Table of Contents
What is FRRouting?
Free Range Routing (FRR) is a free and open source routing protocol suit for UNIX/Linux platforms forked from Quagga. FRR implements a variety of routing protocols such as BGP/OSPF/RIP/MPLS. It also supports Cisco’s own EIGRP.
Link
FRRouting Web Site
This article is based on the following article on the GNS3 website. “Create a Router with Docker and Free Range Routing”
You can add an FRR container to GNS3 and use it as a software router. This page explains how to add an FRR container and provides an example of interconnection with a Cisco IOS router.
Note that this article is based on the following environment.
| Host OS | Windows10 Pro |
| GNS3 version | 2.2.17 |
| GNS3 VM version | 2.2.17 |
| Virtualization hypervisor | VMware Workstation 16.6.2 |
How to add FRR containers
The steps to add the FRR container in GNS3 and use it as a software router are as follows.
- Create the FRR Container Template
- Add an FRR container to the project
- Start the FRR container
Create the FRR Container Template
In order to use FRR containers in GNS3, first create a template. Go to [Edit]->[Preference]->[Docker Containers] and click [New].
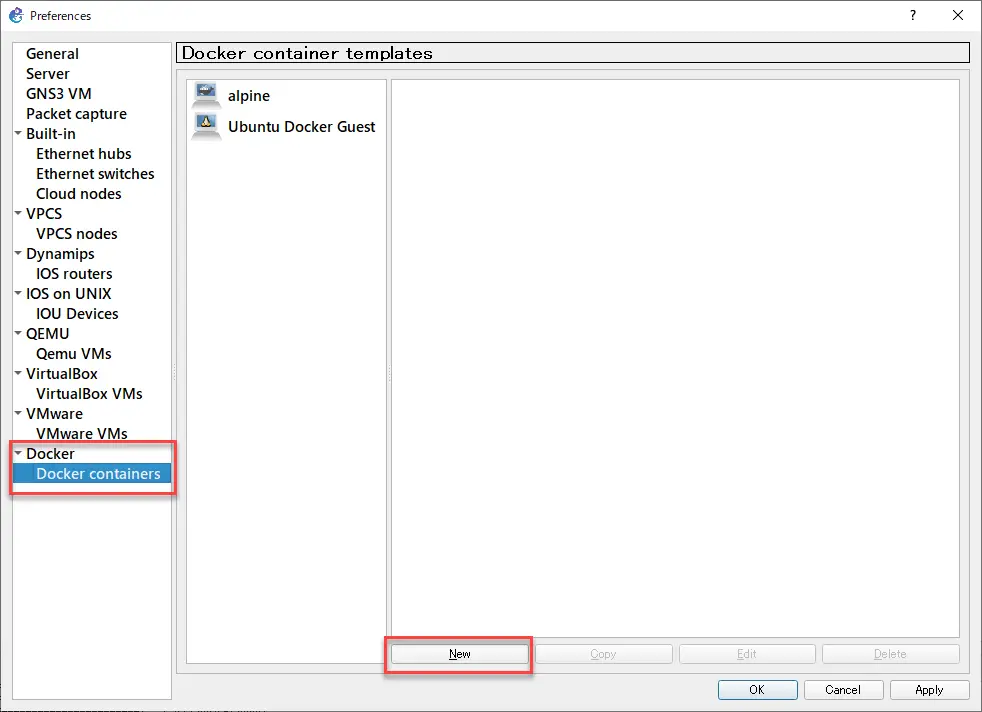
Select [Run this Docker container on the GNS3 VM] and click [Next].
