Table of Contents
What is Router ID?
The router ID is a 32-bit number that identifies the OSPF router. Just like IPv4 addresses, it’s an 8-bit decimal number separated by “. (dot)” and then write four of them in a row.
The router ID is the name of the OSPF router, so to speak, and a unique router ID is always required for OSPF processing. The router ID recognizes the neighbor. The LSA is also marked with the router ID of the generated router.
How to determine the router ID
The router ID is determined as follows.
- Manual configuration using the router-id command
- Largest IP address of the active loopback interfaces
- Largest IP address of any active interfaces other than loopback
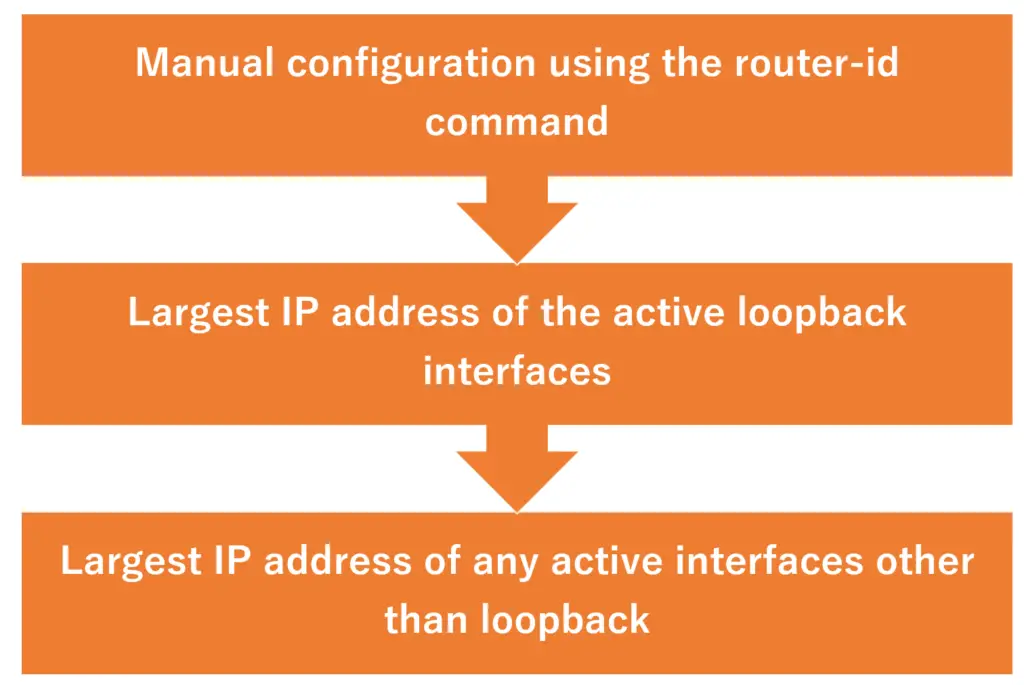
Here’s how to determine the highest priority router IDs, from top to bottom. If the router ID changes, the OSPF process will have to be redone from the establishment of the neighbor. Therefore, the above priority levels are determined so that the router IDs do not change.
Manual configuration using the router-id command
You can set the router ID manually. On Cisco routers, within the OSPF routing process, use the following command to configure the router ID.
(config)#router ospf <process-id>
(config-router)#router-id <router-id>
<process-id> : process ID
<router-id> : Router ID
Make sure that the router ID to be set does not conflict with the router ID of another router. If you set it manually with the router-id command, the router ID will not change unless you change the configuration.
Largest IP address of the active loopback interfaces
The loopback interface is a virtual interface that you create in your configuration. If any one router interface is active, it is a stable interface that will not go down unless you explicitly shutdown it. The IP address of a stable loopback interface can be automatically used as the router ID. You can create multiple loopback interfaces. If there are multiple loopback interfaces, the largest IP address is used as the router ID.
