Table of Contents
What is VPCS?
VPCS (Virtual PC Simulator) is a light-load PC simulator that allows you to use VPCS on your GNS3 project’s network diagram to verify network connectivity such as pings and traceroute. Using VPCS will reduce the load on your PC.
This section explains how to configure VPCS and the operations such as Ping and Traceroute.
VPCS Configuration
IP address/subnet mask and default gateway configuration (static)
Connect to the VPCS console and configure the IP address/subnet mask and default gateway with the following commands.
VPCS>ip <ip-address> <subnetmask> <default-gateway>
<ip-address> : IP address
<subnetmask> : Subnetmask
<default-gateway> : Default gateway IP address
Configuring the IP address of the DNS server
The following command is used to configure the IP address of the DNS server.
VPCS>ip dns <dns-server>
<dns-server> : DNS server IP address
DHCP Client
As a DHCP client, the following commands can be used to obtain IP addresses and other information from the DHCP server.
VPCS>ip dhcp
Configuring host name
To change the host name, enter the following command
VPCS>set pcname <name>
<name> : Host name
Verify TCP/IP configuration.
To verify the IP address and other TCP/IP configurations, enter the following commands.
VPCS>show ip
Clear TCP/IP Configuration
To remove the IP address and other TCP/IP configurations, you can use the following command.
VPC>clear ip
Saving Configurations
To save your configuration, use the save command.
VPCS>save <file-name>
<file-name> : 設定ファイル名
If you omit the configuration file name, the configuration is saved in the default starup.vpc file. The path to the configuration file is<GNS project path>\project-files\vpcs\<VPCS UUID>\.
VPCS Operation
Ping
To execute a ping, use the following command.
VPCS>ping <ip-address>
<ip-address> : destination IP address
TCP Ping/UDP Ping
In addition to regular pings, TCP and UDP pings can also be executed. You can easily send TCP segments and UDP datagrams from VPCS. You can send TCP segments via TCP ping with the following command.
VPCS>ping <ip-address> -P 6 -p <port>
<ip-address> : 宛先IPアドレス
<port> : 宛先ポート番号
The “-P 6” stands for TCP, where 6 is the protocol number for TCP.
To send a UDP datagram with a UDP ping, use the following command.
VPCS>ping <ip-address> -P 17 -p <port>
<ip-address> : 宛先IPアドレス
<port> : 宛先ポート番号
The “-P 17” represents UDP, where 17 is the protocol number for UDP.
traceroute
To execute a traceroute, use the following command
VPCS>trace <ip-address>
<ip-address> : 宛先IPアドレス
Display the ARP cache
To verify the ARP cache, you can use the following command.
VPCS>show arp
VPCS Configuration Example
Consider an example of a VPCS configuration.
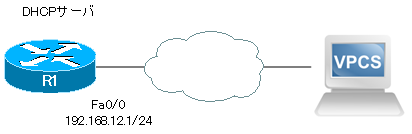
RR1 has a DHCP pool configured as a DHCP server. Also, ACLs are applied to Fa0/0.
R1#show running-config | section ip dhcp no ip dhcp use vrf connected ip dhcp pool AAA network 192.168.12.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.12.1 dns-server 8.8.8.8 R1#show running-config | section access-list access-list 100 permit tcp any any eq 80 access-list 100 permit udp any any eq 53 access-list 100 permit ip any any R1#show run int fa 0/0 Building configuration... Current configuration : 121 bytes ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 ip access-group 100 in duplex auto speed auto end
TCP/IP configuration (static)
Configure TCP/IP settings to VPCS statically.
- IP address/subnetmask : 192.168.12.100/24
- Default gateway : 192.168.12.1
- DNS server : 8.8.8.8
VPCS
VPCS> ip 192.168.12.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1 Checking for duplicate address... PC1 : 192.168.12.100 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.12.1 VPCS> ip dns 8.8.8.8 VPCS> show ip NAME : VPCS[1] IP/MASK : 192.168.12.100/24 GATEWAY : 192.168.12.1 DNS : 8.8.8.8 MAC : 00:50:79:66:68:00 LPORT : 10016 RHOST:PORT : 127.0.0.1:10017 MTU: : 1500
TCP/IP Configuration (DHCP)
Remove the VPCS static configuration and make it a DHCP client.
VPCS
VPCS> clear ip IPv4 address/mask, gateway, DNS, and DHCP cleared VPCS> ip dhcp DDORA IP 192.168.12.3/24 GW 192.168.12.1 VPCS> show ip NAME : VPCS[1] IP/MASK : 192.168.12.3/24 GATEWAY : 192.168.12.1 DNS : 8.8.8.8 DHCP SERVER : 192.168.12.1 DHCP LEASE : 86396, 86400/43200/75600 MAC : 00:50:79:66:68:00 LPORT : 10016 RHOST:PORT : 127.0.0.1:10017 MTU: : 1500
Ping
Ping from VPCS to R1.
VPCS
VPCS> ping 192.168.12.1 84 bytes from 192.168.12.1 icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=6.259 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.12.1 icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=6.433 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.12.1 icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=7.197 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.12.1 icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=5.321 ms 84 bytes from 192.168.12.1 icmp_seq=5 ttl=255 time=6.258 ms
TCP Ping/UDP Ping
Execute a TCP ping on destination port number 80 and a UDP ping on destination port number 53 from VPCS to R1.
VPCS
VPCS> ping 192.168.12.1 -P 6 -p 80 Connect [email protected] RST returned Connect [email protected] RST returned Connect [email protected] RST returned Connect [email protected] RST returned Connect [email protected] RST returned VPCS> ping 192.168.12.1 -P 17 -p 53 *192.168.12.1 udp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=10.087 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) *192.168.12.1 udp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=3.372 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) *192.168.12.1 udp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=5.326 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) *192.168.12.1 udp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=8.978 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable) *192.168.12.1 udp_seq=5 ttl=255 time=6.009 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
If you look at show access-lists on R1, you can see that it is receiving a TCP segment on destination port number 80 and a UDP segment on destination port number 53.
R1
R1#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 100
10 permit tcp any any eq www (30 matches)
20 permit udp any any eq domain (30 matches)
30 permit ip any any (128 matches)
traceroute
Execute a traceroute from VPCS to R1.
VPCS
VPCS> trace 192.168.12.1 trace to 192.168.12.1, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 *192.168.12.1 9.203 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
Display the ARP cache
Use the show arp command to display the VPCS ARP cache.
VPCS
VPCS> show arp cc:01:29:a8:00:00 192.168.12.1 expires in 63 seconds
How to use GNS3
- Installation of GNS3 (Windows10)
- How to Upgrade GNS3 version
- How to download IOS of the real router to PC
- Creating IOS Router Template
- Setting up the GNS3 VM server
- What to do when GNS3 VM does not turn green in Servers Summary?
- Creating an IOS router template (VM server)
- How to Use IOU(IOS on Unix) on GNS3
- How to Use CSR1000v on GNS3
- Creating GNS3 project
- Link to Host OS
- Example of linking to the host OS
- How to add a VMware virtual machine to a GNS3 topology
- VPCS Configuration and Operation
- How to Add Docker Container Linux Hosts
- How to use FRR (Free Range Routing) container on GNS3
- How to Use GNS3 Appliances
- Managing Snapshots
- Export/Import configuration
- Packet Capture
- Edit startup-config directly
- How to change the Solar-PuTTY font and background color