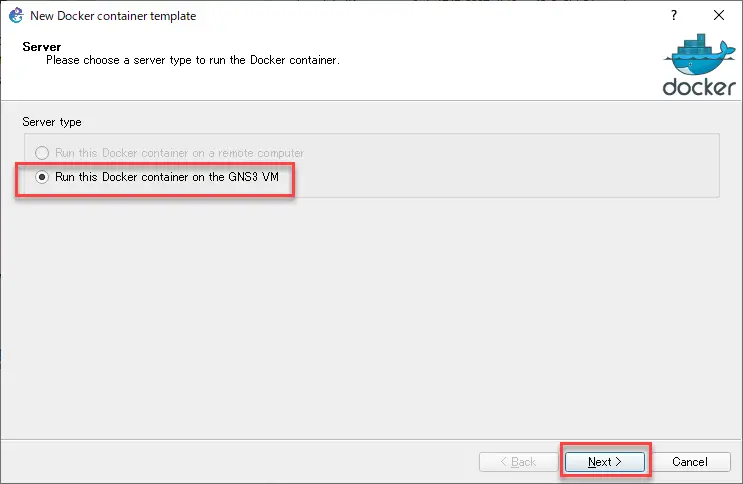
Select [New Image] and enter “frrouting/frr:latest” in the [Image name] field, then click [Next].
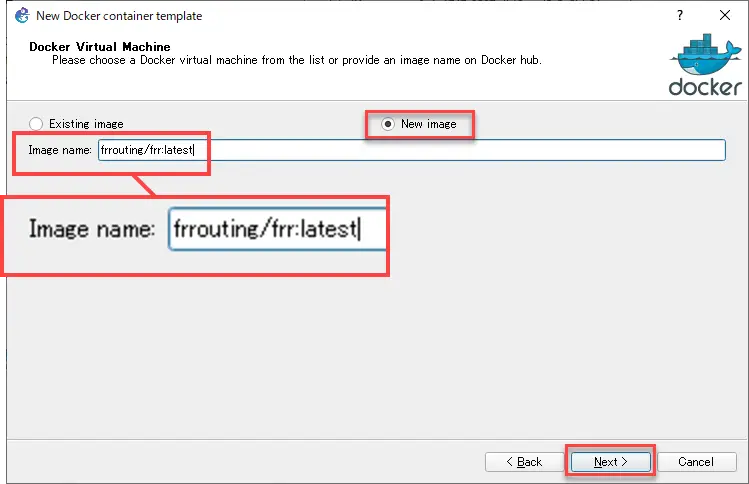
Then, enter the arbitrary display name for the template and click [Next].
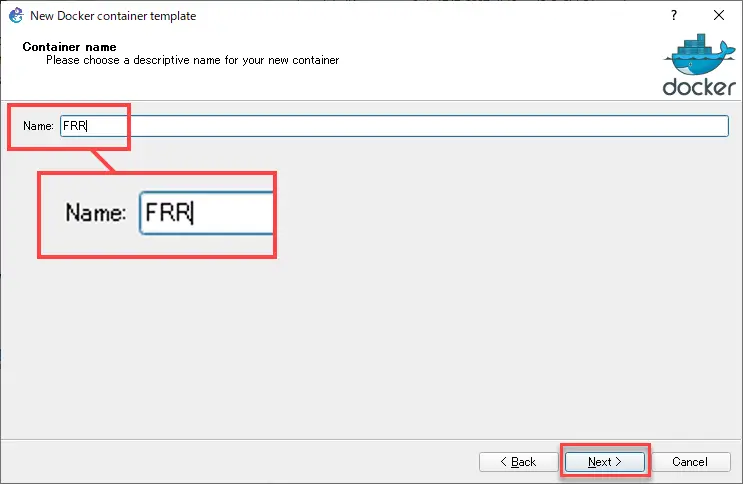
Then, decide on the number of network interfaces (Adapters), and click [Next]. Since we will be using it as a router, we will make it more than two network interfaces.
Enter the command to be executed at startup. Enter “sh” to start a shell.
Specify the console type. You can leave the default “telnet”.
You can specify environment variables if necessary. Click [Finish] to finish creating the template.