If the router ID is determined from the IP address of the loopback interface, the possibility of the router ID changing depending on the state of a particular interface is reduced. However, if a loopback interface is added later, the router ID may change along with it.
Largest IP address of any active interfaces other than loopback
Creating a loopback interface is optional. For routers that do not have a loopback interface, the maximum IP address of the active interface is used as the router ID.
If the interface of the IP address being used as the router ID goes down, the router ID may change.
Router ID verification (Cisco)
The following are the main show commands for verifying the router ID on a Cisco router.
- show ip protocols
- show ip ospf
- show ip ospf interface
Here is sample output for each show command
show ip protocols
R1#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 1.1.1.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
show ip ospf
R1#show ip ospf
Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 1.1.1.1
Start time: 00:00:02.000, Time elapsed: 00:03:16.636
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Supports area transit capability
Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Incremental-SPF disabled
Minimum LSA interval 5 secs
Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs
LSA group pacing timer 240 secs
Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs
Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs
Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge external and opaque AS LSA 0
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Number of areas transit capable is 0
External flood list length 0
Area BACKBONE(0)
Number of interfaces in this area is 2
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:00:56.772 ago
SPF algorithm executed 4 times
Area ranges are
Number of LSA 3. Checksum Sum 0x01F21D
Number of opaque link LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of DCbitless LSA 0
Number of indication LSA 0
Number of DoNotAge LSA 0
Flood list length 0
show ip ospf interface
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.12.1/24, Area 0
Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State BDR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 2.2.2.2, Interface address 192.168.12.2
Backup Designated router (ID) 1.1.1.1, Interface address 192.168.12.1
Flush timer for old DR LSA due in 00:00:27
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:00
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1
Adjacent with neighbor 2.2.2.2 (Designated Router)
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
How the OSPF works
- OSPF Overview
- OSPF process flow
- OSPF Router ID : Identify OSPF routers
- What if the router ID of the OSPF router is duplicated?
- OSPF Neighbor and Adjacency
- OSPF DR/BDR
- How show ip ospf neighbor looks on Ethernet
- OSPF Network Type : Classification of OSPF-enabled interfaces
- Synchronization process of OSPF LSDB
- Problems with large-scale OSPF network
- OSPF Area – Inside the area, in detail; outside the area, just a summary
- OSPF Router Type
- OSPF LSA Type
- OSPF Area Type
- OSPF Basic Configuration and Verification Commands
- Details of enabling OSPF on the interface
- OSPF Advertising Loopback Interface
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Hello/Dead interval
- OSPF Cost Configuration and Verification
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Router Priority
- Configuring OSPF Neighbor Authentication
- Neighbor Authentication over Virtual-link
- OSPF Configuring and Verifying Stub area [Cisco]
- OSPF Stub Area Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF default route generation : default-information originate command
- Configuration Example of OSPF default route generation : stub area
- OSPF Virtual-Link : Virtual area 0 point-to-point link
- Configuring and Verifying OSPF Virtual-link [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link Configuration Example [Cisco]
- OSPF Virtual-link for discontinuous backbone configuration example
- OSPF Route Summary and Configuration
- Cisco OSPF Route Summary Configuration Example
- OSPF Route Type Preference
- Why the OSPF neighbor state gets stuck in Exstart?
- OSPF packet type and header format
- OSPF Hello Packet
- OSPF DD(Database Description) Packet
- OSPF LSR(Link State Request) Packet
- OSPF LSU(Link State Update) Packet
- OSPF LSAck(Link State Acknowledgement) Packet
- Limitation of OSPF redistribution routes – redistribute maximum-prefix command
- Overview of LSA Filters for OSPF – Filter LSA Type 3/Type 5
- Configuration example of LSA type 3 filter
- Configuration example of LSA type 5 filter
- OSPFv3 Configuration Example [Cisco]
- Configuration Example of OSPFv3 Route Summary [Cisco]
