) – Area 3 around the backbone area on the right can be communicated. However, communication between Area 1 and Area 3 is not possible. Also, communication between Area 0, which is divided, is not possible.
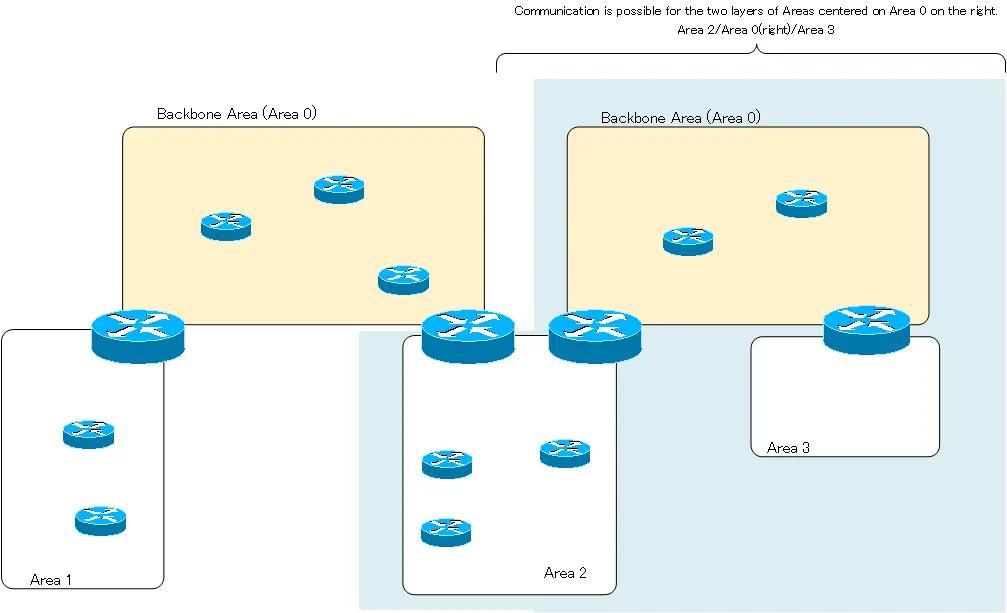
Virtual-link allows integration of discontinuous backbone areas so that they can communicate across the entire OSPF domain.
Summary
Point
- Virtual link is a virtual area 0 point-to-point link.
- Virtual link is configured between two ABRs that belong to a common transit area.
- Usage of virtual-link is the following
- Virtually connect to area 0
- Integrating Discontinuous Backbone Areas
Related article
The following article explains the configuration and verification commands for OSPF virtual-link on Cisco routers.
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]