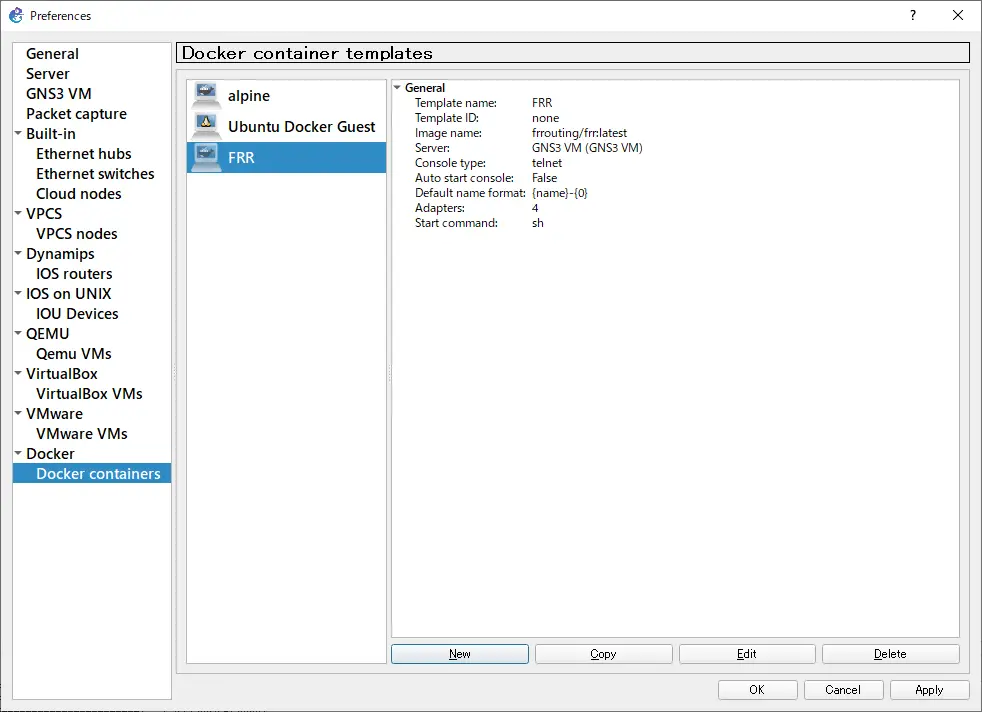
Add an FRR container to the project
Once you have created a Docker container template for FRR, it will appear in the [End Device] toolbar.
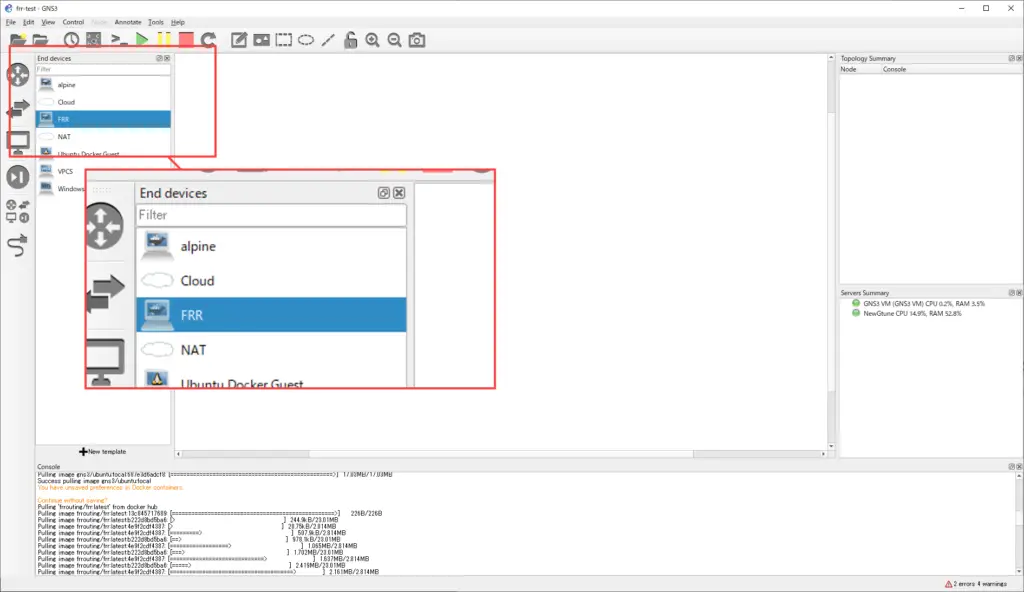
Drag and drop the FRR template onto your workspace. The docker pull command will be automatically executed on the GNS3 VM and the specified container image will be downloaded from Docker Hub to the GNS3 VM. The container image will be downloaded only for the first time, and the log of the docker pull command being executed will be displayed on the GNS3 console.
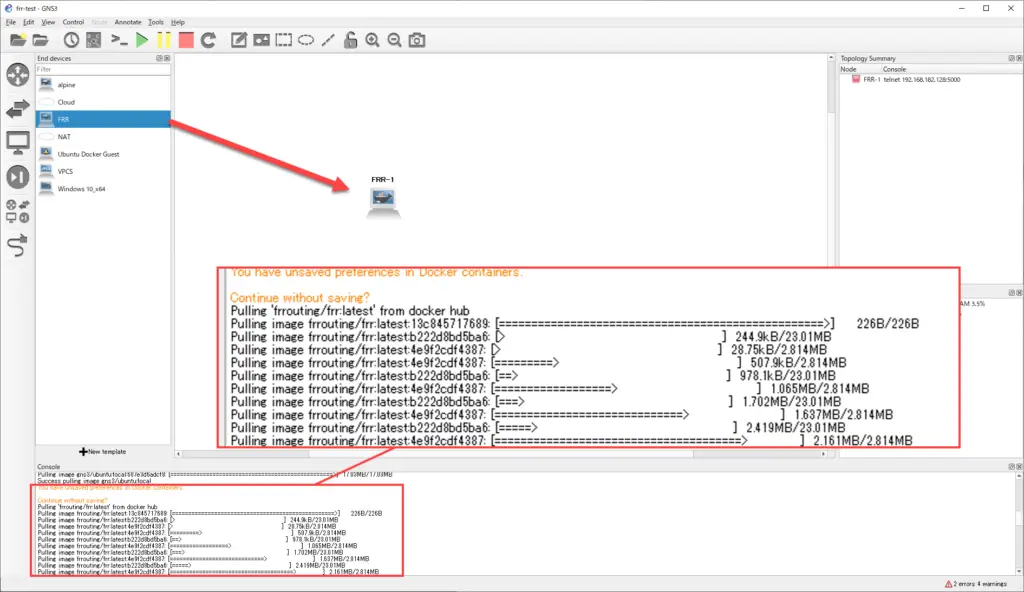
After that, you just need to establish a link between your router or other devices and the FRR container.
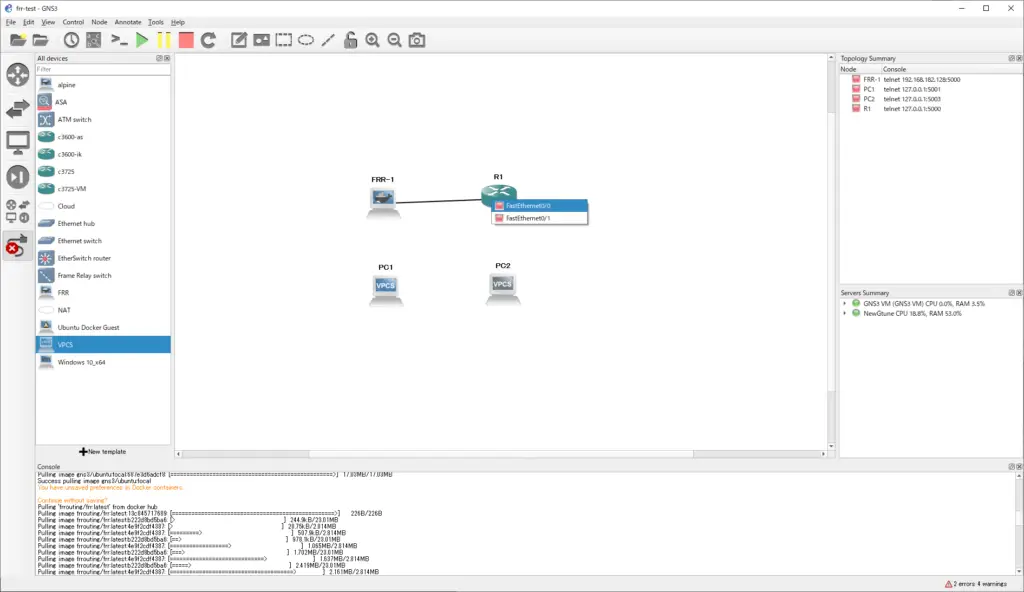
Start the FRR container
Once you have placed the FRR container in your project, start it up. Then, double-click on the icon to connect to the console. Manually start the required routing daemon from the shell; the FRR library is located in /usr/lib/frr. Go to /usr/lib/frr and start the required routing daemon. Enter a command similar to the following
cd /usr/lib/frr ./watchfrr zebra ospfd &
The above command example starts three daemons. “watchfrr” monitors other daemons in FRR. “zebra” does basic IP routing. The “ospfd” daemon performs OSPFv2 routing. If there are any other routing daemons you need, start them as well. “&” to run the daemon in the background. After starting the daemon, press Enter to return to the shell.
FRR-1 console is now available... Press RETURN to get started. / # cd /usr/lib/frr /usr/lib/frr # ./watchfrr zebra ospfd & /usr/lib/frr # 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [ZG9QC-QRCJZ] failed to mkdir "/var/tmp/frr/watchfrr.46": File exists 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [M1DC0-ZDNYJ] crashlog and per-thread log buffering unavailable! 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [T83RR-8SM5G] watchfrr 8.1_git starting: vty@0 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [ZCJ3S-SPH5S] zebra state -> down : initial connection attempt failed 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [ZCJ3S-SPH5S] ospfd state -> down : initial connection attempt failed 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [YFT0P-5Q5YX] Forked background command [pid 47]: /usr/lib/frr/watchfrr.sh restart all Cannot stop staticd: pid 65 not running Cannot stop zebra: pid 60 not running 2022/01/26 02:00:24 ZEBRA: [ZG9QC-QRCJZ] failed to mkdir "/var/tmp/frr/zebra.59": File exists 2022/01/26 02:00:24 ZEBRA: [M1DC0-ZDNYJ] crashlog and per-thread log buffering unavailable! 2022/01/26 02:00:24 ZEBRA: [NNACN-54BDA][EC 4043309110] Disabling MPLS support (no kernel support) 2022/01/26 02:00:24 STATIC: [ZG9QC-QRCJZ] failed to mkdir "/var/tmp/frr/staticd.64": File exists 2022/01/26 02:00:24 STATIC: [M1DC0-ZDNYJ] crashlog and per-thread log buffering unavailable! 2022/01/26 02:00:24 WATCHFRR: [QDG3Y-BY5TN] zebra state -> up : connect succeeded 2022/01/26 02:00:29 WATCHFRR: [YFT0P-5Q5YX] Forked background command [pid 67]: /usr/lib/frr/watchfrr.sh restart ospfd Cannot stop ospfd: pid 88 not running 2022/01/26 02:00:29 WATCHFRR: [QDG3Y-BY5TN] ospfd state -> up : connect succeeded 2022/01/26 02:00:29 WATCHFRR: [KWE5Q-QNGFC] all daemons up, doing startup-complete notify /usr/lib/frr #
You can then use the vtysh command to launch a Cisco IOS-like interactive shell.
vtysh
The log when you enter the vtysh command will look like this
/usr/lib/frr # vtysh % Can't open configuration file /etc/frr/vtysh.conf due to 'No such file or directory'. Hello, this is FRRouting (version 8.1_git). Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al. FRR-1#
After that, you can configure the router with the same commands as Cisco IOS.
Link
For detailed information on how to configure FRRouting and the commands of each daemon, please refer to the official website.
Interconnecting FRR and Cisco IOS
The following simple network diagram will be used to interconnect FRR and Cisco IOS. Uses OSPFv2 as the routing protocol.
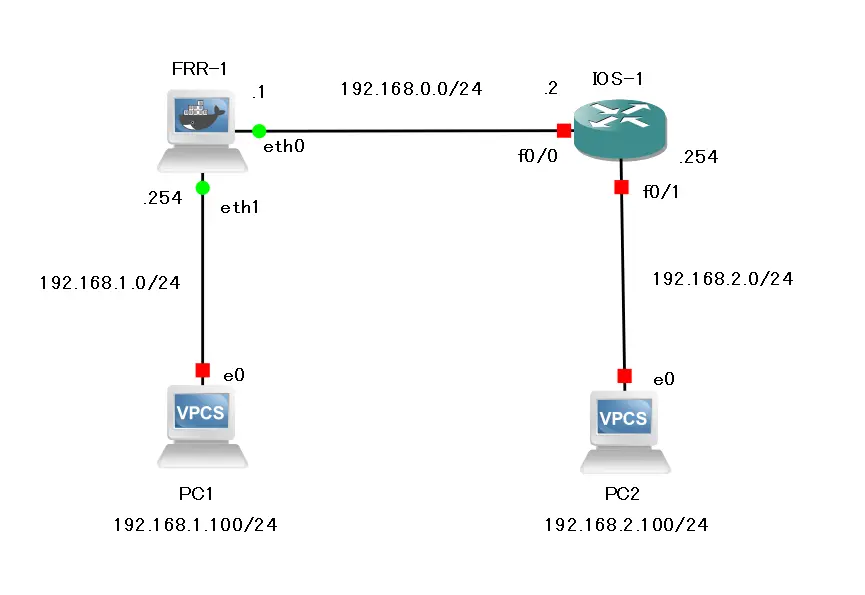
Configuration of FRR-1
interface eth0 ip address 192.168.0.1/24 exit ! interface eth1 ip address 192.168.1.254/24 exit ! router ospf network 192.168.0.0/24 area 0 network 192.168.1.0/24 area 0 exit
Configuration of IOS-1
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
Verify routing table and communication
The routing table on FRR-1 looks like this
FRR-1# show ip route
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP,
O - OSPF, I - IS-IS, B - BGP, E - EIGRP, N - NHRP,
T - Table, v - VNC, V - VNC-Direct, A - Babel, F - PBR,
f - OpenFabric,
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued, r - rejected, b - backup
t - trapped, o - offload failure
O 192.168.0.0/24 [110/10000] is directly connected, eth0, weight 1, 00:01:05
C>* 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, eth0, 00:01:53
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/10000] is directly connected, eth1, weight 1, 00:01:48
C>* 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, eth1, 00:01:53
O>* 192.168.2.0/24 [110/10010] via 192.168.0.2, eth0, weight 1, 00:01:00
The routing table on IOS-1 looks like this
IOS-1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/10010] via 192.168.0.1, 00:01:44, FastEthernet0/0
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
The necessary OSPF routes have been registered in the routing tables of FRR-1 and IOS-1, so communication between PC1 and PC2 is possible. when a ping is executed from PC1 to PC2, a response is returned. Pinging from PC1 to PC2 will result in a response.
PC1> ping 192.168.2.100 84 bytes from 192.168.2.100 icmp_seq=1 ttl=62 time=31.817 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.2.100 icmp_seq=2 ttl=62 time=32.801 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.2.100 icmp_seq=3 ttl=62 time=31.506 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.2.100 icmp_seq=4 ttl=62 time=31.073 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.2.100 icmp_seq=5 ttl=62 time=30.563 ms
How to use GNS3
- Installation of GNS3 (Windows10)
- How to Upgrade GNS3 version
- How to download IOS of the real router to PC
- Creating IOS Router Template
- Setting up the GNS3 VM server
- What to do when GNS3 VM does not turn green in Servers Summary?
- Creating an IOS router template (VM server)
- How to Use IOU(IOS on Unix) on GNS3
- How to Use CSR1000v on GNS3
- Creating GNS3 project
- Link to Host OS
- Example of linking to the host OS
- How to add a VMware virtual machine to a GNS3 topology
- VPCS Configuration and Operation
- How to Add Docker Container Linux Hosts
- How to use FRR (Free Range Routing) container on GNS3
- How to Use GNS3 Appliances
- Managing Snapshots
- Export/Import configuration
- Packet Capture
- Edit startup-config directly
- How to change the Solar-PuTTY font and background color